Ferroelectrics in microwave technology
... ferroelectric phases, in microwave devices and systems. A strong preference will be given to experimental papers with RF/microwave device or circuit demonstrations, and papers that address existing limitations of the technology with respect to RF losses, measurements, and circuit performance. Purely ...
... ferroelectric phases, in microwave devices and systems. A strong preference will be given to experimental papers with RF/microwave device or circuit demonstrations, and papers that address existing limitations of the technology with respect to RF losses, measurements, and circuit performance. Purely ...
Final Presentation
... ● Simple pull-up configuration ● Simple circuit for debouncing ● Using time constant of 3.3ms ...
... ● Simple pull-up configuration ● Simple circuit for debouncing ● Using time constant of 3.3ms ...
Article - I
... implemented, and also has all the good properties of the DDCC, such as high-input impedance, employs fewer active and passive components, and easy implementation of differential and floating input circuits. Moreover, the differential voltage current conveyor transconductance amplifier (DVCCTA) can e ...
... implemented, and also has all the good properties of the DDCC, such as high-input impedance, employs fewer active and passive components, and easy implementation of differential and floating input circuits. Moreover, the differential voltage current conveyor transconductance amplifier (DVCCTA) can e ...
Stop-band limitations of the Sallen-Key, low
... Sallen-Key filter (see Figure 1) are R1 = 2.74 kW, R2 = 19.6 kW, C1 = 10 nF, and C2 = 47 nF. These resistors and capacitors, combined with the amplifier, form a Butterworth, maximally flat response. After the cutoff frequency (Figure 3), the responses of all three of the filters show a slope of –40 ...
... Sallen-Key filter (see Figure 1) are R1 = 2.74 kW, R2 = 19.6 kW, C1 = 10 nF, and C2 = 47 nF. These resistors and capacitors, combined with the amplifier, form a Butterworth, maximally flat response. After the cutoff frequency (Figure 3), the responses of all three of the filters show a slope of –40 ...
Simulated Inductance
... – Determine the transfer function – Calculate the output voltage in phasor notation at the corner frequency. – obtain a Bode plot ...
... – Determine the transfer function – Calculate the output voltage in phasor notation at the corner frequency. – obtain a Bode plot ...
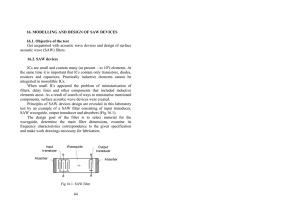
16. Modelling and design of SAW devices
... ICs are small and contain many (at present – to 108) elements. At the same time it is important that ICs contain only transistors, diodes, resistors and capacitors. Practically inductive elements cannot be integrated in monolithic ICs. When small ICs appeared the problem of miniaturisation of filter ...
... ICs are small and contain many (at present – to 108) elements. At the same time it is important that ICs contain only transistors, diodes, resistors and capacitors. Practically inductive elements cannot be integrated in monolithic ICs. When small ICs appeared the problem of miniaturisation of filter ...
- Glenair
... diodes (for EMP applications) to “strip off” unwanted noise or transient voltages from the signal. Types include tubular, planar array, chip on flex/board, EE seal and others “Low-pass” filters attenuate high-frequency noise and allow lowfrequency signals to pass Each application environment d ...
... diodes (for EMP applications) to “strip off” unwanted noise or transient voltages from the signal. Types include tubular, planar array, chip on flex/board, EE seal and others “Low-pass” filters attenuate high-frequency noise and allow lowfrequency signals to pass Each application environment d ...
Analog Sensor Amplification/ Attenuation 8th Order Low Pass Filter
... The original customer requirement for this project was for a universal sensor input. This could not be accomplished while accomplishing the other requirements as well. So the input of the system was changed to be from 0-10V. The microcontroller that was selected only has an input range of 0-3.3V. To ...
... The original customer requirement for this project was for a universal sensor input. This could not be accomplished while accomplishing the other requirements as well. So the input of the system was changed to be from 0-10V. The microcontroller that was selected only has an input range of 0-3.3V. To ...
Relevant RF Semiconductor Developments
... from commercial deployment, since it was done in a 45nm CMOS process, and the rest of the transceiver circuitry may not yet be available in such a process. ...
... from commercial deployment, since it was done in a 45nm CMOS process, and the rest of the transceiver circuitry may not yet be available in such a process. ...
Frequency Response And Passive Filters
... components result from vibration. We will use a low pass filter to pass the 100 Hz component and reject the vibration components. Then we will use a high pass filter to pass the vibration components and reject the 100 Hz component. 2. Set the waveform generator to sinusoidal mode. Switch to the AM m ...
... components result from vibration. We will use a low pass filter to pass the 100 Hz component and reject the vibration components. Then we will use a high pass filter to pass the vibration components and reject the 100 Hz component. 2. Set the waveform generator to sinusoidal mode. Switch to the AM m ...
Chapter 2 - Portal UniMAP
... – Attenuation refers to a loss introduced by a circuit or component. If the output signal is lower in amplitude than the input, the circuit has loss or attenuation. – The letter A is used to represent attenuation – Attenuation A = output/input = Vout/Vin – Circuits that introduce attenuation have a ...
... – Attenuation refers to a loss introduced by a circuit or component. If the output signal is lower in amplitude than the input, the circuit has loss or attenuation. – The letter A is used to represent attenuation – Attenuation A = output/input = Vout/Vin – Circuits that introduce attenuation have a ...
High-Input and Low-Output Impedance Voltage
... low-output impedance voltage-mode universal biquadratic filter using three DDCCs, two grounded capacitors and resistors. In this paper, although the use of FDCCII can be divided into two separate DDCC’s, the proposed circuit still maintains the following advantages: (i) employment of two current con ...
... low-output impedance voltage-mode universal biquadratic filter using three DDCCs, two grounded capacitors and resistors. In this paper, although the use of FDCCII can be divided into two separate DDCC’s, the proposed circuit still maintains the following advantages: (i) employment of two current con ...
Part A: Low Pass Filter Frequency Response
... the universal bridge on the instructor’s table. Enter these values on the data sheet. 2. Construct the high pass filter circuit illustrated in Figure 2. It is convenient to use banana leads for the component connections, but we suggest using probes for the scope measurements (remember to check that ...
... the universal bridge on the instructor’s table. Enter these values on the data sheet. 2. Construct the high pass filter circuit illustrated in Figure 2. It is convenient to use banana leads for the component connections, but we suggest using probes for the scope measurements (remember to check that ...