the Scanned PDF
... shalesrich in alumina and lime. However, the departure of these xenoIiths from the compositionof most shalesis striking (Table 2),and, as was shown by Thomas (1922)for some aluminousxenolithsfrom Mull, Scotland, is most likely a result of metasomatic exchangeduring equilibration of magma and shale. ...
... shalesrich in alumina and lime. However, the departure of these xenoIiths from the compositionof most shalesis striking (Table 2),and, as was shown by Thomas (1922)for some aluminousxenolithsfrom Mull, Scotland, is most likely a result of metasomatic exchangeduring equilibration of magma and shale. ...
Nobelova nagrada za fiziko 2010 Različni materiali na osnovi ogljika
... have been created Recent announcement by IBM that graphene transistor was operated at a terahertz frequency Tunable band gap from 0 to 0.25 eV Excellent conduc>vity makes graphene ideal for electrical ...
... have been created Recent announcement by IBM that graphene transistor was operated at a terahertz frequency Tunable band gap from 0 to 0.25 eV Excellent conduc>vity makes graphene ideal for electrical ...
New Innovative Material The Kings School Robin HillsLonsdaleite
... Lonsdaleite is an allotrope of carbon, also called “hexagonal diamond”, because of the hexagonal lattice. It occurs naturally, forming when meteorites containing graphite hit the Earth. The graphite transforms into diamond due to the extreme heat and pressure of the impact. Scientists have also mana ...
... Lonsdaleite is an allotrope of carbon, also called “hexagonal diamond”, because of the hexagonal lattice. It occurs naturally, forming when meteorites containing graphite hit the Earth. The graphite transforms into diamond due to the extreme heat and pressure of the impact. Scientists have also mana ...
full text pdf
... Graphite is a kind of crystal compound with layer structure. Expandable graphite can be prepared when non-carbonaceous reactants are inserted into graphite layers through chemical or electrochemical reaction. Expandable graphite has many favourable properties: it can be used as a catalyst [1]; and p ...
... Graphite is a kind of crystal compound with layer structure. Expandable graphite can be prepared when non-carbonaceous reactants are inserted into graphite layers through chemical or electrochemical reaction. Expandable graphite has many favourable properties: it can be used as a catalyst [1]; and p ...
Geology: Diamonds from the Popigai impact structure, Russia
... Russia (Masaitis et al., 1972). The Popigai impact structure, centered at lat 71°38′N and long 111°11′E, at the northeast slope of the Anabar shield in northern Siberia, dates to about 35.7 Ma (Bottomley et al., 1997). The target rocks consist of Archean crystalline rocks and an overlying sequence o ...
... Russia (Masaitis et al., 1972). The Popigai impact structure, centered at lat 71°38′N and long 111°11′E, at the northeast slope of the Anabar shield in northern Siberia, dates to about 35.7 Ma (Bottomley et al., 1997). The target rocks consist of Archean crystalline rocks and an overlying sequence o ...
Review on graphite foam as thermal material for heat exchangers
... drop. Because of the complex internal structure of the foam, the flow resistance inside the graphite foam is very high. This causes a high pressure drop through the graphite foam. Due to the high flow resistance, it is difficult for the cooling air to reach all the inter - faces and transfer the hea ...
... drop. Because of the complex internal structure of the foam, the flow resistance inside the graphite foam is very high. This causes a high pressure drop through the graphite foam. Due to the high flow resistance, it is difficult for the cooling air to reach all the inter - faces and transfer the hea ...
Bonding + Physical Properties
... For more awesome GCSE and A level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk ...
... For more awesome GCSE and A level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk ...
Clay—uses
... • It takes places only between ions differing by less than about 10% to 15% in crystal radii. • In tetrahedral coordination, Al3+ for Si4+ and in octahedral coordination Mg2+, Fe2+, Fe3+ for Al3+. • Charges developed as a result of isomorphous substitution are permanent and not pH-dependent. ...
... • It takes places only between ions differing by less than about 10% to 15% in crystal radii. • In tetrahedral coordination, Al3+ for Si4+ and in octahedral coordination Mg2+, Fe2+, Fe3+ for Al3+. • Charges developed as a result of isomorphous substitution are permanent and not pH-dependent. ...
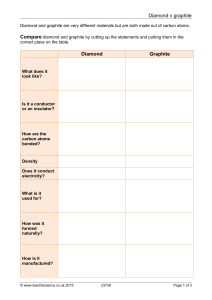
Graphite

Graphite /ˈɡræfaɪt/, archaically referred to as Plumbago, is a crystalline form of carbon, a semimetal, a native element mineral, and one of the allotropes of carbon. Graphite is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Therefore, it is used in thermochemistry as the standard state for defining the heat of formation of carbon compounds. Graphite may be considered the highest grade of coal, just above anthracite and alternatively called meta-anthracite, although it is not normally used as fuel because it is difficult to ignite.