Lab 2: DC Measurements - University of Florida
... displacement is shown by the meter needle against a scale. The current that causes full-scale deflection (needle deflects to the maximum extent of the meter) is labeled on the galvanometer. Meter movements are usually rated by current and resistance. For our meters, this full-scale current is 1.0 mA ...
... displacement is shown by the meter needle against a scale. The current that causes full-scale deflection (needle deflects to the maximum extent of the meter) is labeled on the galvanometer. Meter movements are usually rated by current and resistance. For our meters, this full-scale current is 1.0 mA ...
Balanced Modulator/Demodulator AD630
... and instrumentation applications requiring wide dynamic range. When used as a synchronous demodulator in a lock-in amplifier configuration, it can recover a small signal from 100 dB of interfering noise (see lock-in amplifier application). Although optimized for operation up to 1 kHz, the circuit is ...
... and instrumentation applications requiring wide dynamic range. When used as a synchronous demodulator in a lock-in amplifier configuration, it can recover a small signal from 100 dB of interfering noise (see lock-in amplifier application). Although optimized for operation up to 1 kHz, the circuit is ...
Switching frequency Harmonic selection for Single Phase Multilevel
... reduces harmonics, resulting in a lower THD by which high quality output voltage waveforms of desired fundamental r.m.s value and frequency which are as close as possible to sinusoidal wave shape can be obtained. Higher switching frequency can be employed for low and medium power inverters, whereas, ...
... reduces harmonics, resulting in a lower THD by which high quality output voltage waveforms of desired fundamental r.m.s value and frequency which are as close as possible to sinusoidal wave shape can be obtained. Higher switching frequency can be employed for low and medium power inverters, whereas, ...
Hardware manual
... Pinning of the controller board .................................................................................................................. 7 Pinning of the power board ........................................................................................................................ 7 D ...
... Pinning of the controller board .................................................................................................................. 7 Pinning of the power board ........................................................................................................................ 7 D ...
LM5160A, LM5160 Wide Input 65-V, 2
... The LM5160 family is a 65-V, 1.5-A synchronous step-down converter with integrated high-side and low-side MOSFETs. The constant-on-time control scheme requires no loop compensation and supports high step-down ratios with fast transient response. An internal feedback amplifier maintains ±1% output vo ...
... The LM5160 family is a 65-V, 1.5-A synchronous step-down converter with integrated high-side and low-side MOSFETs. The constant-on-time control scheme requires no loop compensation and supports high step-down ratios with fast transient response. An internal feedback amplifier maintains ±1% output vo ...
MAX11190 4-Channel, Dual, Simultaneous Sampling, 3mm x 3mm TQFN Package
... The device features two dual, single-ended analog inputs connected to two ADC cores using 2:1 MUXs. The device also includes a separate supply input for data interface and dedicated inputs for reference voltage. This device operates from a 2.2V to 3.6V supply and consumes only 10.5mW at 3Msps. The d ...
... The device features two dual, single-ended analog inputs connected to two ADC cores using 2:1 MUXs. The device also includes a separate supply input for data interface and dedicated inputs for reference voltage. This device operates from a 2.2V to 3.6V supply and consumes only 10.5mW at 3Msps. The d ...
LP5951 - Texas Instruments
... The LP5951 will remain stable and in regulation with no external load. This is an important consideration in some circuits, for example CMOS RAM keep-alive applications. 7.3.2 Enable Operation The LP5951 may be switched ON or OFF by a logic input at the Enable pin, EN. A logic high at this pin will ...
... The LP5951 will remain stable and in regulation with no external load. This is an important consideration in some circuits, for example CMOS RAM keep-alive applications. 7.3.2 Enable Operation The LP5951 may be switched ON or OFF by a logic input at the Enable pin, EN. A logic high at this pin will ...
LP5951 - Texas Instruments
... The LP5951 will remain stable and in regulation with no external load. This is an important consideration in some circuits, for example CMOS RAM keep-alive applications. 7.3.2 Enable Operation The LP5951 may be switched ON or OFF by a logic input at the Enable pin, EN. A logic high at this pin will ...
... The LP5951 will remain stable and in regulation with no external load. This is an important consideration in some circuits, for example CMOS RAM keep-alive applications. 7.3.2 Enable Operation The LP5951 may be switched ON or OFF by a logic input at the Enable pin, EN. A logic high at this pin will ...
