lecture1430873461
... Because of the minus sign decibel attenuation always is a positive number. Decibel attenuation uses the midband output voltage as a reference. Basically, we are comparing the output voltage at any frequency to the output voltage in the midband of the filter. Because attenuation is almost always expr ...
... Because of the minus sign decibel attenuation always is a positive number. Decibel attenuation uses the midband output voltage as a reference. Basically, we are comparing the output voltage at any frequency to the output voltage in the midband of the filter. Because attenuation is almost always expr ...
Experiment V: The AC Circuit, Impedance, and Applications to High
... allocated to you, so you can hear your conversation, and not everyone elses! Your cell phone “tunes” to a frequency band in much the same way as your radio tunes to a particular station. We will start here with simple AC circuits that contain either an inductor or a capacitor, but not both. Along wi ...
... allocated to you, so you can hear your conversation, and not everyone elses! Your cell phone “tunes” to a frequency band in much the same way as your radio tunes to a particular station. We will start here with simple AC circuits that contain either an inductor or a capacitor, but not both. Along wi ...
EMC filters 3-phase dv/dt output reactors 520 V AC, 8 1500 A, 40
... certain areas of application. These statements are based on our knowledge of typical requirements that are often placed on our products in the areas of application concerned. We nevertheless expressly point out that such statements cannot be regarded as binding statements about the suitability of ou ...
... certain areas of application. These statements are based on our knowledge of typical requirements that are often placed on our products in the areas of application concerned. We nevertheless expressly point out that such statements cannot be regarded as binding statements about the suitability of ou ...
A Practical Micropower Programmable Bandpass Filter for use in Bionic Ears
... function of the ear in stimulating neurons in the cochlea in response to sound. Fig. 1 shows an overview of a common signal-processing chain: sound is first sensed by a microphone. Preemphasis and gain control are then performed on the input. Bandpass filters (BPFs) then divide the sound into differ ...
... function of the ear in stimulating neurons in the cochlea in response to sound. Fig. 1 shows an overview of a common signal-processing chain: sound is first sensed by a microphone. Preemphasis and gain control are then performed on the input. Bandpass filters (BPFs) then divide the sound into differ ...
REFINEMENT OF HARMONICS USING APF WITH SINUSOIDAL
... is used for the enhancement of the power quality and power factor in three phase power systems. Active power filters are widely used for the elimination of non-sinusoidal currents. The pulse width modulated control of the active filter allows independent control of lower order harmonics for improvem ...
... is used for the enhancement of the power quality and power factor in three phase power systems. Active power filters are widely used for the elimination of non-sinusoidal currents. The pulse width modulated control of the active filter allows independent control of lower order harmonics for improvem ...
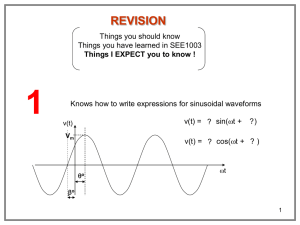
Revision AC
... Impedance: A ratio between voltage and current phasors – it is a complex number but NOT a phasor ...
... Impedance: A ratio between voltage and current phasors – it is a complex number but NOT a phasor ...
Operational Amplifiers (Op Amps)
... If R4=R3 and R2=R1, then it becomes amplified difference op-amp Vout=(V2-V1)R3/R1 ...
... If R4=R3 and R2=R1, then it becomes amplified difference op-amp Vout=(V2-V1)R3/R1 ...
Introduction and Digital Images
... •A band-pass filter allows frequencies between two critical frequencies and rejects all others. • A band-stop filter rejects frequencies between two critical frequencies and passes all others. • Band-pass and band-stop filters can be made from both series and parallel resonant circuits. •The bandwid ...
... •A band-pass filter allows frequencies between two critical frequencies and rejects all others. • A band-stop filter rejects frequencies between two critical frequencies and passes all others. • Band-pass and band-stop filters can be made from both series and parallel resonant circuits. •The bandwid ...
