PD-PR-083: Laboratory protocol for manual
... • Air or water incubator at 50°C (Note: The false bottom tube will float in a water incubator, therefore an air incubator may be preferred.) • Ethanol (95% to 100%) at room temperature • DNA buffer: TE (10 mM Tris-HCl, 1mM EDTA, pH 8.0) or similar solution • (Optional) Glycogen (20 mg/mL) (e.g., ...
... • Air or water incubator at 50°C (Note: The false bottom tube will float in a water incubator, therefore an air incubator may be preferred.) • Ethanol (95% to 100%) at room temperature • DNA buffer: TE (10 mM Tris-HCl, 1mM EDTA, pH 8.0) or similar solution • (Optional) Glycogen (20 mg/mL) (e.g., ...
vertebrate genome evolution and function illuminated by chicken
... Genome-wide local alignment chains Human: 2.9 Gb assembly. Mask interspersed repeats, break into 300 segments of 10 Mb. ...
... Genome-wide local alignment chains Human: 2.9 Gb assembly. Mask interspersed repeats, break into 300 segments of 10 Mb. ...
TUTORIAL FIGURES: Basic Molecular Biology
... Figure 5: RNA processing. The DNA segment corresponding to a gene (top) consists of coding regions called exons and these regions are interrupted with intervening non-coding regions called introns (blue). During transcription the whole segment of DNA corresponding to the gene is copied to RNA. An RN ...
... Figure 5: RNA processing. The DNA segment corresponding to a gene (top) consists of coding regions called exons and these regions are interrupted with intervening non-coding regions called introns (blue). During transcription the whole segment of DNA corresponding to the gene is copied to RNA. An RN ...
Replication, Transcription, and Translation
... DNA Polymerase brings in new nucleotides Ligase zips the new DNA back together Why is DNA Replication important? The important idea is that an exact duplication of the DNA message is required, so that each new cell in the body has the same set of genetic instructions as the cells that preceded it. ...
... DNA Polymerase brings in new nucleotides Ligase zips the new DNA back together Why is DNA Replication important? The important idea is that an exact duplication of the DNA message is required, so that each new cell in the body has the same set of genetic instructions as the cells that preceded it. ...
Gen660_Lecture12B_NetworkEvo_2014
... How do regulatory networks evolve? Module = group of genes co-regulated by the same regulatory system * Evolution of individual gene targets Gain or loss of genes from a module * Evolution of activating signals Change in responsiveness but not regulators * Wholesale evolution of the entire module Tr ...
... How do regulatory networks evolve? Module = group of genes co-regulated by the same regulatory system * Evolution of individual gene targets Gain or loss of genes from a module * Evolution of activating signals Change in responsiveness but not regulators * Wholesale evolution of the entire module Tr ...
DNA Electrophoresis Electrophoresis Electrophoresis using DNA
... middle, using foreceps and lower them again without catching air bubbles, in order to achieve an even distribution of the liquid (fig. 5 A). Repeat this procedure during the first 15 min. Very even rehydration is also obtained when performing it on a shaker at a slow rotation rate (fig. 5 B). 90 min ...
... middle, using foreceps and lower them again without catching air bubbles, in order to achieve an even distribution of the liquid (fig. 5 A). Repeat this procedure during the first 15 min. Very even rehydration is also obtained when performing it on a shaker at a slow rotation rate (fig. 5 B). 90 min ...
Encyclopedia in Sequence
... 3. The DNA is purified and extracted. This DNA is then cut by restriction enzymes into many exact fragments. 4. Once the DNA is divided, it is treated in one of two ways. The DNA is either "amplified" with primers specific for ribosomes and transferred onto a gel using polymerase chain reaction (PCR ...
... 3. The DNA is purified and extracted. This DNA is then cut by restriction enzymes into many exact fragments. 4. Once the DNA is divided, it is treated in one of two ways. The DNA is either "amplified" with primers specific for ribosomes and transferred onto a gel using polymerase chain reaction (PCR ...
