Chapter 32 - Alternating Current (AC)
... There are different ways to graphically represent a sinusoidal voltage. One way is to graph the voltage versus time on rectangular axes. A second way is to represent the oscillations with a rotating phasor (vector or rotor). The phasor is an arrow whose length equals the amplitude of the voltage and ...
... There are different ways to graphically represent a sinusoidal voltage. One way is to graph the voltage versus time on rectangular axes. A second way is to represent the oscillations with a rotating phasor (vector or rotor). The phasor is an arrow whose length equals the amplitude of the voltage and ...
Chapter 20 Electricity
... 26. A material that has almost zero resistance when it is cooled to low temperatures is a(an) _________________________. 27. A complete path through which charge can flow is an electric ____________________. 28. A(An) ____________________ signal encodes information as a string of 1’s and 0’s. ...
... 26. A material that has almost zero resistance when it is cooled to low temperatures is a(an) _________________________. 27. A complete path through which charge can flow is an electric ____________________. 28. A(An) ____________________ signal encodes information as a string of 1’s and 0’s. ...
Electrical Power Supplies
... which is negative (zinc). If the two plates are connected by a conductor, a current will flow through the solution (as ions) and through the conductor (as electrons). The solution is called the electrolyte. This kind of chemical generator is called a wet cell. Cells in which the electrolyte is absor ...
... which is negative (zinc). If the two plates are connected by a conductor, a current will flow through the solution (as ions) and through the conductor (as electrons). The solution is called the electrolyte. This kind of chemical generator is called a wet cell. Cells in which the electrolyte is absor ...
Chapter 25 Electric Currents and Resistance
... The variation in electrical resistance with temperature can be used to make precise temperature measurements. Platinum is commonly used since it is relatively free from corrosive effects and has a high melting point. Suppose at 20.0°C the resistance of a platinum resistance thermometer is 164.2 Ω. W ...
... The variation in electrical resistance with temperature can be used to make precise temperature measurements. Platinum is commonly used since it is relatively free from corrosive effects and has a high melting point. Suppose at 20.0°C the resistance of a platinum resistance thermometer is 164.2 Ω. W ...
Chapter # 3: Multi-Level Combinational Logic Contemporary Logic
... VLSI -- very large scale IC -- thousands of gates Power dissipation -- gates consume power as they perform their logic functions, generating heat that must be dissipated ...
... VLSI -- very large scale IC -- thousands of gates Power dissipation -- gates consume power as they perform their logic functions, generating heat that must be dissipated ...
PDF (Publisher`s version)
... 4(ln 2)−2 rμ (1 + rμ )−4 Here, we approximate the MOS gate capacitance as COX · W · L. As the FOM is, by its definition, independent of admittance scaling, it only makes sense to optimize the FOM of the FF by changing width ratios such as rμ and rl . We used rμ = 2.5 to match the rise and fall delay ...
... 4(ln 2)−2 rμ (1 + rμ )−4 Here, we approximate the MOS gate capacitance as COX · W · L. As the FOM is, by its definition, independent of admittance scaling, it only makes sense to optimize the FOM of the FF by changing width ratios such as rμ and rl . We used rμ = 2.5 to match the rise and fall delay ...
L26 - University of Iowa Physics
... electric circuits Exercise: given a battery, some wire and a light bulb, connect them so that the bulb is on. The battery polarity ...
... electric circuits Exercise: given a battery, some wire and a light bulb, connect them so that the bulb is on. The battery polarity ...
Front-end performance and charge collection properties of
... without exceeding the 300 fF target detector capacitance. Finally, the analog section and the substrate are shielded from the digital signals, routed through metal 5 and metal 6, by means of large metal 4 strips, also used for power distribution. However, it is worth noticing here that the Apsel3T1 ...
... without exceeding the 300 fF target detector capacitance. Finally, the analog section and the substrate are shielded from the digital signals, routed through metal 5 and metal 6, by means of large metal 4 strips, also used for power distribution. However, it is worth noticing here that the Apsel3T1 ...
Diapositiva 1
... Kirchhoff’s current law (or Kirchhoff’s current rule) results from the conservation of charge. It applies to a junction or node in a circuit (a point in the circuit where charge has several possible paths to travel). In the figure, we see that i1 is the only current flowing into the node. However, t ...
... Kirchhoff’s current law (or Kirchhoff’s current rule) results from the conservation of charge. It applies to a junction or node in a circuit (a point in the circuit where charge has several possible paths to travel). In the figure, we see that i1 is the only current flowing into the node. However, t ...
Program-Controlled High-Voltage Pulse Generator for Ion Beams
... voltage values, applied to two micro controller inputs. In our case they are: 1 – the signal of HVPG overload and 2 – the magnitude of guard current setting. As a overload signals sensor the current transformer (CT) is used. It is inserted in the primary supply-line threephase transformer circuit of ...
... voltage values, applied to two micro controller inputs. In our case they are: 1 – the signal of HVPG overload and 2 – the magnitude of guard current setting. As a overload signals sensor the current transformer (CT) is used. It is inserted in the primary supply-line threephase transformer circuit of ...
Low Power Tips for CoolRunner Design Summary
... accomplished as quickly as possible. Additionally, many CMOS signal lines are terminated by pull-up resistors; if the output signal driving this line is not equivalent to VCC, then current will flow into the output, thereby increasing total system power consumption. Refer to XAPP329, Understanding T ...
... accomplished as quickly as possible. Additionally, many CMOS signal lines are terminated by pull-up resistors; if the output signal driving this line is not equivalent to VCC, then current will flow into the output, thereby increasing total system power consumption. Refer to XAPP329, Understanding T ...
HMC723LC3C
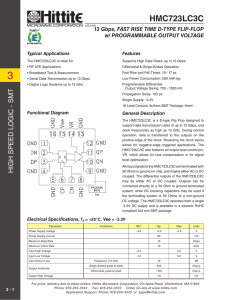
... support data transmission rates of up to 13 Gbps, and clock frequencies as high as 13 GHz. During normal operation, data is transferred to the outputs on the positive edge of the clock. Reversing the clock inputs allows for negative-edge triggered applications. The HMC723LC3C also features an output ...
... support data transmission rates of up to 13 Gbps, and clock frequencies as high as 13 GHz. During normal operation, data is transferred to the outputs on the positive edge of the clock. Reversing the clock inputs allows for negative-edge triggered applications. The HMC723LC3C also features an output ...
EUP2624 620kHz/1.25MHz Step-up DC/DC Converter DESCRIPTION
... together and route them in a “star” ground configuration using component-side coper, then connect the star ground to internal ground using multiple vias. ...
... together and route them in a “star” ground configuration using component-side coper, then connect the star ground to internal ground using multiple vias. ...
www.BDTIC.com/TI Using High-Speed CMOS and Advanced CMOS Logic in Systems With Multiple V
... in Systems With Multiple VCC Supplies or Partial Power Down CMOS devices offer a designer many desirable features, the most important one being low-power consumption. However, in some systems a designer finds that even the low-power consumption of CMOS is insufficient to meet power supply constraint ...
... in Systems With Multiple VCC Supplies or Partial Power Down CMOS devices offer a designer many desirable features, the most important one being low-power consumption. However, in some systems a designer finds that even the low-power consumption of CMOS is insufficient to meet power supply constraint ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.