Optimizing the Heathkit HW-101, SB100-102 Transceivers
... 70's and are fairly plentiful on the used market even today, nearly 30 years later. This series of modifications will increase the audio quality of both receive and transmit, improve operation on CW, enhance strong signal handling of the rigs, and make the units useable with the low-Z headphones so ...
... 70's and are fairly plentiful on the used market even today, nearly 30 years later. This series of modifications will increase the audio quality of both receive and transmit, improve operation on CW, enhance strong signal handling of the rigs, and make the units useable with the low-Z headphones so ...
Unit_III
... For a load impedance ZL=60-j80Ω, design two single-stub (short circuit) shunt tunning networks to matching this load to a 50 Ω line. Assuming that the load is matched at 2GHz and that load consists of a resistor and capacitor in series. ...
... For a load impedance ZL=60-j80Ω, design two single-stub (short circuit) shunt tunning networks to matching this load to a 50 Ω line. Assuming that the load is matched at 2GHz and that load consists of a resistor and capacitor in series. ...
3. Proposed Universal Biquad Employing only
... It is, thus, seen that the proposed circuit employs one less active building block (ABB) in comparison to the universal biquads published earlier in [3]-[6] and yet exhibits all the properties of the earlier circuits, in that, it realizes all the five basic filter functions with electronic tunabilit ...
... It is, thus, seen that the proposed circuit employs one less active building block (ABB) in comparison to the universal biquads published earlier in [3]-[6] and yet exhibits all the properties of the earlier circuits, in that, it realizes all the five basic filter functions with electronic tunabilit ...
Document
... rises more rapidly than the spring force • top plate snaps down toward the bottom plate • limits controllable increase in capacitance for this type of variable capacitor to 50% • parasitic capacitance lowers the possible tuning range. ...
... rises more rapidly than the spring force • top plate snaps down toward the bottom plate • limits controllable increase in capacitance for this type of variable capacitor to 50% • parasitic capacitance lowers the possible tuning range. ...
21. Frequency Response
... • The roots of the numerator, N(s), are called the zeros since they cause the transfer function H(s) to become zero, i.e., H(zi)=0 • The roots of the denominator, D(s), are called the poles and they cause the transfer function H(s) to become infinity, i.e., H(pi)= ...
... • The roots of the numerator, N(s), are called the zeros since they cause the transfer function H(s) to become zero, i.e., H(zi)=0 • The roots of the denominator, D(s), are called the poles and they cause the transfer function H(s) to become infinity, i.e., H(pi)= ...
PreLab 3: ECG Measurement System (12 problems for 40 pts)
... PROBLEM 1: Let your instrumentation amplifier be powered by +/-9 V. Assume the maximum signal output is 1V less than the power supply. What is the maximum usable gain for the instrumentation amplifier? Note: For Lab3, we will be a little conservative and use a gain Ad = 20 (produced by RG = 2.61 koh ...
... PROBLEM 1: Let your instrumentation amplifier be powered by +/-9 V. Assume the maximum signal output is 1V less than the power supply. What is the maximum usable gain for the instrumentation amplifier? Note: For Lab3, we will be a little conservative and use a gain Ad = 20 (produced by RG = 2.61 koh ...
A 40 meters CW QRP Transceiver
... It employs a double tuned circuit, made using two common 10.7 MHz FM transfomers. In this manner a good withstanding was obtained against overloading signals and inter-modulation. The input is protected against over-voltages by two opposed diodes. An emitter-follower transistor transfers the signal ...
... It employs a double tuned circuit, made using two common 10.7 MHz FM transfomers. In this manner a good withstanding was obtained against overloading signals and inter-modulation. The input is protected against over-voltages by two opposed diodes. An emitter-follower transistor transfers the signal ...
DMPX07f - School of Computer Science
... (i) Gain response has gradual ‘roll-off’ and becomes -6 dB down at the cut-off frequency.It will have a well defined stop-band decreasing in gain from 0dB at 0 Hz to -6 dB at the cut-off frequency. The stop-band gain will have stop-band ripples, the maximum amplitude being about ...
