Electricity-and-Magnetism
... 2. Current: the amount of charge that passes a given point in a specified period of time, measured in amperes(amps, A); flow of electrons through a circuit. 3. Closed Circuit- direction of current flow from positive to negative terminal when powered by a battery 4. Schematic- special type of diagram ...
... 2. Current: the amount of charge that passes a given point in a specified period of time, measured in amperes(amps, A); flow of electrons through a circuit. 3. Closed Circuit- direction of current flow from positive to negative terminal when powered by a battery 4. Schematic- special type of diagram ...
MP1410 2A Step Down DC to DC Converter
... adequate ripple current rating. Its RMS current rating should be greater than approximately 1/2 of the DC load current. For insuring stable operation C2 should be placed as close to the IC as possible. Alternately a smaller high quality ceramic 0.1µF capacitor may be placed closer to the IC and a la ...
... adequate ripple current rating. Its RMS current rating should be greater than approximately 1/2 of the DC load current. For insuring stable operation C2 should be placed as close to the IC as possible. Alternately a smaller high quality ceramic 0.1µF capacitor may be placed closer to the IC and a la ...
HY2596A Description Features 3A 150kHz DC-DC BUCK REGULATOR
... requiring a smaller heat-sink or even no heat-sink. HY2596A performs well with standard inductors from several manufacturers and simplifying the design of switch mode power supplies. HY2596A guarantees 4% tolerance on output voltage within specified input voltages and output load conditions and 15% ...
... requiring a smaller heat-sink or even no heat-sink. HY2596A performs well with standard inductors from several manufacturers and simplifying the design of switch mode power supplies. HY2596A guarantees 4% tolerance on output voltage within specified input voltages and output load conditions and 15% ...
Impedance
... Impedance is a complex quantity that can be made up of resistance (real part) and reactance (imaginary part). ...
... Impedance is a complex quantity that can be made up of resistance (real part) and reactance (imaginary part). ...
AMS5105 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... Dropout Voltage: The input-output voltage differential at which the circuit stops to regulate against further reduction in input voltage. Measured when the output voltage has dropped 100mV from the nominal voltage obtained at 1V input, dropout voltage is dependent upon load current and junction temp ...
... Dropout Voltage: The input-output voltage differential at which the circuit stops to regulate against further reduction in input voltage. Measured when the output voltage has dropped 100mV from the nominal voltage obtained at 1V input, dropout voltage is dependent upon load current and junction temp ...
Interface Circuits Word Document
... Transistors can operate either as switches or as amplifiers. When we use the transistor as an amplifier we need to use the linear region and avoid the cutoff and saturation regions When the transistor is being used as a switch, we operate in the cut-off and saturation regions of the characteristic, ...
... Transistors can operate either as switches or as amplifiers. When we use the transistor as an amplifier we need to use the linear region and avoid the cutoff and saturation regions When the transistor is being used as a switch, we operate in the cut-off and saturation regions of the characteristic, ...
+ collecting electrode
... overlaying the NMOS transistors on the collecting electrode * Use of the deep n-well was proposed by Turchetta et al. (2004 IEEE NSS Conference Record, N28-1) to address radiation hardness issues ...
... overlaying the NMOS transistors on the collecting electrode * Use of the deep n-well was proposed by Turchetta et al. (2004 IEEE NSS Conference Record, N28-1) to address radiation hardness issues ...
Ohm’s Law
... How much current will flow through a lamp that has a resistance of 60 Ω when 12V are impressed across it? voltage Current = resistance ...
... How much current will flow through a lamp that has a resistance of 60 Ω when 12V are impressed across it? voltage Current = resistance ...
HMC746LC3C 数据资料DataSheet下载
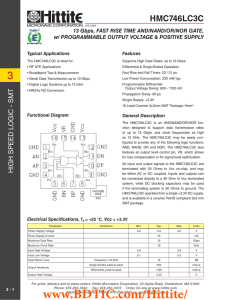
... as 13 GHz. The HMC746LC3C may be easily configured to provide any of the following logic functions: AND, NAND, OR and NOR. The HMC746LC3C also features an output level control pin, VR, which allows for loss compensation or for signal level optimization. All input and output signals to the HMC746LC3C ...
... as 13 GHz. The HMC746LC3C may be easily configured to provide any of the following logic functions: AND, NAND, OR and NOR. The HMC746LC3C also features an output level control pin, VR, which allows for loss compensation or for signal level optimization. All input and output signals to the HMC746LC3C ...
Transistor Switch Example
... "buffer" for this reason and is used in digital circuits with basic gates. ...
... "buffer" for this reason and is used in digital circuits with basic gates. ...
Ohm`s Law I: Engineering Physics II
... Equipment: 560, 680, ohm (or similar) resistors, assorted connectors, ...
... Equipment: 560, 680, ohm (or similar) resistors, assorted connectors, ...
LTC1798 Series - Micropower Low Dropout References
... Longer Battery Life Series references have an advantage over shunt style references. To operate, shunt references require a resistor between the power supply and the output. This resistor must be chosen to supply the maximum current that is demanded by the circuit being regulated. When the circuit b ...
... Longer Battery Life Series references have an advantage over shunt style references. To operate, shunt references require a resistor between the power supply and the output. This resistor must be chosen to supply the maximum current that is demanded by the circuit being regulated. When the circuit b ...
Current Electricity Lab
... Students will construct series and parallel circuits with both bulbs and resistors. The lab begins with bulbs, but since taking measurements with bulbs can often be imprecise, the measurement portion of the lab uses resistors and a DC power supply. Students will observe these properties of series ci ...
... Students will construct series and parallel circuits with both bulbs and resistors. The lab begins with bulbs, but since taking measurements with bulbs can often be imprecise, the measurement portion of the lab uses resistors and a DC power supply. Students will observe these properties of series ci ...
WCS1500
... The WCS1500 consists of a precise, low-temperature drift linear hall sensor IC with temperature compensation circuit and a diameter 9.0mm through hole. Users can use system’s own electric wire by pass it through this hole to measure passing current. This design allows system designers to monitor any ...
... The WCS1500 consists of a precise, low-temperature drift linear hall sensor IC with temperature compensation circuit and a diameter 9.0mm through hole. Users can use system’s own electric wire by pass it through this hole to measure passing current. This design allows system designers to monitor any ...
2.5 A high-side driver industrial intelligent power switch
... the load, the output devices is driven in linear mode, sourcing the Isc current (typically 3.2 A) for a time interval (ton) defined by means of the external CON capacitor connected between the ONDELAY pin and GND. Whether the short circuit crease within the ton interval the DIAG2 output status is no ...
... the load, the output devices is driven in linear mode, sourcing the Isc current (typically 3.2 A) for a time interval (ton) defined by means of the external CON capacitor connected between the ONDELAY pin and GND. Whether the short circuit crease within the ton interval the DIAG2 output status is no ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.