V - Chi K. Tse
... One important point: The nodal method is over-complex when applied to circuits with voltage source(s). WHY? We don’t need N equations for circuits with voltage source(s) because the node voltages are partly known! ...
... One important point: The nodal method is over-complex when applied to circuits with voltage source(s). WHY? We don’t need N equations for circuits with voltage source(s) because the node voltages are partly known! ...
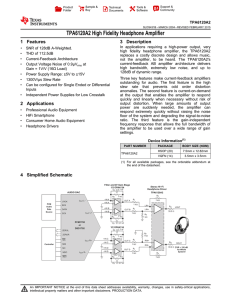
High Fidelity Headphone Amplifier (Rev. B)
... Stresses beyond those listed under “absolute maximum ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under “recommended operating conditions” is not implied. Exposure to a ...
... Stresses beyond those listed under “absolute maximum ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under “recommended operating conditions” is not implied. Exposure to a ...
Electronics Lab Manual
... For each pair of terminals, there is an equivalent circuit that would mimic the behavior of those terminals. There is no equivalent circuit for the entire circuit, but only for specific pairs of terminals. Knowing the equivalent for a pair of terminals makes it easy to think about what will happen t ...
... For each pair of terminals, there is an equivalent circuit that would mimic the behavior of those terminals. There is no equivalent circuit for the entire circuit, but only for specific pairs of terminals. Knowing the equivalent for a pair of terminals makes it easy to think about what will happen t ...
shunts, current shunts, and current-sensing
... A shunt is a resistive device employed to divert most of the current in an electric circuit. The earliest shunts were meter shunts used as external accessories to ammeters allowing one meter to be used for a variety of current levels depending upon which shunt was chosen. These were often massive fo ...
... A shunt is a resistive device employed to divert most of the current in an electric circuit. The earliest shunts were meter shunts used as external accessories to ammeters allowing one meter to be used for a variety of current levels depending upon which shunt was chosen. These were often massive fo ...
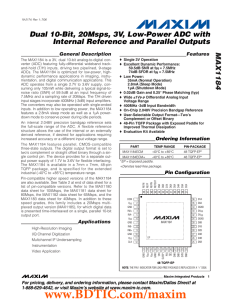
MAX1184 Dual 10-Bit, 20Msps, 3V, Low-Power ADC with General Description
... three-state outputs. The digital output format is set to two’s complement or straight offset binary through a single control pin. The device provides for a separate output power supply of 1.7V to 3.6V for flexible interfacing. The MAX1184 is available in a 7mm x 7mm, 48-pin TQFP package, and is spec ...
... three-state outputs. The digital output format is set to two’s complement or straight offset binary through a single control pin. The device provides for a separate output power supply of 1.7V to 3.6V for flexible interfacing. The MAX1184 is available in a 7mm x 7mm, 48-pin TQFP package, and is spec ...
Detection of optical radiation
... signals reach the photoreceiver, the noise optimisation of a system — i.e., to obtain maximum S/N is a very important problem [2]. Optimum design of a preamplifier can be obtained by analysis of particular noise sources in a detector-preamplifier circuit. The equivalent input noise Vni will be used to ...
... signals reach the photoreceiver, the noise optimisation of a system — i.e., to obtain maximum S/N is a very important problem [2]. Optimum design of a preamplifier can be obtained by analysis of particular noise sources in a detector-preamplifier circuit. The equivalent input noise Vni will be used to ...
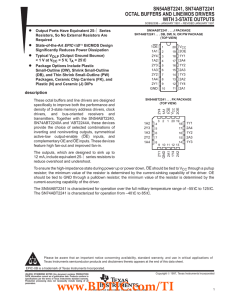
SN54ABT2241, SN74ABT2241 OCTAL BUFFERS AND LINE/MOS DRIVERS WITH 3-STATE OUTPUTS
... VCC = 5.5 V, One input at 3.4 V, Other inputs at VCC or GND VI = 2.5 V or 0.5 V VO = 2.5 V or 0.5 V ...
... VCC = 5.5 V, One input at 3.4 V, Other inputs at VCC or GND VI = 2.5 V or 0.5 V VO = 2.5 V or 0.5 V ...
