Chapter-5: MEASUREMENT OF ELECTRICAL CURRENT
... function. The switch however must be of make-beforebreak type (figure 5.18) that makes the contact with the ...
... function. The switch however must be of make-beforebreak type (figure 5.18) that makes the contact with the ...
ER Week8, Resistors
... o Function: Resistors restrict the flow of electric current, for example a resistor is placed in series with a light-emitting diode (LED) to limit the current passing through the LED. They convert electrical energy into mechanical energy (heat). Resistors are used to: Provide a voltage drop Pr ...
... o Function: Resistors restrict the flow of electric current, for example a resistor is placed in series with a light-emitting diode (LED) to limit the current passing through the LED. They convert electrical energy into mechanical energy (heat). Resistors are used to: Provide a voltage drop Pr ...
AAT3681 数据资料DataSheet下载
... pin and ground. The accuracy of the fast charge, as well as the preconditioning trickle charge current, is dominated by the tolerance of the set resistor used. For this reason, a 1% tolerance metal film resistor is recommended for the set resistor function. Fast charge constant current levels from 1 ...
... pin and ground. The accuracy of the fast charge, as well as the preconditioning trickle charge current, is dominated by the tolerance of the set resistor used. For this reason, a 1% tolerance metal film resistor is recommended for the set resistor function. Fast charge constant current levels from 1 ...
1. Study of OP AMPs - IC 741, IC 555, IC 565, IC 566, IC 1496
... flip-flop to change its states. On the other hand, if the trigger voltage falls below +1/3 VCC, it causes lower comparator to change its states. Thus the output of the flip flop is controlled by the voltages of the two comparators. A change in state occurs when the threshold voltage rises above +2/3 ...
... flip-flop to change its states. On the other hand, if the trigger voltage falls below +1/3 VCC, it causes lower comparator to change its states. Thus the output of the flip flop is controlled by the voltages of the two comparators. A change in state occurs when the threshold voltage rises above +2/3 ...
Improvement to Load-pull Technique for Design of Large
... and difficult task. Manufacturer of the microwave transistor usually provides a large-signal model that a microwave engineer can work with and use it to design a device working under a large-signal conditions. Unfortunately in many cases accuracy of these models is still far from being acceptable in ...
... and difficult task. Manufacturer of the microwave transistor usually provides a large-signal model that a microwave engineer can work with and use it to design a device working under a large-signal conditions. Unfortunately in many cases accuracy of these models is still far from being acceptable in ...
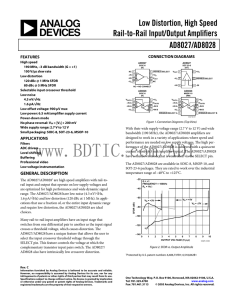
AD8027
... Many rail-to-rail input amplifiers have an input stage that switches from one differential pair to another as the input signal crosses a threshold voltage, which causes distortion. The AD8027/AD8028 have a unique feature that allows the user to select the input crossover threshold voltage through th ...
... Many rail-to-rail input amplifiers have an input stage that switches from one differential pair to another as the input signal crosses a threshold voltage, which causes distortion. The AD8027/AD8028 have a unique feature that allows the user to select the input crossover threshold voltage through th ...
Dual, Wideband, High Output Current Operational Amplifier with Active Off-Line Control OPA2673 FEATURES
... Specified on ±6V supplies (to support +12V operation), the OPA2673 also supports up to +13V single or ±6.5V dual supplies. Video applications benefit from a very high output current to drive up to 10 parallel video loads (15Ω) with < 0.1%/0.1° dG/dΦ nonlinearity. ...
... Specified on ±6V supplies (to support +12V operation), the OPA2673 also supports up to +13V single or ±6.5V dual supplies. Video applications benefit from a very high output current to drive up to 10 parallel video loads (15Ω) with < 0.1%/0.1° dG/dΦ nonlinearity. ...
Reciprocity condition in terms of two port parameters
... In an initially relaxed linear network containing one independent source only. The ratio of the response to the excitation is invariant to an interchange of the position of the excitation and the response. i.e if a single voltage source Ex in branch X produces a current response I y the branch Y, t ...
... In an initially relaxed linear network containing one independent source only. The ratio of the response to the excitation is invariant to an interchange of the position of the excitation and the response. i.e if a single voltage source Ex in branch X produces a current response I y the branch Y, t ...