... (i) Gain response has gradual ‘roll-off’ and becomes -6 dB down at the cut-off frequency.It will have a well defined stop-band decreasing in gain from 0dB at 0 Hz to -6 dB at the cut-off frequency. The stop-band gain will have stop-band ripples, the maximum amplitude being about ...
Class-AB Amplifier
... Ferrite Bead + Shunt Cap Filter - Filter output impedance is generally reactive (inductive or capacitive). - This is especially true when the ferrite bead is in saturation, because its impedance becomes more like that of an inductor. ...
... Ferrite Bead + Shunt Cap Filter - Filter output impedance is generally reactive (inductive or capacitive). - This is especially true when the ferrite bead is in saturation, because its impedance becomes more like that of an inductor. ...
EC312 Lecture 11
... we have seen the frequency vs time relationship. We understand that when we want to communicate wirelessly, we will need to modulate our baseband or information signal and that it is important to know the frequencies that are transmitted and the bandwidth. We have introduced the idea of filtering in ...
... we have seen the frequency vs time relationship. We understand that when we want to communicate wirelessly, we will need to modulate our baseband or information signal and that it is important to know the frequencies that are transmitted and the bandwidth. We have introduced the idea of filtering in ...
Connecting Outputs in Series to Achieve High Voltage Transients
... considered to be positive as long as the real part of Z or Y is positive, as it will be for passive components. (Note, however, that transfer impedance of passive networks can exhibit negative real parts). For resistors, a common convention is to consider Q to be positive if the component is inducti ...
... considered to be positive as long as the real part of Z or Y is positive, as it will be for passive components. (Note, however, that transfer impedance of passive networks can exhibit negative real parts). For resistors, a common convention is to consider Q to be positive if the component is inducti ...
Distributed element filter
A distributed element filter is an electronic filter in which capacitance, inductance and resistance (the elements of the circuit) are not localised in discrete capacitors, inductors and resistors as they are in conventional filters. Its purpose is to allow a range of signal frequencies to pass, but to block others. Conventional filters are constructed from inductors and capacitors, and the circuits so built are described by the lumped element model, which considers each element to be ""lumped together"" at one place. That model is conceptually simple, but it becomes increasingly unreliable as the frequency of the signal increases, or equivalently as the wavelength decreases. The distributed element model applies at all frequencies, and is used in transmission line theory; many distributed element components are made of short lengths of transmission line. In the distributed view of circuits, the elements are distributed along the length of conductors and are inextricably mixed together. The filter design is usually concerned only with inductance and capacitance, but because of this mixing of elements they cannot be treated as separate ""lumped"" capacitors and inductors. There is no precise frequency above which distributed element filters must be used but they are especially associated with the microwave band (wavelength less than one metre).Distributed element filters are used in many of the same applications as lumped element filters, such as selectivity of radio channel, bandlimiting of noise and multiplexing of many signals into one channel. Distributed element filters may be constructed to have any of the bandforms possible with lumped elements (low-pass, band-pass, etc.) with the exception of high-pass, which is usually only approximated. All filter classes used in lumped element designs (Butterworth, Chebyshev, etc.) can be implemented using a distributed element approach.There are many component forms used to construct distributed element filters, but all have the common property of causing a discontinuity on the transmission line. These discontinuities present a reactive impedance to a wavefront travelling down the line, and these reactances can be chosen by design to serve as approximations for lumped inductors, capacitors or resonators, as required by the filter.The development of distributed element filters was spurred on by the military need for radar and electronic counter measures during World War II. Lumped element analogue filters had long before been developed but these new military systems operated at microwave frequencies and new filter designs were required. When the war ended, the technology found applications in the microwave links used by telephone companies and other organisations with large fixed-communication networks, such as television broadcasters. Nowadays the technology can be found in several mass-produced consumer items, such as the converters (figure 1 shows an example) used with satellite television dishes.