AND9031 - Constant Current Regulator
... board is designed for two CCRs in parallel, Q4 and Q5. (It is possible to connect more than two CCR’s in parallel so any current that you desire can be reached). For the experiments discussed in this application note the CCR ...
... board is designed for two CCRs in parallel, Q4 and Q5. (It is possible to connect more than two CCR’s in parallel so any current that you desire can be reached). For the experiments discussed in this application note the CCR ...
Series Circuits
... series circuit. • Compute voltage drops across resistors using the voltage divider formula. • Describe the basic function of a fuse and a switch. • Draw a schematic of a typical electrical circuit, and explain the purpose of each component and indicate the polarity and current direction. • Explain a ...
... series circuit. • Compute voltage drops across resistors using the voltage divider formula. • Describe the basic function of a fuse and a switch. • Draw a schematic of a typical electrical circuit, and explain the purpose of each component and indicate the polarity and current direction. • Explain a ...
Amplifiers_p108..
... The amplitude of the voltage difference across the small resistor, R1, is V1 = V*R1/(R1+R2), where V is the voltage amplitude from the function generator. Since R1=10 Ohm here and R2 is 10 kOhm, the amplitude V1 is about 1000 times smaller than V (which is less than 20 Volts peak-to-peak). The compl ...
... The amplitude of the voltage difference across the small resistor, R1, is V1 = V*R1/(R1+R2), where V is the voltage amplitude from the function generator. Since R1=10 Ohm here and R2 is 10 kOhm, the amplitude V1 is about 1000 times smaller than V (which is less than 20 Volts peak-to-peak). The compl ...
Ohm`s Law and Electrical Circuits
... circuit elements. There are specific elements called resistors that control the distribution of currents in the circuit by introducing known resistances into the circuit. The currents and voltages at different parts of the circuit can be calculated by using circuit theory that will be discussed late ...
... circuit elements. There are specific elements called resistors that control the distribution of currents in the circuit by introducing known resistances into the circuit. The currents and voltages at different parts of the circuit can be calculated by using circuit theory that will be discussed late ...
past paper questions electrical circuits
... (ii) During his investigations the student measures the voltage across the lamp as 3.0V and the current passing through the lamp as 0.3A. Calculate the resistance of the lamp. State the formula that you use and show your working. formula used ...
... (ii) During his investigations the student measures the voltage across the lamp as 3.0V and the current passing through the lamp as 0.3A. Calculate the resistance of the lamp. State the formula that you use and show your working. formula used ...
High-Speed, Precision Difference Amplifiers
... The information provided herein is believed to be reliable; however, BURR-BROWN assumes no responsibility for inaccuracies or omissions. BURR-BROWN assumes no responsibility for the use of this information, and all use of such information shall be entirely at the user’s own risk. Prices and specific ...
... The information provided herein is believed to be reliable; however, BURR-BROWN assumes no responsibility for inaccuracies or omissions. BURR-BROWN assumes no responsibility for the use of this information, and all use of such information shall be entirely at the user’s own risk. Prices and specific ...
DMOS Delivers Dramatic Performance Gains to
... fueled the growth of the lowFigure dropout (LDO)-regulator market and put extreme pressure on several key performance requirements, including low-dropout voltage, high efficiency (low ground-pin current), lowboard-space usage, and stability. One of the most important LDO-regulator requirements is ac ...
... fueled the growth of the lowFigure dropout (LDO)-regulator market and put extreme pressure on several key performance requirements, including low-dropout voltage, high efficiency (low ground-pin current), lowboard-space usage, and stability. One of the most important LDO-regulator requirements is ac ...
BDTIC Power-Factor Controller (PFC) TDA 4862 IC for High Power Factor
... switched mode power supplies with sinusoidal line current consumption and a power factor approaching unity. The TDA 4862 controls a boost converter as an active harmonics filter in a discontinuous mode (free oscillating triangular shaped current mode). The TDA 4862 comprises an internal start-up tim ...
... switched mode power supplies with sinusoidal line current consumption and a power factor approaching unity. The TDA 4862 controls a boost converter as an active harmonics filter in a discontinuous mode (free oscillating triangular shaped current mode). The TDA 4862 comprises an internal start-up tim ...