8 - MyWeb at WIT
... – Input circuitry of gate 2 is represented as a resistance tied to +VCC —the positive terminal of a power supply. – When gate 1 output goes LOW, current will flow from the input circuit of gate 2 back through the output resistance of gate 1, to ground. • Circuit output that drives the input of gate ...
... – Input circuitry of gate 2 is represented as a resistance tied to +VCC —the positive terminal of a power supply. – When gate 1 output goes LOW, current will flow from the input circuit of gate 2 back through the output resistance of gate 1, to ground. • Circuit output that drives the input of gate ...
MAX17017 Quad-Output Controller for Low-Power Architecture General Description
... step-up converter (for 1 Li+ cell applications). The internal switching regulators include 5V synchronous MOSFETs that can be powered directly from a single Li+ cell or from the main 3.3V/5V power stages. Finally, the linear regulator is capable of sourcing and sinking 2A to support DDR termination ...
... step-up converter (for 1 Li+ cell applications). The internal switching regulators include 5V synchronous MOSFETs that can be powered directly from a single Li+ cell or from the main 3.3V/5V power stages. Finally, the linear regulator is capable of sourcing and sinking 2A to support DDR termination ...
A Grid Current-Controlling Shunt Active Power Filter
... achieved using bipolar PWM switching. The upper and lower power switches of each half-bridge are switched on a complementary basis. As a result, the inverter output current, as well as the grid current, can always be controlled to ramp up and down continuously. Therefore, the direct control of the g ...
... achieved using bipolar PWM switching. The upper and lower power switches of each half-bridge are switched on a complementary basis. As a result, the inverter output current, as well as the grid current, can always be controlled to ramp up and down continuously. Therefore, the direct control of the g ...
Miteq DR-125G-A, 12-GHZ Fiber
... has its share of unique issues. The MITEQ DR-125G-A detector consists of a PIN diode and a high-gain transimpedance amplifier. Its total responsivity is approximately 1900 V/W. The detector’s 3-dB bandwidth ranges from 10 kHz to 12.5 GHz, and maximum output can reach up to 3.5 V. Each channel in the ...
... has its share of unique issues. The MITEQ DR-125G-A detector consists of a PIN diode and a high-gain transimpedance amplifier. Its total responsivity is approximately 1900 V/W. The detector’s 3-dB bandwidth ranges from 10 kHz to 12.5 GHz, and maximum output can reach up to 3.5 V. Each channel in the ...
Document
... theorem any two-terminal resistive circuit to a single equivalent voltage source in series with an equivalent resistance. Superposition A method for analyzing circuits with two or more sources by examining the effects of each source by itself and then combining the effects. Maximum Power The conditi ...
... theorem any two-terminal resistive circuit to a single equivalent voltage source in series with an equivalent resistance. Superposition A method for analyzing circuits with two or more sources by examining the effects of each source by itself and then combining the effects. Maximum Power The conditi ...
Resistance vs Temperature
... A superconductor is a material that loses all resistance to the flow of electric current when it is cooled below a certain temperature, called the critical temperature or transition temperature. Above this temperature, there is usually little or no indication that the material might be a superconduc ...
... A superconductor is a material that loses all resistance to the flow of electric current when it is cooled below a certain temperature, called the critical temperature or transition temperature. Above this temperature, there is usually little or no indication that the material might be a superconduc ...
Operational Amplifiers
... different ways using resistors and other components • Most configurations use feedback • Op amps can provide a buffer between two circuits • Op amps can be used to implement integrators and differentiators • Lowpass and bandpass filters Lect8 ...
... different ways using resistors and other components • Most configurations use feedback • Op amps can provide a buffer between two circuits • Op amps can be used to implement integrators and differentiators • Lowpass and bandpass filters Lect8 ...
LT3759 - Wide Input Voltage Range Boost/SEPIC/Inverting Controller
... The LT3759 uses a fixed frequency, current mode control scheme to provide excellent line and load regulation. Operation can be best understood by referring to the Block Diagram in Figure 1. The start of each oscillator cycle sets the SR latch (SR1) and turns on the external power MOSFET switch M1 th ...
... The LT3759 uses a fixed frequency, current mode control scheme to provide excellent line and load regulation. Operation can be best understood by referring to the Block Diagram in Figure 1. The start of each oscillator cycle sets the SR latch (SR1) and turns on the external power MOSFET switch M1 th ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.