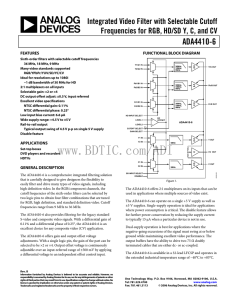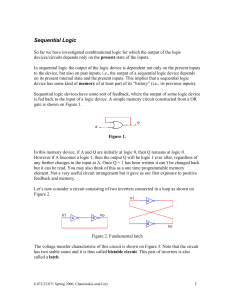
Sequential Logic
... 1. R = 0, S = 1. In this case the output of NOR gate GS must be 0 ( Q = 0). Now both inputs of gate GR are 0 and so the output of GR must be 1. So Q = 1 and Q = 0. In this case we say that the flip-flop is SET 2. R = 1, S = 0. In this case the output of NOR gate GR must be 0 (Q = 0). Now both inputs ...
... 1. R = 0, S = 1. In this case the output of NOR gate GS must be 0 ( Q = 0). Now both inputs of gate GR are 0 and so the output of GR must be 1. So Q = 1 and Q = 0. In this case we say that the flip-flop is SET 2. R = 1, S = 0. In this case the output of NOR gate GR must be 0 (Q = 0). Now both inputs ...
ADA4410-6 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... Changes to Features, General Description, and Figure 1.............1 Changes to Table 1.............................................................................3 Changes to Table 2.............................................................................5 Changes to Figure 4.................. ...
... Changes to Features, General Description, and Figure 1.............1 Changes to Table 1.............................................................................3 Changes to Table 2.............................................................................5 Changes to Figure 4.................. ...
IGBT Driver Application Manual - idc
... protection circuit. Then, gate output depending on input signals becomes possible. If the input signal is ON when specific time elapses, the latch status is not canceled: it is canceled when the signal becomes OFF. The flowchart shown to the right shows the operation flow regarding short‐circuit ...
... protection circuit. Then, gate output depending on input signals becomes possible. If the input signal is ON when specific time elapses, the latch status is not canceled: it is canceled when the signal becomes OFF. The flowchart shown to the right shows the operation flow regarding short‐circuit ...
10.3.1.3 Electrical sparks (spark discharges) Electrical sparks (Fig
... choice of discharges can, therefore, be made, i.e., undercritically damped discharges, and overcritically damped, long-lasting, low current, arc-like discharges. Spark frequencies of the oscillating discharges may be 2 < f < 20 kHz with a spark duration of 0.1 - 2 ms. ...
... choice of discharges can, therefore, be made, i.e., undercritically damped discharges, and overcritically damped, long-lasting, low current, arc-like discharges. Spark frequencies of the oscillating discharges may be 2 < f < 20 kHz with a spark duration of 0.1 - 2 ms. ...
MAX5065/MAX5067 Dual-Phase, +0.6V to +3.3V Output Parallelable, Average-Current-Mode Controllers General Description
... The MAX5065/MAX5067 dual-phase, PWM controllers provide high-output-current capability in a compact package with a minimum number of external components. The MAX5065/MAX5067 utilize a dual-phase, average-current-mode control that enables optimal use of low RDS(ON) MOSFETs, eliminating the need for e ...
... The MAX5065/MAX5067 dual-phase, PWM controllers provide high-output-current capability in a compact package with a minimum number of external components. The MAX5065/MAX5067 utilize a dual-phase, average-current-mode control that enables optimal use of low RDS(ON) MOSFETs, eliminating the need for e ...
SN65LVEL11 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... Maximum switching frequency measured at output amplitude of 300 mVpp. Within-device skew is defined as identical transitions on similar paths through a device. Device-Device Skew is defined as identical transitions at identical Vcc levels. Duty cycle skew is the difference between a tPLH and tPHL pr ...
... Maximum switching frequency measured at output amplitude of 300 mVpp. Within-device skew is defined as identical transitions on similar paths through a device. Device-Device Skew is defined as identical transitions at identical Vcc levels. Duty cycle skew is the difference between a tPLH and tPHL pr ...
LTC6800 - Rail-to-Rail, Input and Output
... charged up to the new input voltage via CS. This results in an input charging current during each input sampling period. Eventually, CH and CS will reach VIN and, ideally, the input current would go to zero for DC inputs. In reality, there are additional parasitic capacitors which disturb the charge ...
... charged up to the new input voltage via CS. This results in an input charging current during each input sampling period. Eventually, CH and CS will reach VIN and, ideally, the input current would go to zero for DC inputs. In reality, there are additional parasitic capacitors which disturb the charge ...
