Answers to End-of-Chapter Questions – Brooker et al ARIS site
... 2. How does shotgun DNA sequencing differ from procedures that involve mapping? What are an advantage and a disadvantage of the shotgun DNA sequencing approach? Answer: One strategy requires mapping the genome prior to sequencing. After mapping is completed each region of the genome is then sequence ...
... 2. How does shotgun DNA sequencing differ from procedures that involve mapping? What are an advantage and a disadvantage of the shotgun DNA sequencing approach? Answer: One strategy requires mapping the genome prior to sequencing. After mapping is completed each region of the genome is then sequence ...
3687317_mlbio10_Ch14_TestA_3rd.indd
... a. Females cannot have hemophilia. b. A colorblind boy’s mother must carry the gene for colorblindness. c. A sex-linked allele cannot be dominant. d. A colorblind boy’s father must carry the gene for colorblindness. 4. Which of the following form(s) a Barr body? a. one of the Y chromosomes in a male ...
... a. Females cannot have hemophilia. b. A colorblind boy’s mother must carry the gene for colorblindness. c. A sex-linked allele cannot be dominant. d. A colorblind boy’s father must carry the gene for colorblindness. 4. Which of the following form(s) a Barr body? a. one of the Y chromosomes in a male ...
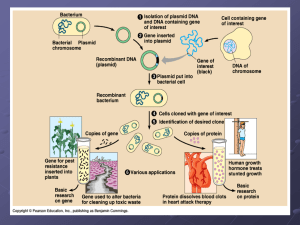
Leq: what is cloning and how is it done?
... Completed in 2003, the Human Genome Project (HGP) was a 13-year project coordinated by the U.S. Department of Energy and the National Institutes of Health. During the early years of the HGP, the Wellcome Trust (U.K.) became a major partner; additional contributions came from Japan, France, Germany, ...
... Completed in 2003, the Human Genome Project (HGP) was a 13-year project coordinated by the U.S. Department of Energy and the National Institutes of Health. During the early years of the HGP, the Wellcome Trust (U.K.) became a major partner; additional contributions came from Japan, France, Germany, ...
Sequencing
... The heat makes DNA’s molecules vibrate faster than they would at lower temperatures. This heat-induced movement causes the two strands of DNA to separate. What type of bonds form between the complementary bases? Hydrogen bonds. Circle the difference(s) between the structures. ...
... The heat makes DNA’s molecules vibrate faster than they would at lower temperatures. This heat-induced movement causes the two strands of DNA to separate. What type of bonds form between the complementary bases? Hydrogen bonds. Circle the difference(s) between the structures. ...
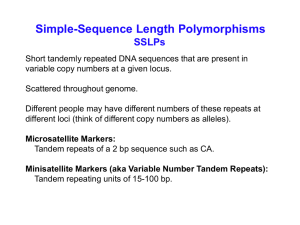
Using microsatellites as molecular markers
... Can detect SSLPs by PCR, therefore, need very little DNA for diagnostic tests. Because a single minisatellite probe can detect multiple VNTRs, can simultaneously examine multiple VNTR loci at a time. ...
... Can detect SSLPs by PCR, therefore, need very little DNA for diagnostic tests. Because a single minisatellite probe can detect multiple VNTRs, can simultaneously examine multiple VNTR loci at a time. ...
Human Genetics and Molecular Biology Review Packet
... c) Define SNP: single nucleotide polymorphism. d) Give two examples of human genetic diseases that result from a SNP. 2) Draw concept map that includes meaningful connecting words or phrases using the following vocabulary terms: genome, gene, chromosome, genomics, sequence, alleles, sequence variati ...
... c) Define SNP: single nucleotide polymorphism. d) Give two examples of human genetic diseases that result from a SNP. 2) Draw concept map that includes meaningful connecting words or phrases using the following vocabulary terms: genome, gene, chromosome, genomics, sequence, alleles, sequence variati ...