DNA Structure and Sequencing - SP14
... Figure 3 Compartmentalization enables a eukaryotic cell to divide processes into discrete steps so it can build more complex protein and RNA products. But there is an advantage to having a single compartment as well: RNA and protein synthesis occurs much more quickly in a prokaryotic cell. ...
... Figure 3 Compartmentalization enables a eukaryotic cell to divide processes into discrete steps so it can build more complex protein and RNA products. But there is an advantage to having a single compartment as well: RNA and protein synthesis occurs much more quickly in a prokaryotic cell. ...
Mouse Genome Informatics - Gene Ontology Consortium
... Formed to develop a shared language adequate for the annotation of molecular characteristics across organisms; a common language to share knowledge. ...
... Formed to develop a shared language adequate for the annotation of molecular characteristics across organisms; a common language to share knowledge. ...
SUPPORTING INFORMATION FULL LEGENDS Figure S1
... Figure S9. HA:RAP2.12 protein is stabilised by the proteasome inhibitor MG132. Ten days old XVEHA:RAP2.12 plants were treated with 5 μM estradiol for 24 hours to induce the expression of HA:RAP2.12 protein. Total protein was extracted with extraction buffer that did not contain MG132. The protein ex ...
... Figure S9. HA:RAP2.12 protein is stabilised by the proteasome inhibitor MG132. Ten days old XVEHA:RAP2.12 plants were treated with 5 μM estradiol for 24 hours to induce the expression of HA:RAP2.12 protein. Total protein was extracted with extraction buffer that did not contain MG132. The protein ex ...
Control of gene expression in prokaryotes and eukaryotes
... Gene expression is transcription of DNA to make RNA and then using the RNA to make proteins. This process can’t be left on indefinitely. The turning on and off of genes is critical to the development of an organism and the organism functioning properly throughout its life. Eukaryotic control Pretran ...
... Gene expression is transcription of DNA to make RNA and then using the RNA to make proteins. This process can’t be left on indefinitely. The turning on and off of genes is critical to the development of an organism and the organism functioning properly throughout its life. Eukaryotic control Pretran ...
teach-eng-mod2
... • Method is handicapped by the large number of possible candidates that WPA can be studied ...
... • Method is handicapped by the large number of possible candidates that WPA can be studied ...
Protein Synthesis Simulation
... DNA carries the information for the synthesis of all the proteins of an organism. Protein molecules are large and complex, composed of hundreds of amino acids. The sequence of amino acids in a protein molecule is determined by the sequence of the nucleotides in the DNA of an organism. In the first s ...
... DNA carries the information for the synthesis of all the proteins of an organism. Protein molecules are large and complex, composed of hundreds of amino acids. The sequence of amino acids in a protein molecule is determined by the sequence of the nucleotides in the DNA of an organism. In the first s ...
Chapter 7: Microbial Genetics
... DNA → Polymerase → Transcription → mRNA → Ribosome (protein+rRNA) → Translation → tRNA +Amino acid → Peptide bond → Polypeptide → Protein Mutation – Change in the genetic sequence of DNA in a cell which may or may not cause a change in the amino acid sequence coded from that section of DNA. ...
... DNA → Polymerase → Transcription → mRNA → Ribosome (protein+rRNA) → Translation → tRNA +Amino acid → Peptide bond → Polypeptide → Protein Mutation – Change in the genetic sequence of DNA in a cell which may or may not cause a change in the amino acid sequence coded from that section of DNA. ...
Biogeography 3/e
... Monophyletic – A group of organisms that include an ancestral taxon and all of its descendents Paraphyletic – A group that includes an ancestral taxon and some but not all of its descendents Polyphyletic – A grouping different from above that is an artificial taxon Clade – A monophyletic evolutionar ...
