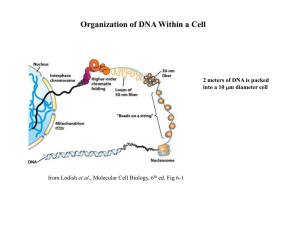
Nature Rev.Mol.Cell Biol
... The 4.6 kb Bam HI fragment is present when the b-globin gene is inactive and histones are deacetylated ...
... The 4.6 kb Bam HI fragment is present when the b-globin gene is inactive and histones are deacetylated ...
Prentice Hall Biology
... code? Why or why not? How do the proteins made affect the type and function of cells? Cells do not make all of the proteins for which they have genes (DNA). The structure and function of each cell are determined by the types of proteins present. 2. Consider what you now know about genes and protein ...
... code? Why or why not? How do the proteins made affect the type and function of cells? Cells do not make all of the proteins for which they have genes (DNA). The structure and function of each cell are determined by the types of proteins present. 2. Consider what you now know about genes and protein ...
DNA Fingerprinting
... We will be looking at a young woman who is suspected to have the Li-Fraumeni syndrome. The Human Genome Project has provided information to link the identification of many types of cancers and other diseases to DNA sequence information. (Edvotek) Cancer has been found to be linked to mutations in a ...
... We will be looking at a young woman who is suspected to have the Li-Fraumeni syndrome. The Human Genome Project has provided information to link the identification of many types of cancers and other diseases to DNA sequence information. (Edvotek) Cancer has been found to be linked to mutations in a ...
March 13
... encode ~ 100 proteins, 4 rRNA &~30 tRNA 5 classes of proteins 1. ribosomal & other proteins involved in translation 2. proteins involved in transcription 3. proteins involved in photosynthesis 4. proteins involved in respiration ...
... encode ~ 100 proteins, 4 rRNA &~30 tRNA 5 classes of proteins 1. ribosomal & other proteins involved in translation 2. proteins involved in transcription 3. proteins involved in photosynthesis 4. proteins involved in respiration ...
File
... Answer: What is genomics? 1. DNA present in single copy within the genome Answer: What are unique sequences? 2. DNA present in several copies in end-to-end arrays Answer: What are tandem repeats? 3. Most abundant type of sequence present in the human genome Answer: What are transposable elements? (o ...
... Answer: What is genomics? 1. DNA present in single copy within the genome Answer: What are unique sequences? 2. DNA present in several copies in end-to-end arrays Answer: What are tandem repeats? 3. Most abundant type of sequence present in the human genome Answer: What are transposable elements? (o ...
Getting a grip on how DNA polymerases function
... DNA polymerases play a central role in maintenance of genetic information, and the structures of polymerases in complex with DNA and dNTP provide valuable insights into mechanisms utilized by DNA polymerases to achieve high fidelity. Comparison of several high resolution complexes of DNA polymerases ...
... DNA polymerases play a central role in maintenance of genetic information, and the structures of polymerases in complex with DNA and dNTP provide valuable insights into mechanisms utilized by DNA polymerases to achieve high fidelity. Comparison of several high resolution complexes of DNA polymerases ...
CH 16 and 17 PowerPoint
... • match organ donors with recipients in transplant programs • determine pedigree for seed or livestock breeds • authenticate consumables such as caviar and wine ...
... • match organ donors with recipients in transplant programs • determine pedigree for seed or livestock breeds • authenticate consumables such as caviar and wine ...
Final Report - Rufford Small Grants
... decomposition, it was necessary to perform many repetitions and test different extraction methods in order to obtain higher DNA yields, which took a considerable amount of time. Polymerase Chain Reaction amplifications also had to be performed several times to improve product quality, since DNA sequ ...
... decomposition, it was necessary to perform many repetitions and test different extraction methods in order to obtain higher DNA yields, which took a considerable amount of time. Polymerase Chain Reaction amplifications also had to be performed several times to improve product quality, since DNA sequ ...
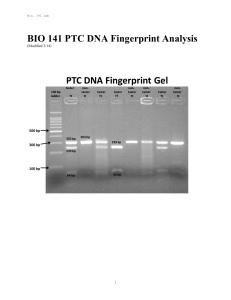
BIO 141 PTC DNA Fingerprint Analysis
... known individual can be matched to a sample from an unidentified individual. Several methods to detect DNA differences exist in DNA fingerprint analysis. Basically, scientists isolate DNA from individuals, measure the size of certain variable fragments of DNA, and compare these DNA fragments to each ...
... known individual can be matched to a sample from an unidentified individual. Several methods to detect DNA differences exist in DNA fingerprint analysis. Basically, scientists isolate DNA from individuals, measure the size of certain variable fragments of DNA, and compare these DNA fragments to each ...
2657/113 Recombinant DNA……To Exempt or Non
... Using more than 10 liters of culture. Cloning of toxin molecules with LD50 of less than 100 ng per kg of body weight. Deliberate transfer of recombinant DNA, or DNA or RNA derived from rDNA into one or more human subjects. Deliberate transfer of a drug resistant trait to microorganisms not known to ...