Student handout - Avida-ED
... Understanding the Introduction of Genetic Variations by Random Mutation ...
... Understanding the Introduction of Genetic Variations by Random Mutation ...
Transcriptome Profiling in Human Congenital Heart Disease
... which are nonsynonymous • SAMTOOLS is the software of choice for variant calling relative to your reference genome. ...
... which are nonsynonymous • SAMTOOLS is the software of choice for variant calling relative to your reference genome. ...
Case study: PacBio and Dovetail - For cashew genome, combining
... “There are lots of published plant genomes that are not very good quality because they were done exclusively with short-read sequencing, so there are lots of 'holes' in these Swiss-cheese-like genomes.” The scientists had previously worked with Single Molecule, Real-Time (SMRT®) Sequencing from PacB ...
... “There are lots of published plant genomes that are not very good quality because they were done exclusively with short-read sequencing, so there are lots of 'holes' in these Swiss-cheese-like genomes.” The scientists had previously worked with Single Molecule, Real-Time (SMRT®) Sequencing from PacB ...
genome433
... microsatellite marker. A microsatellite is an STS which contains a tandem repeat of a very simple DNA sequence, e.g., (CA)n. Because errors are made in replicating such sequences the “n” often varies from one individual to another (i.e., it is polymorphic.) ...
... microsatellite marker. A microsatellite is an STS which contains a tandem repeat of a very simple DNA sequence, e.g., (CA)n. Because errors are made in replicating such sequences the “n” often varies from one individual to another (i.e., it is polymorphic.) ...
a version - SEA
... After the isolation and sequencing of Mycobacterium phage LittleLaf, various bioinformatic tools were utilized in the annotation of its genome; these tools included the annotation software DNA Master, the gene prediction software GeneMark, the Starterator and Phamerator reports, Shine-Dalgarno value ...
... After the isolation and sequencing of Mycobacterium phage LittleLaf, various bioinformatic tools were utilized in the annotation of its genome; these tools included the annotation software DNA Master, the gene prediction software GeneMark, the Starterator and Phamerator reports, Shine-Dalgarno value ...
human-genome-project
... • Humans share most of the same protein families with worms, flies, and plants; but the number of gene family members has expanded in humans, especially in proteins involved in development and immunity. Scientists have identified about 3 million locations where single-base DNA differences (SNPs) occ ...
... • Humans share most of the same protein families with worms, flies, and plants; but the number of gene family members has expanded in humans, especially in proteins involved in development and immunity. Scientists have identified about 3 million locations where single-base DNA differences (SNPs) occ ...
Human Genome
... much higher in the distal regions (around 20 Mb) of chromosomes and on shorter chromosome arms. In general, in a pattern that promotes the occurrence of at least one crossover per chromosome per arm in each meiosis 11. >1.4 million SNPs have been identified. ...
... much higher in the distal regions (around 20 Mb) of chromosomes and on shorter chromosome arms. In general, in a pattern that promotes the occurrence of at least one crossover per chromosome per arm in each meiosis 11. >1.4 million SNPs have been identified. ...
Lecture 32 Slides
... 5% of the human genome is found to be recently-duplicated large segments (>500bp, identity>95%). [JA Bailey, Science, 2002] The duplicated regions create mosaic structure. Some of the duplicated segments contain new genes. ...
... 5% of the human genome is found to be recently-duplicated large segments (>500bp, identity>95%). [JA Bailey, Science, 2002] The duplicated regions create mosaic structure. Some of the duplicated segments contain new genes. ...
Whole genome sequence analysis of Mycobacteria tuberculosis
... derail efforts to control tuberculosis, which remains a major global public health problem. Whole-genome sequencing of M. tuberculosis clinical isolates is facilitating the characterisation of mutations associated with drug resistance. Their detection offers a means of rapidly assessing susceptibili ...
... derail efforts to control tuberculosis, which remains a major global public health problem. Whole-genome sequencing of M. tuberculosis clinical isolates is facilitating the characterisation of mutations associated with drug resistance. Their detection offers a means of rapidly assessing susceptibili ...
