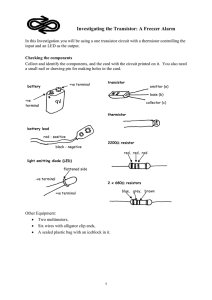
Interconnect Coupling Noise in CMOS VLSI Circuits 48
... In the design of high speed VLSI circuits, it is there fore important to be able to predict coupling noise at the system (or chip) level [S]. Thii information permits circuit malfunctions or extra power consumption caused by the coupling noise to be avoided [9]. The design cycle and cost can therefo ...
... In the design of high speed VLSI circuits, it is there fore important to be able to predict coupling noise at the system (or chip) level [S]. Thii information permits circuit malfunctions or extra power consumption caused by the coupling noise to be avoided [9]. The design cycle and cost can therefo ...
DG535/536
... from being coupled back to the analog signal source and C2 blocks the dc bias from the output signal. Both C1 and C2 should be tantalum or ceramic disc type capacitors in order to operate efficiently at high frequencies. Active bias circuits are recommended if rapid switching time between channels i ...
... from being coupled back to the analog signal source and C2 blocks the dc bias from the output signal. Both C1 and C2 should be tantalum or ceramic disc type capacitors in order to operate efficiently at high frequencies. Active bias circuits are recommended if rapid switching time between channels i ...
Ari Polisois Simplex
... other words, P1 controls the voltage drop across Ra2. What is the purpose of Rx? This hi-wattage resistor supplies an extra current to Rk2, adding to V1b's idle anode current. This layout has two main effects: a) the local negative feed-back, taking place because of the absence of a by-pass condense ...
... other words, P1 controls the voltage drop across Ra2. What is the purpose of Rx? This hi-wattage resistor supplies an extra current to Rk2, adding to V1b's idle anode current. This layout has two main effects: a) the local negative feed-back, taking place because of the absence of a by-pass condense ...
Feb 2000 Tiny SOT-23 Step-Down Regulator Switches at 1MHz for
... the need for progressively smaller components increases. To use smaller capacitors and inductors, switching regulators need to run at ever higher frequencies in ever smaller packages. To help meet this growing demand, Linear Technology introduces the LTC1701 5-lead SOT-23, step-down, current mode, D ...
... the need for progressively smaller components increases. To use smaller capacitors and inductors, switching regulators need to run at ever higher frequencies in ever smaller packages. To help meet this growing demand, Linear Technology introduces the LTC1701 5-lead SOT-23, step-down, current mode, D ...
TPS6102x 96% Efficient Synchronous Boost Converters (Rev. A)
... conversion efficiency reaches 96%. To avoid ground shift due to the high currents in the NMOS switch, two separate ground pins are used. The reference for all control functions is the GND pin. The source of the NMOS switch is connected to PGND. Both grounds must be connected on the PCB at only one p ...
... conversion efficiency reaches 96%. To avoid ground shift due to the high currents in the NMOS switch, two separate ground pins are used. The reference for all control functions is the GND pin. The source of the NMOS switch is connected to PGND. Both grounds must be connected on the PCB at only one p ...
common-mode voltage gain
... minus one may not be zero. It may have have an offset like an analog meter which is not zeroed. The inputs may draw current. The characteristics may drift with age and temperature. Gain may be reduced at high frequencies, and phase may shift from input to output. These imperfection may cause no noti ...
... minus one may not be zero. It may have have an offset like an analog meter which is not zeroed. The inputs may draw current. The characteristics may drift with age and temperature. Gain may be reduced at high frequencies, and phase may shift from input to output. These imperfection may cause no noti ...
ISL59482 Datasheet
... performance switchers and routers. Key features include internal fixed gain of 2, high impedance buffered analog inputs and excellent AC performance at output loads down to 150Ω for video cable-driving. The current feedback output amplifiers are stable operating into capacitive loads. ...
... performance switchers and routers. Key features include internal fixed gain of 2, high impedance buffered analog inputs and excellent AC performance at output loads down to 150Ω for video cable-driving. The current feedback output amplifiers are stable operating into capacitive loads. ...
DIM2 - Atkinson Electronics Inc
... The DIM2 in conjunction with the UI8CH can display eight different temperature or voltage signals. The DIM2 is configured for the lowest and highest display value to be indicated. The UI8CH is customized for the various input signals to provide signal scaling, pullup resistors for sensors, or load r ...
... The DIM2 in conjunction with the UI8CH can display eight different temperature or voltage signals. The DIM2 is configured for the lowest and highest display value to be indicated. The UI8CH is customized for the various input signals to provide signal scaling, pullup resistors for sensors, or load r ...
International Electrical Engineering Journal (IEEJ) Vol. 5 (2014) No.10, pp. 1553-1558
... Loads are connected to. The proposed microgrid consists of a photovoltaic array, proton exchange membrane fuel cell and lithium ion storage battery. The photovoltaic array operates main generation unit of the microgrid. During the sunless hours proton exchange membrane fuel cell operates the main ge ...
... Loads are connected to. The proposed microgrid consists of a photovoltaic array, proton exchange membrane fuel cell and lithium ion storage battery. The photovoltaic array operates main generation unit of the microgrid. During the sunless hours proton exchange membrane fuel cell operates the main ge ...
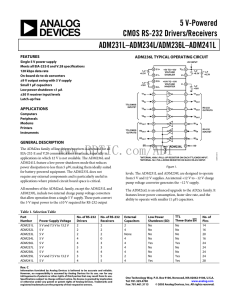
ADM231L 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... Receiver Outputs. These are TTL/CMOS levels. Enable Input. Active low on ADM236L, ADM239L, and ADM241L. This input is used to enable/disable the receiver outputs. With EN = low, the receiver outputs are enabled. With EN = high, the outputs are placed in a high impedance state. This facility is usefu ...
... Receiver Outputs. These are TTL/CMOS levels. Enable Input. Active low on ADM236L, ADM239L, and ADM241L. This input is used to enable/disable the receiver outputs. With EN = low, the receiver outputs are enabled. With EN = high, the outputs are placed in a high impedance state. This facility is usefu ...
Switching Angles and DC Link Voltages Optimization for Multilevel
... Semiconductor switch ratings and problems concerned with series connection of these switches have limited the development of high power inverters. This limitation can be overcome by the multilevel structure for the voltage source inverter [1-3]. The concept of multilevel inverter drives was introduc ...
... Semiconductor switch ratings and problems concerned with series connection of these switches have limited the development of high power inverters. This limitation can be overcome by the multilevel structure for the voltage source inverter [1-3]. The concept of multilevel inverter drives was introduc ...
AN-4 Monolithic Op Amp—The Universal Linear
... negative feedback than positive feedback. This can be a problem with many “textbook” multi-vibrators. Since the operational amplifier is used open loop, the usual frequency compensation components are not required since they will only slow it down. But even without the 30 pF capacitor, the LM101 doe ...
... negative feedback than positive feedback. This can be a problem with many “textbook” multi-vibrators. Since the operational amplifier is used open loop, the usual frequency compensation components are not required since they will only slow it down. But even without the 30 pF capacitor, the LM101 doe ...
ECE1250U14_Lab4ThevEquiv CMF
... circuit as consisting of building blocks. The Thevenin equivalent allows us to model circuit outputs and inputs as very simple circuits. This approach, in turn, allows us to determine how our circuit building blocks behave when connected together. For example, it allows us to determine how much one ...
... circuit as consisting of building blocks. The Thevenin equivalent allows us to model circuit outputs and inputs as very simple circuits. This approach, in turn, allows us to determine how our circuit building blocks behave when connected together. For example, it allows us to determine how much one ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.