... Using more than 10 liters of culture. Cloning of toxin molecules with LD50 of less than 100 ng per kg of body weight. Deliberate transfer of recombinant DNA, or DNA or RNA derived from rDNA into one or more human subjects. Deliberate transfer of a drug resistant trait to microorganisms not known to ...
RayBio Genomic DNA Magnetic Beads Kit
... (see Section 7.A). As such, the experienced user may wish to adjust various steps in the standard protocol to optimize the results for the desired downstream application. Listed below are suggested customization options. A. Starting Sample Amount The amount of starting sample material used directly ...
... (see Section 7.A). As such, the experienced user may wish to adjust various steps in the standard protocol to optimize the results for the desired downstream application. Listed below are suggested customization options. A. Starting Sample Amount The amount of starting sample material used directly ...
2013 Training Handout
... DNA polymerase (III) proceeds along a single-stranded molecule of DNA, recruiting free dNTP's (deoxy-nucleotide-triphosphates) to hydrogen bond with their appropriate complementary dNTP on the single strand (A with T and G with C), and to form a covalent phosphodiester bond with the previous nucleot ...
... DNA polymerase (III) proceeds along a single-stranded molecule of DNA, recruiting free dNTP's (deoxy-nucleotide-triphosphates) to hydrogen bond with their appropriate complementary dNTP on the single strand (A with T and G with C), and to form a covalent phosphodiester bond with the previous nucleot ...
DNA and replication
... Check-up Questions: DNA replication 1. When is DNA replication going to occur? 2. Explain why DNA replication needs to occur at this time 3. Draw a diagram that shows how a DNA molecule “unzips” and then produces two new molecules 4. Explain how the DNA molecule makes an exact copy of itself during ...
... Check-up Questions: DNA replication 1. When is DNA replication going to occur? 2. Explain why DNA replication needs to occur at this time 3. Draw a diagram that shows how a DNA molecule “unzips” and then produces two new molecules 4. Explain how the DNA molecule makes an exact copy of itself during ...
CHAPTER 8 Recombinant DNA Technology
... 6. All copies of a chromosome will contain the same restriction sites, and will be cut into identical fragments. 7. Based on probability, a specific short DNA sequence occurs more frequently than a longer one. a. In a 50% G-C organism with random distribution of bases, the probability of a specific ...
... 6. All copies of a chromosome will contain the same restriction sites, and will be cut into identical fragments. 7. Based on probability, a specific short DNA sequence occurs more frequently than a longer one. a. In a 50% G-C organism with random distribution of bases, the probability of a specific ...
Distinguishing Different DNA Heterozygotes by
... SNP of interest may or may not interfere with genotyping, depending on the analysis method (10 ). All PCR-based methods can be compromised if polymorphisms occur under the primers and lead to undesired allele-specific PCR. The same concern applies to internal primers used for sequencing or extension ...
... SNP of interest may or may not interfere with genotyping, depending on the analysis method (10 ). All PCR-based methods can be compromised if polymorphisms occur under the primers and lead to undesired allele-specific PCR. The same concern applies to internal primers used for sequencing or extension ...
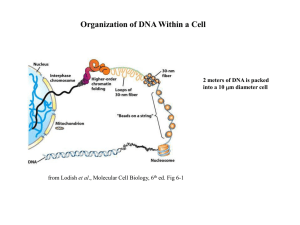
Nature Rev.Mol.Cell Biol
... avidin conjugated to alkaline phosphatase AP substrate results in the formation of an insoluble precipitate at the site of hybridization from Lodish et al., Molecular Cell Biology, 6th ed. Fig 6-44 ...
... avidin conjugated to alkaline phosphatase AP substrate results in the formation of an insoluble precipitate at the site of hybridization from Lodish et al., Molecular Cell Biology, 6th ed. Fig 6-44 ...
Epigenetic Regulation of the Glucocorticoid receptor in human brain
... cellular phenotype caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA nucleotide sequence. DNA methylation and histone deacetylation are two processes which can cause these heritable changes. ...
... cellular phenotype caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA nucleotide sequence. DNA methylation and histone deacetylation are two processes which can cause these heritable changes. ...
Bisulfite sequencing

Bisulphite sequencing (also known as bisulfite sequencing) is the use of bisulphite treatment of DNA to determine its pattern of methylation. DNA methylation was the first discovered epigenetic mark, and remains the most studied. In animals it predominantly involves the addition of a methyl group to the carbon-5 position of cytosine residues of the dinucleotide CpG, and is implicated in repression of transcriptional activity.Treatment of DNA with bisulphite converts cytosine residues to uracil, but leaves 5-methylcytosine residues unaffected. Thus, bisulphite treatment introduces specific changes in the DNA sequence that depend on the methylation status of individual cytosine residues, yielding single- nucleotide resolution information about the methylation status of a segment of DNA. Various analyses can be performed on the altered sequence to retrieve this information. The objective of this analysis is therefore reduced to differentiating between single nucleotide polymorphisms (cytosines and thymidine) resulting from bisulphite conversion (Figure 1).