Fundamentals of Passive Component Behavior at High Frequencies
... frequency increases. The final characteristic in this article is electromagnetic radiation and coupling. Radiation causes losses and creates interference within, and external to, the circuit. Coupling between components may be included in the category of internal interference, or it can also be an i ...
... frequency increases. The final characteristic in this article is electromagnetic radiation and coupling. Radiation causes losses and creates interference within, and external to, the circuit. Coupling between components may be included in the category of internal interference, or it can also be an i ...
Active_Filter_Lab
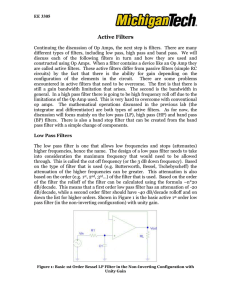
... Continuing the discussion of Op Amps, the next step is filters. There are many different types of filters, including low pass, high pass and band pass. We will discuss each of the following filters in turn and how they are used and constructed using Op Amps. When a filter contains a device like an O ...
... Continuing the discussion of Op Amps, the next step is filters. There are many different types of filters, including low pass, high pass and band pass. We will discuss each of the following filters in turn and how they are used and constructed using Op Amps. When a filter contains a device like an O ...
1. Introduction - About the journal
... large bandwidth, lower nonlinear distortion and wider dynamic range, and the power consumption is low. A fully balanced filter can suppress even order distortion and common-mode interference effectively. It has an important application in communication systems. In literature [5], systematic designs ...
... large bandwidth, lower nonlinear distortion and wider dynamic range, and the power consumption is low. A fully balanced filter can suppress even order distortion and common-mode interference effectively. It has an important application in communication systems. In literature [5], systematic designs ...
4.2.3 – Resonant Filters
... they need some sort of amplification to improve their operation and are outside the scope of this introductory unit. You will be introduced to the start of this area of work in ET5 when you look at Active Filters. So far we have assumed that all the components we have used are ‘ideal’. In practice o ...
... they need some sort of amplification to improve their operation and are outside the scope of this introductory unit. You will be introduced to the start of this area of work in ET5 when you look at Active Filters. So far we have assumed that all the components we have used are ‘ideal’. In practice o ...
Specifications - Lucas
... The UniTrain-I system is a computer-based training and experimentation system for vocational and further training and education in the areas of basic and advanced electrical engineering and electronics. Its multimedia courses combine cognitive and hands-on (haptic) training units into a comprehensi ...
... The UniTrain-I system is a computer-based training and experimentation system for vocational and further training and education in the areas of basic and advanced electrical engineering and electronics. Its multimedia courses combine cognitive and hands-on (haptic) training units into a comprehensi ...
Experiment 5 Active filters and tuned amplifiers
... will be intentionally added to the signal. This noise will be obtained from the noise generator circuit available on the reference job board. The relevant part of the reference job board circuit is shown. The 5837 digital noise generator IC produces 10 V pulses that have varying durations. The pulse ...
... will be intentionally added to the signal. This noise will be obtained from the noise generator circuit available on the reference job board. The relevant part of the reference job board circuit is shown. The 5837 digital noise generator IC produces 10 V pulses that have varying durations. The pulse ...
Section_6_-_Summary_
... improves the resolution capabilities of the EMD method, in terms of detecting weak higher frequency modes, as well as separating closely spaced modal frequencies. In Chapter 21 reference is made to ideal supply conditions which allow recognising the frequencies and the origins of those interharmoni ...
... improves the resolution capabilities of the EMD method, in terms of detecting weak higher frequency modes, as well as separating closely spaced modal frequencies. In Chapter 21 reference is made to ideal supply conditions which allow recognising the frequencies and the origins of those interharmoni ...
Analog Path Amplification/Attenuation Resistive divider --
... This DAQ device is being powered by a 3.7V Lithium Polymer battery. This battery will be charged using a USB. USB was chosen because USB has a 5V pin. Also the FRDM KL25Z board is charged via a USB. The MCP73831 chip will be used to charge the LiPo battery. This chip is a linear charge management i ...
... This DAQ device is being powered by a 3.7V Lithium Polymer battery. This battery will be charged using a USB. USB was chosen because USB has a 5V pin. Also the FRDM KL25Z board is charged via a USB. The MCP73831 chip will be used to charge the LiPo battery. This chip is a linear charge management i ...
Experiment 2
... The resonant frequency of an RLC circuit tells us where it reaches a maximum or minimum. This can define the center of the band (on a band filter) or the location of the transition (on a high ...
... The resonant frequency of an RLC circuit tells us where it reaches a maximum or minimum. This can define the center of the band (on a band filter) or the location of the transition (on a high ...
2 Impedance and Transfer Functions
... Filters are mostly used for eliminating noise, so to see them in action we need to create a noisy signal. This can be achieved by adding a high frequency signal from the function generator to a 60 Hz signal derived from the wall power lines. To start, locate the 6.3 V transformer and plug it in. Obs ...
... Filters are mostly used for eliminating noise, so to see them in action we need to create a noisy signal. This can be achieved by adding a high frequency signal from the function generator to a 60 Hz signal derived from the wall power lines. To start, locate the 6.3 V transformer and plug it in. Obs ...
A Reconfigurable FIR Filter Embedded in a 9b Successive
... filter suppression can be enhanced or relaxed during system operation by increasing or decreasing the number of available filter zeros, respectively. Both of these changes require few modifications to the existing hardware. The first case typically requires only the addition of sampling related cont ...
... filter suppression can be enhanced or relaxed during system operation by increasing or decreasing the number of available filter zeros, respectively. Both of these changes require few modifications to the existing hardware. The first case typically requires only the addition of sampling related cont ...
Analog and digital filters
... frequency signals accurately. As the speed of DSP technology continues to increase, digital filters are being applied to high frequency signals in the RF (radio frequency) domain, which in the past was the exclusive preserve of analog technology. 5. Digital filters are very much more versatile in th ...
... frequency signals accurately. As the speed of DSP technology continues to increase, digital filters are being applied to high frequency signals in the RF (radio frequency) domain, which in the past was the exclusive preserve of analog technology. 5. Digital filters are very much more versatile in th ...