Comparative genomics is a study that combines combination of
... In the genomic age, invaluable insights can be derived from comparisons between properties of different organisms. Such contextual information, including both phenotypic and genomic data, often results in important biological findings, such as the characterization of novel proteins (Pellegrini, et a ...
... In the genomic age, invaluable insights can be derived from comparisons between properties of different organisms. Such contextual information, including both phenotypic and genomic data, often results in important biological findings, such as the characterization of novel proteins (Pellegrini, et a ...
Chapter 14 Review
... Amino acids are joined until a stop codon is reached. mRNA leaves the nucleus tRNA brings methionine to the start codon mRNA goes to ribosome ...
... Amino acids are joined until a stop codon is reached. mRNA leaves the nucleus tRNA brings methionine to the start codon mRNA goes to ribosome ...
Transcriptomics: A general overview By Todd, Mark, and Tom
... from each cancer, for use in quantification of transcript abundance (fluorescence intensity in relation to reference pool). • Hybridizations carried out on micoarrays (synthesized by inkjet technology) containing ~ 25,000 human genes • ~ 5,000 genes found to be significantly regulated across the gro ...
... from each cancer, for use in quantification of transcript abundance (fluorescence intensity in relation to reference pool). • Hybridizations carried out on micoarrays (synthesized by inkjet technology) containing ~ 25,000 human genes • ~ 5,000 genes found to be significantly regulated across the gro ...
Unit 3 * Molecular Genetics
... Define the following terms: nucleotide, complementary base pairing, phosphodiester bond, NTP. ...
... Define the following terms: nucleotide, complementary base pairing, phosphodiester bond, NTP. ...
交通大學特色研究計畫邀請 - 國立交通大學生物資訊研究所
... Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic chromosomes are organized into many independent topological domains. These topological domains may be formed through constraining each DNA end from rotating by interacting with nuclear proteins, i.e., DNA-binding proteins. However, so far, evidence to support this hyp ...
... Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic chromosomes are organized into many independent topological domains. These topological domains may be formed through constraining each DNA end from rotating by interacting with nuclear proteins, i.e., DNA-binding proteins. However, so far, evidence to support this hyp ...
Making probes/primers
... single stranded DNA that are complimentary to the single stranded target on the membrane. ...
... single stranded DNA that are complimentary to the single stranded target on the membrane. ...
E. Coli
... a cell resulting from the uptake and expression of foreign genetic material (DNA). i.e. the act of putting foreign DNA into a bacterial cell Occurs in nature, but rarely If the foreign DNA has an origin of replication recognized by the host cell DNA polymerases, the bacteria will replicate the f ...
... a cell resulting from the uptake and expression of foreign genetic material (DNA). i.e. the act of putting foreign DNA into a bacterial cell Occurs in nature, but rarely If the foreign DNA has an origin of replication recognized by the host cell DNA polymerases, the bacteria will replicate the f ...
Protein Synthesis Project 1516
... In a process called transcription, which takes place in the nucleus of the cell, messenger RNA (mRNA) reads and copies the DNA’s nucleotide sequences in the form of a complementary RNA molecule. Then ...
... In a process called transcription, which takes place in the nucleus of the cell, messenger RNA (mRNA) reads and copies the DNA’s nucleotide sequences in the form of a complementary RNA molecule. Then ...
Plasmid
... Genetic engineering, also known as recombinant DNA technology, means altering the genes in a living organism to produce a Genetically Modified Organism (GMO) with a new genotype. ...
... Genetic engineering, also known as recombinant DNA technology, means altering the genes in a living organism to produce a Genetically Modified Organism (GMO) with a new genotype. ...
Topic 3 - GEOCITIES.ws
... restriction enzymes cut DNA only at specific sequences, allowing two different DNA strands to be cut with the same restriction enzyme and reattached. DNA fragments from another organism are then cleaved by the same restriction enzyme as described previously and these pieces can be added to the open ...
... restriction enzymes cut DNA only at specific sequences, allowing two different DNA strands to be cut with the same restriction enzyme and reattached. DNA fragments from another organism are then cleaved by the same restriction enzyme as described previously and these pieces can be added to the open ...
Protein Synthesis Notes
... (Change in chromosome structure) Different Kinds 1. Deletion: when part of a chromosome is left out. 2. Insertion: part of a chromosome breaks off and inserts into another causing a duplication in the other chromosome. 3. Inversion: genes break off and are reinserted backwards 4. Translocation: gen ...
... (Change in chromosome structure) Different Kinds 1. Deletion: when part of a chromosome is left out. 2. Insertion: part of a chromosome breaks off and inserts into another causing a duplication in the other chromosome. 3. Inversion: genes break off and are reinserted backwards 4. Translocation: gen ...