LTC3552
... Mode operation or pulse-skipping mode is selected, respectively. Do not float this pin. The oscillation frequency can be synchronized to an external oscillator applied to this pin and pulse-skipping mode is automatically selected. SW2 (Pin 5): Regulator 2 Switch Node Connection to the Inductor. This ...
... Mode operation or pulse-skipping mode is selected, respectively. Do not float this pin. The oscillation frequency can be synchronized to an external oscillator applied to this pin and pulse-skipping mode is automatically selected. SW2 (Pin 5): Regulator 2 Switch Node Connection to the Inductor. This ...
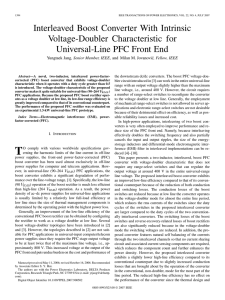
Interleaved Boost Converter With Intrinsic Voltage
... the downstream dc/dc converters. The boost PFC voltage-doubler circuit introduced in [3] can work in the entire universal-line range with an output voltage slightly higher than the maximum line voltage, i.e., around 400 V. However, the circuit requires a number of range-select switches to reconfigur ...
... the downstream dc/dc converters. The boost PFC voltage-doubler circuit introduced in [3] can work in the entire universal-line range with an output voltage slightly higher than the maximum line voltage, i.e., around 400 V. However, the circuit requires a number of range-select switches to reconfigur ...
Overhead-Conscious Voltage Selection for Dynamic and Leakage
... CMOS technology to reduce the supply voltage levels and consequently the threshold voltages (in order to maintain peak performance) is resulting in the fact that a substantial portion of the overall power dissipation will be due to leakage currents [3, 10]. This makes the adaptive body biasing appro ...
... CMOS technology to reduce the supply voltage levels and consequently the threshold voltages (in order to maintain peak performance) is resulting in the fact that a substantial portion of the overall power dissipation will be due to leakage currents [3, 10]. This makes the adaptive body biasing appro ...
Worksheet: Electric current, battery and bulb
... differently when placed in a direct electric circuit. Try to sum up in what points these elements differ from each other. In terms of which physical quantity can we describe their differences? Now you are going to investigate how temperature influences the resistance of an electric element. You will ...
... differently when placed in a direct electric circuit. Try to sum up in what points these elements differ from each other. In terms of which physical quantity can we describe their differences? Now you are going to investigate how temperature influences the resistance of an electric element. You will ...
Step-Up Regulator and High-Voltage Step-Up with Temperature Compensation MAX17106 General Description
... ICs. The converter is a 1.2MHz current-mode regulator with an integrated 20V n-channel power MOSFET. The high switching frequency allows the use of ultra-small inductors and ceramic capacitors. The current-mode control architecture provides fast transient response to pulsed loads. The step-up regula ...
... ICs. The converter is a 1.2MHz current-mode regulator with an integrated 20V n-channel power MOSFET. The high switching frequency allows the use of ultra-small inductors and ceramic capacitors. The current-mode control architecture provides fast transient response to pulsed loads. The step-up regula ...
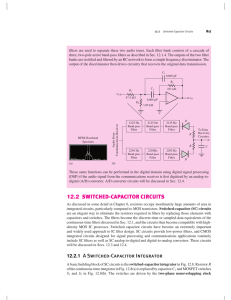
12.2 switched-capacitor circuits
... As discussed in some detail in Chapter 6, resistors occupy inordinately large amounts of area in integrated circuits, particularly compared to MOS transistors. Switched-capacitor (SC) circuits are an elegant way to eliminate the resistors required in filters by replacing those elements with capacito ...
... As discussed in some detail in Chapter 6, resistors occupy inordinately large amounts of area in integrated circuits, particularly compared to MOS transistors. Switched-capacitor (SC) circuits are an elegant way to eliminate the resistors required in filters by replacing those elements with capacito ...
MAX3643 Evaluation Kit Evaluates: General Description Features
... (R52) and MODSET (R20) variable resistors for the desired average optical power and extinction ratio. Turning the variable resistors clockwise increases bias and modulation current. In a DC-coupled open-loop configuration, MODSET affects the P1 power level and BIASSET affects the average power level ...
... (R52) and MODSET (R20) variable resistors for the desired average optical power and extinction ratio. Turning the variable resistors clockwise increases bias and modulation current. In a DC-coupled open-loop configuration, MODSET affects the P1 power level and BIASSET affects the average power level ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.