LTC2057/LTC2057HV - High Voltage, Low
... The LTC®2057 is a high voltage, low noise, zero-drift operational amplifier that offers precision DC performance over a wide supply range of 4.75V to 36V or 4.75V to 60V for the LTC2057HV. Offset voltage and 1/f noise are suppressed, allowing this amplifier to achieve a maximum offset voltage of 4μV ...
... The LTC®2057 is a high voltage, low noise, zero-drift operational amplifier that offers precision DC performance over a wide supply range of 4.75V to 36V or 4.75V to 60V for the LTC2057HV. Offset voltage and 1/f noise are suppressed, allowing this amplifier to achieve a maximum offset voltage of 4μV ...
LT3741/LT3741-1 - High Power, Constant Current, Constant Voltage
... the SYNC pulse frequency. This pin is current limited to 60µA. Do not leave this pin open. SYNC (Pin 13/Pin 15): Frequency Synchronization Pin. This pin allows the switching frequency to be synchronized to an external clock. The RT resistor should be chosen to operate the internal clock at 20% slowe ...
... the SYNC pulse frequency. This pin is current limited to 60µA. Do not leave this pin open. SYNC (Pin 13/Pin 15): Frequency Synchronization Pin. This pin allows the switching frequency to be synchronized to an external clock. The RT resistor should be chosen to operate the internal clock at 20% slowe ...
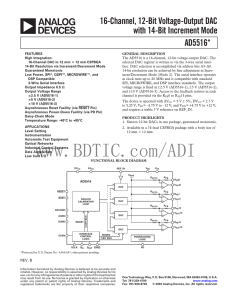
AD5516: 英文产品数据手册下载
... Serial Clock Input. Data is clocked into the shift register on the falling edge of SCLK. This operates at clock speeds up to 20 MHz. Serial Data Input. Data must be valid on the falling edge of SCLK. Serial Data Output. DOUT can be used for daisy-chaining a number of devices together or for reading ...
... Serial Clock Input. Data is clocked into the shift register on the falling edge of SCLK. This operates at clock speeds up to 20 MHz. Serial Data Input. Data must be valid on the falling edge of SCLK. Serial Data Output. DOUT can be used for daisy-chaining a number of devices together or for reading ...
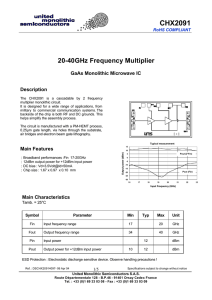
CHX2091 - Richardson RFPD
... Information furnished is believed to be accurate and reliable. However United Monolithic Semiconductors S.A.S. assumes no responsability for the consequences of use of such information nor for any infringement of patents or other rights of third parties which may result from its use. No license is g ...
... Information furnished is believed to be accurate and reliable. However United Monolithic Semiconductors S.A.S. assumes no responsability for the consequences of use of such information nor for any infringement of patents or other rights of third parties which may result from its use. No license is g ...
CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) /ˈsiːmɒs/ is a technology for constructing integrated circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. In 1963, while working for Fairchild Semiconductor, Frank Wanlass patented CMOS (US patent 3,356,858).CMOS is also sometimes referred to as complementary-symmetry metal–oxide–semiconductor (or COS-MOS).The words ""complementary-symmetry"" refer to the fact that the typical design style with CMOS uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistors (MOSFETs) for logic functions.Two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low static power consumption.Since one transistor of the pair is always off, the series combination draws significant power only momentarily during switching between on and off states. Consequently, CMOS devices do not produce as much waste heat as other forms of logic, for example transistor–transistor logic (TTL) or NMOS logic, which normally have some standing current even when not changing state. CMOS also allows a high density of logic functions on a chip. It was primarily for this reason that CMOS became the most used technology to be implemented in VLSI chips.The phrase ""metal–oxide–semiconductor"" is a reference to the physical structure of certain field-effect transistors, having a metal gate electrode placed on top of an oxide insulator, which in turn is on top of a semiconductor material. Aluminium was once used but now the material is polysilicon. Other metal gates have made a comeback with the advent of high-k dielectric materials in the CMOS process, as announced by IBM and Intel for the 45 nanometer node and beyond.