Mutated
... 1. Which type of mutations had the biggest effect on the protein sequence? WHY? 2. Which type of mutations had the smallest effect on the protein sequence? WHY? 3. Which examples would you predict to have the biggest effects on a trait? WHY? 4. Which examples would you predict to have the smallest e ...
... 1. Which type of mutations had the biggest effect on the protein sequence? WHY? 2. Which type of mutations had the smallest effect on the protein sequence? WHY? 3. Which examples would you predict to have the biggest effects on a trait? WHY? 4. Which examples would you predict to have the smallest e ...
WHAT IS A GENE? II.
... There are important implications of this definition. Collapsing in simple cases In simple cases where the gene is not discontinuous or there are no overlapping products, our definition collapses to the classical version of being a DNA sequence that codes for a protein or RNA product Projecting down ...
... There are important implications of this definition. Collapsing in simple cases In simple cases where the gene is not discontinuous or there are no overlapping products, our definition collapses to the classical version of being a DNA sequence that codes for a protein or RNA product Projecting down ...
DNA App Notes
... either storage temperature. No differences in DNA quality or integrity were observed between DNA stored frozen and DNA stored in GenTegra™ DNA tubes, indicating that GenTegra™ DNA Tubes preserved DNA integrity during the ...
... either storage temperature. No differences in DNA quality or integrity were observed between DNA stored frozen and DNA stored in GenTegra™ DNA tubes, indicating that GenTegra™ DNA Tubes preserved DNA integrity during the ...
Carlson - Karola Stotz
... with their organization into introns and exons and immense amounts of repetitive DNA. The cytoplasm of the cell turned out to be more complex and feedback relations from the cell surface to the nucleus and back to components of the cytoplasm made it harder to describe a gene as simply the maker of a ...
... with their organization into introns and exons and immense amounts of repetitive DNA. The cytoplasm of the cell turned out to be more complex and feedback relations from the cell surface to the nucleus and back to components of the cytoplasm made it harder to describe a gene as simply the maker of a ...
Document
... • Changing the order of the DNA letters will change the information carried by the gene. • We will talk about how this happens later! ...
... • Changing the order of the DNA letters will change the information carried by the gene. • We will talk about how this happens later! ...
Gene Cloning Technology
... The frequency with which this particular sequence of 6 base pairs will occur in a very large DNA molecule can be calculated on the basis of: the probability of occurrence of any specified base at each position: ...
... The frequency with which this particular sequence of 6 base pairs will occur in a very large DNA molecule can be calculated on the basis of: the probability of occurrence of any specified base at each position: ...
Gene Cloning Technology
... The frequency with which this particular sequence of 6 base pairs will occur in a very large DNA molecule can be calculated on the basis of: the probability of occurrence of any specified base at each position: ...
... The frequency with which this particular sequence of 6 base pairs will occur in a very large DNA molecule can be calculated on the basis of: the probability of occurrence of any specified base at each position: ...
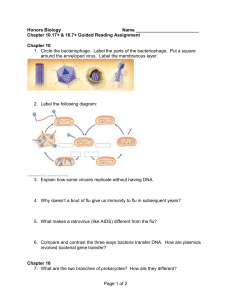
5echap10n16guidedreading
... 4. Why doesn’t a bout of flu give us immunity to flu in subsequent years? ...
... 4. Why doesn’t a bout of flu give us immunity to flu in subsequent years? ...
BISC219 F12 – Designing Primers for Amplifying and Sequencing
... 21. Make the screen bigger by dragging on the bottom right corner so you can see the peaks better 22. You can use the + and – magnifying glasses on the left hand side of the screen to make the peaks easier to see. 23. Using the scroll bar bubble at the bottom of the window, scroll to the right looki ...
... 21. Make the screen bigger by dragging on the bottom right corner so you can see the peaks better 22. You can use the + and – magnifying glasses on the left hand side of the screen to make the peaks easier to see. 23. Using the scroll bar bubble at the bottom of the window, scroll to the right looki ...
For the Tutorial Programme in Proteomics High
... the toxic gene kills the host cell. This type of selection is important to avoid the growth of cells carrying by-products of the cloning process. Negative selection markers can be propagated in special strains that are resistant to them. Cloning sites. Vectors also have specific sequences to allow t ...
... the toxic gene kills the host cell. This type of selection is important to avoid the growth of cells carrying by-products of the cloning process. Negative selection markers can be propagated in special strains that are resistant to them. Cloning sites. Vectors also have specific sequences to allow t ...