... Monophyletic – A group of organisms that include an ancestral taxon and all of its descendents Paraphyletic – A group that includes an ancestral taxon and some but not all of its descendents Polyphyletic – A grouping different from above that is an artificial taxon Clade – A monophyletic evolutionar ...
Isolating Hereditary Material
... infected cells by mechanically shearing them off in an ordinary kitchen blender. The ghosts and bacterial cells were then physically separated using a centrifuge. The larger bacterial cells moved rapidly to the bottom of the centrifuge tube, where they formed a pellet. The smaller, lighter phage gho ...
... infected cells by mechanically shearing them off in an ordinary kitchen blender. The ghosts and bacterial cells were then physically separated using a centrifuge. The larger bacterial cells moved rapidly to the bottom of the centrifuge tube, where they formed a pellet. The smaller, lighter phage gho ...
Biotechnology Laboratory (Kallas)
... most of the ~3000 genes in the Synechococcus genome are covered with 7 probes repeated three times on each array. In addition there are ~6000 high-density “tiling” probes covering upstream untranslated (UTR) regions of ~200 genes of interest for the purpose of mapping transcription start sites. In ...
... most of the ~3000 genes in the Synechococcus genome are covered with 7 probes repeated three times on each array. In addition there are ~6000 high-density “tiling” probes covering upstream untranslated (UTR) regions of ~200 genes of interest for the purpose of mapping transcription start sites. In ...
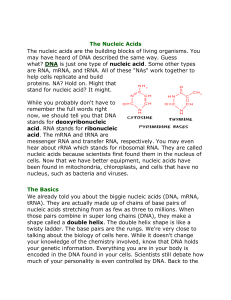
Introduction to Nucleic Acids
... The nucleic acids are the building blocks of living organisms. You may have heard of DNA described the same way. Guess what? DNA is just one type of nucleic acid. Some other types are RNA, mRNA, and tRNA. All of these "NAs" work together to help cells replicate and build proteins. NA? Hold on. Might ...
... The nucleic acids are the building blocks of living organisms. You may have heard of DNA described the same way. Guess what? DNA is just one type of nucleic acid. Some other types are RNA, mRNA, and tRNA. All of these "NAs" work together to help cells replicate and build proteins. NA? Hold on. Might ...
nitrogen bases
... • (Any one with any other one) • The homologous chromosomes can be on the left or right of the midline. • The combination of chromosomes on the left will be very different than the combination on the right which results in haploid cells at the end of Meiosis that are very ...
... • (Any one with any other one) • The homologous chromosomes can be on the left or right of the midline. • The combination of chromosomes on the left will be very different than the combination on the right which results in haploid cells at the end of Meiosis that are very ...
Explain what genetic recombination is, why it is important and ho it
... importance of RFLP analysis and nd DNA fin ...
... importance of RFLP analysis and nd DNA fin ...
HSC – Biology – Maintaining a Balance
... unknown element is selective breeding – the characteristics being bred can be precisely controlled. This type of artificial selection occurs in growing seedless grapes and bananas. In nature, genes are conserved by evolution only if they serve an essential function for the organism. The disadvantage ...
... unknown element is selective breeding – the characteristics being bred can be precisely controlled. This type of artificial selection occurs in growing seedless grapes and bananas. In nature, genes are conserved by evolution only if they serve an essential function for the organism. The disadvantage ...
DNA Cornell notes
... strands of DNA are built from the template strand, using DNA polymerase (enzyme) to bring in the nucleotides. Nucleotides on the leading strands are brought to the template strand in a continuous fashion. Nucleotides on the lagging strand are brought in segments known as Okazaki fragments. The Okaza ...
... strands of DNA are built from the template strand, using DNA polymerase (enzyme) to bring in the nucleotides. Nucleotides on the leading strands are brought to the template strand in a continuous fashion. Nucleotides on the lagging strand are brought in segments known as Okazaki fragments. The Okaza ...