LOC14 Faraday`s Law and Inductors
... For each frequency tested answer the following: 1. What is the value of the peak current flowing in the circuit? What is the value of the RMS current flowing in the circuit? 2. What is the value of the inductive reactance at this frequency? What peak voltage ought to be across the inductor? What RMS ...
... For each frequency tested answer the following: 1. What is the value of the peak current flowing in the circuit? What is the value of the RMS current flowing in the circuit? 2. What is the value of the inductive reactance at this frequency? What peak voltage ought to be across the inductor? What RMS ...
LMP8271 High Common Mode, Gain of 20
... to 16V input common mode voltage range and a supply voltage range of 4.75V to 5.5V. The LMP8271 is part of the LMP® precision amplifier family which will detect, amplify and filter small differential signals in the presence of high common mode voltages. The gain is fixed at 20 and is adequate to dri ...
... to 16V input common mode voltage range and a supply voltage range of 4.75V to 5.5V. The LMP8271 is part of the LMP® precision amplifier family which will detect, amplify and filter small differential signals in the presence of high common mode voltages. The gain is fixed at 20 and is adequate to dri ...
AN147 : Automated Linearization of Sensor Circuits
... Voltage monitor VMON2 monitors the current excitation by tracking the voltage. The VMON2 pin can be programmed to monitor voltages between 1.2V to 4.7V at an accuracy of ± 50mV over temperature. So for instance VMON2 is programmed to monitor 2.5V to within 50mV. Once this voltage node reaches that t ...
... Voltage monitor VMON2 monitors the current excitation by tracking the voltage. The VMON2 pin can be programmed to monitor voltages between 1.2V to 4.7V at an accuracy of ± 50mV over temperature. So for instance VMON2 is programmed to monitor 2.5V to within 50mV. Once this voltage node reaches that t ...
STT-1 Quick Start Guide
... Fuses: For 100-120 VAC mains, use two 5 x 20 mm, 1A, slow blow, 250 V, Littelfuse 218 or equiv. For 200-240 VAC mains, use two 5 x 20 mm, 1A, slow blow, 250 V, Littelfuse 218 or equiv. ...
... Fuses: For 100-120 VAC mains, use two 5 x 20 mm, 1A, slow blow, 250 V, Littelfuse 218 or equiv. For 200-240 VAC mains, use two 5 x 20 mm, 1A, slow blow, 250 V, Littelfuse 218 or equiv. ...
MAX4644 High-Speed, Low-Voltage, 4 SPDT CMOS Analog Switch ,
... between each analog-signal pin and both V+ and GND. One of these diodes conducts if any analog signal exceeds V+ or GND (Figure 1). Virtually all of the analog leakage current comes from the ESD diodes to V+ or GND. Although the ESD diodes on a given signal pin are identical, and therefore fairly we ...
... between each analog-signal pin and both V+ and GND. One of these diodes conducts if any analog signal exceeds V+ or GND (Figure 1). Virtually all of the analog leakage current comes from the ESD diodes to V+ or GND. Although the ESD diodes on a given signal pin are identical, and therefore fairly we ...
MAX16945 30mA Inverting Charge Pump in SOT23 for EMI-Sensitive Automotive Applications General Description
... Good layout is important, primarily for good noise performance. To ensure good layout, mount all components as close together as possible, keep traces short to minimize parasitic inductance and capacitance, and use a ground plane. ...
... Good layout is important, primarily for good noise performance. To ensure good layout, mount all components as close together as possible, keep traces short to minimize parasitic inductance and capacitance, and use a ground plane. ...
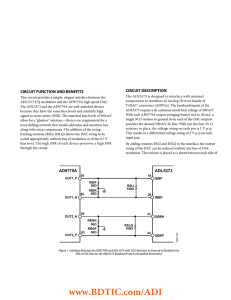
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION CIRCUIT FUNCTION AND BENEFITS
... The value of this ac swing-limiting resistor is chosen based on the desired ac voltage swing. Figure 2 shows the relationship between the swing-limiting resistor and the peak-to-peak ac swing that it produces when 50 Ω bias-setting resistors are used. Note that all Analog Devices I/Q modulators pres ...
... The value of this ac swing-limiting resistor is chosen based on the desired ac voltage swing. Figure 2 shows the relationship between the swing-limiting resistor and the peak-to-peak ac swing that it produces when 50 Ω bias-setting resistors are used. Note that all Analog Devices I/Q modulators pres ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.