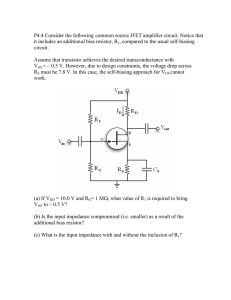
P4.4 Consider the following common source JFET amplifier circuit. Notice... it includes an additional bias resistor, R
... P4.4 Consider the following common source JFET amplifier circuit. Notice that it includes an additional bias resistor, R1, compared to the usual self-biasing circuit. Assume that transistor achieves the desired transconductance with VGS = – 0.5 V. However, due to design constraints, the voltage drop ...
... P4.4 Consider the following common source JFET amplifier circuit. Notice that it includes an additional bias resistor, R1, compared to the usual self-biasing circuit. Assume that transistor achieves the desired transconductance with VGS = – 0.5 V. However, due to design constraints, the voltage drop ...
Experiment 4: Op-Amp Circuits Objective: EQUIPMENT AND PARTS
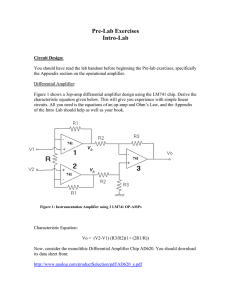
... Operational amplifiers can be basically viewed as voltage amplifiers with very high open loop gain, very high input resistance, and very low output resistance. They are commonly available in an integrated circuit (IC) package. An IC can include many components such as transistors, diodes, resistors, ...
... Operational amplifiers can be basically viewed as voltage amplifiers with very high open loop gain, very high input resistance, and very low output resistance. They are commonly available in an integrated circuit (IC) package. An IC can include many components such as transistors, diodes, resistors, ...
REVIEW FOR ELEC 105 MIDTERM EXAM #1 (FALL 2001)
... - ideal op-amp characteristics o infinite open-loop gain o infinite input resistance between input terminals o zero output resistance o zero current flow into the inverting and noninverting inputs - closed-loop voltage gain vs. open-loop voltage gain - virtual short if neg. feedback is present and o ...
... - ideal op-amp characteristics o infinite open-loop gain o infinite input resistance between input terminals o zero output resistance o zero current flow into the inverting and noninverting inputs - closed-loop voltage gain vs. open-loop voltage gain - virtual short if neg. feedback is present and o ...
DC characteristics Input offset voltage
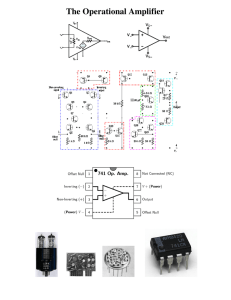
... OPERATION AMPLIFIER An operational amplifier is a direct coupled high gain amplifier consisting of one or more differential amplifiers, followed by a level translator and an output stage. It is a versatile device that can be used to amplify ac as well as dc input signals & designed for computing ma ...
... OPERATION AMPLIFIER An operational amplifier is a direct coupled high gain amplifier consisting of one or more differential amplifiers, followed by a level translator and an output stage. It is a versatile device that can be used to amplify ac as well as dc input signals & designed for computing ma ...
VCC_BAR Power, either postive or negative Grounds
... The output resistance is considered to be zero ohms. (ROUT ≈ 0 ohms) The potential difference between the two input pins is considered to be zero volts. (VIN = V2 – V1 ≈ 0 volts) No current flows into the op-amp. ...
... The output resistance is considered to be zero ohms. (ROUT ≈ 0 ohms) The potential difference between the two input pins is considered to be zero volts. (VIN = V2 – V1 ≈ 0 volts) No current flows into the op-amp. ...
The Operational Amplifier
... The circuit is used to minimise impact on the source where Vin comes from and to provide higher current at Vout without impacting the source circuit. Nevertheless the circuit may become unstable when connected to a capacitive load. A solution may be to use two inverting amplifiers configuration with ...
... The circuit is used to minimise impact on the source where Vin comes from and to provide higher current at Vout without impacting the source circuit. Nevertheless the circuit may become unstable when connected to a capacitive load. A solution may be to use two inverting amplifiers configuration with ...
UTP Cable Connectors
... • Used as a buffer, to prevent a high source resistance from being loaded down by a low-resistance load. In another word it prevents drawing current from the source. ...
... • Used as a buffer, to prevent a high source resistance from being loaded down by a low-resistance load. In another word it prevents drawing current from the source. ...
Sheet 4
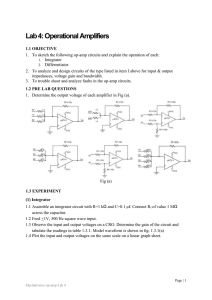
... Lab 4: Operational Amplifiers 1.1 OBJECTIVE 1. To sketch the following op-amp circuits and explain the operation of each: 1. Integrator 2. Differentiator. 2. To analyze and design circuits of the type listed in item I above for input & output impedances, voltage gain and bandwidth. 3. To trouble sho ...
... Lab 4: Operational Amplifiers 1.1 OBJECTIVE 1. To sketch the following op-amp circuits and explain the operation of each: 1. Integrator 2. Differentiator. 2. To analyze and design circuits of the type listed in item I above for input & output impedances, voltage gain and bandwidth. 3. To trouble sho ...
Operational amplifier

An operational amplifier (""op-amp"") is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output. In this configuration, an op-amp produces an output potential (relative to circuit ground) that is typically hundreds of thousands of times larger than the potential difference between its input terminals.Operational amplifiers had their origins in analog computers, where they were used to do mathematical operations in many linear, non-linear and frequency-dependent circuits. The popularity of the op-amp as a building block in analog circuits is due to its versatility. Due to negative feedback, the characteristics of an op-amp circuit, its gain, input and output impedance, bandwidth etc. are determined by external components and have little dependence on temperature coefficients or manufacturing variations in the op-amp itself.Op-amps are among the most widely used electronic devices today, being used in a vast array of consumer, industrial, and scientific devices. Many standard IC op-amps cost only a few cents in moderate production volume; however some integrated or hybrid operational amplifiers with special performance specifications may cost over $100 US in small quantities. Op-amps may be packaged as components, or used as elements of more complex integrated circuits.The op-amp is one type of differential amplifier. Other types of differential amplifier include the fully differential amplifier (similar to the op-amp, but with two outputs), the instrumentation amplifier (usually built from three op-amps), the isolation amplifier (similar to the instrumentation amplifier, but with tolerance to common-mode voltages that would destroy an ordinary op-amp), and negative feedback amplifier (usually built from one or more op-amps and a resistive feedback network).