Green Chapter 17 Test Review
... How is incomplete dominance different from regular genetics? What would it look like? ...
... How is incomplete dominance different from regular genetics? What would it look like? ...
No Slide Title
... Numts* (nuclear mitochondrial DNA sequences) are a type of promiscuous DNA, i.e., nuclear sequences of mitochondrial origin. *pronounced “new mights” ...
... Numts* (nuclear mitochondrial DNA sequences) are a type of promiscuous DNA, i.e., nuclear sequences of mitochondrial origin. *pronounced “new mights” ...
Topic 4: Genetics - Peoria Public Schools
... 2. A gene is a section of DNA that controls a specific characteristic in an organism. 3. An allele is a specific form of a gene, differing from other alleles by one or more base differences in the DNA sequence. 4. Different alleles for the same gene all occupy the same locus on a chromosome. 5. Geno ...
... 2. A gene is a section of DNA that controls a specific characteristic in an organism. 3. An allele is a specific form of a gene, differing from other alleles by one or more base differences in the DNA sequence. 4. Different alleles for the same gene all occupy the same locus on a chromosome. 5. Geno ...
HGP Research
... Genes are made of DNA. DNA provides the genetic instructions for everything cells do. Nitrogen bases play a part in determining whether a person will get sick and how well they will respond to medication. To understand how the body works, scientists must understand the human genome, or the complete ...
... Genes are made of DNA. DNA provides the genetic instructions for everything cells do. Nitrogen bases play a part in determining whether a person will get sick and how well they will respond to medication. To understand how the body works, scientists must understand the human genome, or the complete ...
2D Barcode Quiz
... Thymine, Guanine, Adenine and Cytosine are the four bases or ‘nucleotides’ that make up DNA Adenine and Guanine are Pyrimidines (6-point ring), Cytosine and Thymine are Purines (fused 5- and 6-point rings) DNA has a triple helix structure Adenine pairs with Thymine through 2 Hydrogen bonds, Cytosine ...
... Thymine, Guanine, Adenine and Cytosine are the four bases or ‘nucleotides’ that make up DNA Adenine and Guanine are Pyrimidines (6-point ring), Cytosine and Thymine are Purines (fused 5- and 6-point rings) DNA has a triple helix structure Adenine pairs with Thymine through 2 Hydrogen bonds, Cytosine ...
1_genomics
... system developed specifically for biological databases. The goal of SRS is to provide an efficient access to databases with biological contents no matter in what format are they available and allowing for complex ...
... system developed specifically for biological databases. The goal of SRS is to provide an efficient access to databases with biological contents no matter in what format are they available and allowing for complex ...
Whole genome sequencing

Whole genome sequencing (also known as full genome sequencing, complete genome sequencing, or entire genome sequencing) is a laboratory process that determines the complete DNA sequence of an organism's genome at a single time. This entails sequencing all of an organism's chromosomal DNA as well as DNA contained in the mitochondria and, for plants, in the chloroplast.Whole genome sequencing should not be confused with DNA profiling, which only determines the likelihood that genetic material came from a particular individual or group, and does not contain additional information on genetic relationships, origin or susceptibility to specific diseases. Also unlike full genome sequencing, SNP genotyping covers less than 0.1% of the genome. Almost all truly complete genomes are of microbes; the term ""full genome"" is thus sometimes used loosely to mean ""greater than 95%"". The remainder of this article focuses on nearly complete human genomes.High-throughput genome sequencing technologies have largely been used as a research tool and are currently being introduced in the clinics. In the future of personalized medicine, whole genome sequence data will be an important tool to guide therapeutic intervention. The tool of gene sequencing at SNP level is also used to pinpoint functional variants from association studies and improve the knowledge available to researchers interested in evolutionary biology, and hence may lay the foundation for predicting disease susceptibility and drug response.