Chapter 8 FET Amplifiers
... With the skills acquired thus far, let’s discuss some of the effects of various shorts and opens in this two stage FET amplifier circuit. Certainly knowing what is normal is helpful so basic analysis of the circuit must be done first. ...
... With the skills acquired thus far, let’s discuss some of the effects of various shorts and opens in this two stage FET amplifier circuit. Certainly knowing what is normal is helpful so basic analysis of the circuit must be done first. ...
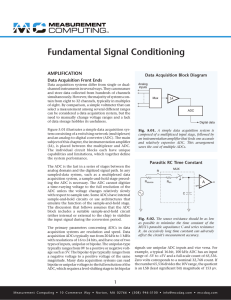
Fundamental Signal Conditioning
... a time-varying voltage to the full resolution of the ADC unless the voltage changes relatively slowly with respect to sample rate. Some ADCs have internal sample-and-hold circuits or use architectures that emulate the function of the sample-and-hold stage. The discussion that follows assumes that th ...
... a time-varying voltage to the full resolution of the ADC unless the voltage changes relatively slowly with respect to sample rate. Some ADCs have internal sample-and-hold circuits or use architectures that emulate the function of the sample-and-hold stage. The discussion that follows assumes that th ...
AD625 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... The diodes to the supplies are only necessary if input voltages outside of the range of the supplies are encountered. In higher gain applications where differential voltages are small, back-toback Zener diodes and smaller resistors, as shown in Figure 26b, provides adequate protection. Figure 26c sh ...
... The diodes to the supplies are only necessary if input voltages outside of the range of the supplies are encountered. In higher gain applications where differential voltages are small, back-toback Zener diodes and smaller resistors, as shown in Figure 26b, provides adequate protection. Figure 26c sh ...
MAX17535 Evaluation Kit Evaluates: General Description Features
... kit is capable of supplying power to a system load while simultaneously charging multichemistry battery packs. During operation, the EV kit circuit automatically selects the AC adapter input or the battery as the main power source for supplying power to the system load. Whenever the EV kit current l ...
... kit is capable of supplying power to a system load while simultaneously charging multichemistry battery packs. During operation, the EV kit circuit automatically selects the AC adapter input or the battery as the main power source for supplying power to the system load. Whenever the EV kit current l ...
Finding the Temperature of a Light Bulb Filament
... Resistor Color Codes. Carbon resistors are often marked with colored stripes to indicate the value of resistance. A summary of the resistor color code is given on the accompanying sheet. 1. Examine the larger of the two “loose” resistors you have (they both have the same color code), record the colo ...
... Resistor Color Codes. Carbon resistors are often marked with colored stripes to indicate the value of resistance. A summary of the resistor color code is given on the accompanying sheet. 1. Examine the larger of the two “loose” resistors you have (they both have the same color code), record the colo ...
Transistors Reduced Base Biased Resistance 2-26-2013
... stability when the base-bias resistance is decreased. ...
... stability when the base-bias resistance is decreased. ...
power quality improvement using hybrid power filter
... filter, six pulses Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) converter are implemented. IMPORTANCE OF THE POWER QUALITY (i). Power quality is defined by the parameters that express the reactive power, harmonic pollution, and unbalance load. (ii). The best ideal electrical supply would be a sinusoidal voltage wav ...
... filter, six pulses Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) converter are implemented. IMPORTANCE OF THE POWER QUALITY (i). Power quality is defined by the parameters that express the reactive power, harmonic pollution, and unbalance load. (ii). The best ideal electrical supply would be a sinusoidal voltage wav ...
TPS65022 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... voltage, peripheral, I/O and memory rails in a processor based system. All three step-down converters enter a low-power mode at light load for maximum efficiency across the widest possible range of load currents. The TPS65022 also integrates two general-purpose 200 mA LDO voltage regulators, which a ...
... voltage, peripheral, I/O and memory rails in a processor based system. All three step-down converters enter a low-power mode at light load for maximum efficiency across the widest possible range of load currents. The TPS65022 also integrates two general-purpose 200 mA LDO voltage regulators, which a ...
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY THE MAXIMUM INVERTER OUTPUT
... shall be not less than 125 percent of the maximum currents calculated in 690.8(A). Exception: Circuits containing an assembly, together with its overcurrent device(s), that is listed for continuous operation at 100 percent of its rating shall be permitted to be used at 100 percent of its rating. / F ...
... shall be not less than 125 percent of the maximum currents calculated in 690.8(A). Exception: Circuits containing an assembly, together with its overcurrent device(s), that is listed for continuous operation at 100 percent of its rating shall be permitted to be used at 100 percent of its rating. / F ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.