LF198/LF298/LF398, LF198A/LF398A Monolithic Sample-and
... Note 3: Although the differential voltage may not exceed the limits given, the common-mode voltage on the logic pins may be equal to the supply voltages without causing damage to the circuit. For proper logic operation, however, one of the logic pins must always be at least 2V below the positive sup ...
... Note 3: Although the differential voltage may not exceed the limits given, the common-mode voltage on the logic pins may be equal to the supply voltages without causing damage to the circuit. For proper logic operation, however, one of the logic pins must always be at least 2V below the positive sup ...
Reverse Biased Capacitance + + + + +
... of generation! The explanation based on the drift current (given earlier) is still valid: generated holes and electrons drift through the depletion layer. ...
... of generation! The explanation based on the drift current (given earlier) is still valid: generated holes and electrons drift through the depletion layer. ...
Chapter 1 - Answers - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
... 1. Define what effect a capacitor and inductor will have on an a.c. circuit. A capacitor will cause a current to lead voltage and an inductor will make current lag voltage in an a.c. circuit. 2. What is impedance? This is the combined effect of capacitors, inductors and resistance in an a.c. circuit ...
... 1. Define what effect a capacitor and inductor will have on an a.c. circuit. A capacitor will cause a current to lead voltage and an inductor will make current lag voltage in an a.c. circuit. 2. What is impedance? This is the combined effect of capacitors, inductors and resistance in an a.c. circuit ...
Electric Current
... Ampere (A) is unit of current (I) I = Δq t Ammeter measures current Electric Circuit is a closed path along which charged particles move Current Calculation A total of 20.0C of charge pass a given point in a conductor in 4.0 seconds. Determine the current in the conductor. I = Δq = 20.0C = 5 ...
... Ampere (A) is unit of current (I) I = Δq t Ammeter measures current Electric Circuit is a closed path along which charged particles move Current Calculation A total of 20.0C of charge pass a given point in a conductor in 4.0 seconds. Determine the current in the conductor. I = Δq = 20.0C = 5 ...
Alternating current
... keeps on blowing.” Kieran: “It sounds as if something is wrong, I would get an electrician to have a look at it.” 16 of 30 ...
... keeps on blowing.” Kieran: “It sounds as if something is wrong, I would get an electrician to have a look at it.” 16 of 30 ...
, One.. Temperature Pressure Dryness Proximity Voltage Current
... Storage Temperature, T«TO Operating Junction Temperature, TJ ...
... Storage Temperature, T«TO Operating Junction Temperature, TJ ...
AD8010
... Figure 29. Ferrite beads (Amidon Associates, Torrance CA, Part Number 43101) are used to suppress high frequency power supply energy on the DUT supply lines at the DUT. C1 and C2 each represent the parallel combination of a 47 µF (16 V) tantalum electrolytic capacitor, a 10 µF (10 V) tantalum electr ...
... Figure 29. Ferrite beads (Amidon Associates, Torrance CA, Part Number 43101) are used to suppress high frequency power supply energy on the DUT supply lines at the DUT. C1 and C2 each represent the parallel combination of a 47 µF (16 V) tantalum electrolytic capacitor, a 10 µF (10 V) tantalum electr ...
Document
... peak output voltage, vo across the load, R ii. Sketch the output voltage, vo and label its peak value. ...
... peak output voltage, vo across the load, R ii. Sketch the output voltage, vo and label its peak value. ...
a Precision Instrumentation Amplifier AD624
... drift is dominant, while at high gains input offset drift dominates. Therefore, the output offset voltage drift is normally specified as drift at G = 1 (where input effects are insignificant), while input offset voltage drift is given by drift specification at a high gain (where output offset effect ...
... drift is dominant, while at high gains input offset drift dominates. Therefore, the output offset voltage drift is normally specified as drift at G = 1 (where input effects are insignificant), while input offset voltage drift is given by drift specification at a high gain (where output offset effect ...
Voltage, Current and Ohm`s Law
... the current flow through both resistors - do not give it a choice). Now set the voltage of the PS to 5 volts and note both the current and the brightness of both bulbs. Are they the same brightness as when you placed five volts across each separately? Is the same current going through each as when y ...
... the current flow through both resistors - do not give it a choice). Now set the voltage of the PS to 5 volts and note both the current and the brightness of both bulbs. Are they the same brightness as when you placed five volts across each separately? Is the same current going through each as when y ...
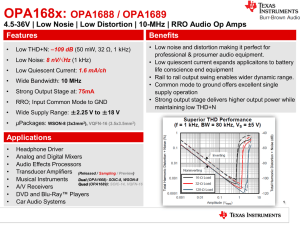
Low Distortion | 10-MHz | RRO Audio Op Amps
... In order to achieve clarity and precision in applications, such as Audio Effects Processors and Car Audio Systems, low noise and distortion op amps are required for success ...
... In order to achieve clarity and precision in applications, such as Audio Effects Processors and Car Audio Systems, low noise and distortion op amps are required for success ...
Microstepping DMOS Driver with Translator A3977
... should be soldered directly onto the board. The load supply terminal, VBB, should be decoupled with an electrolytic capacitor (>47 µF is recommended) placed as close to the device as possible. To avoid problems due to capacitive coupling of the high dv/dt switching transients, route the bridge-outpu ...
... should be soldered directly onto the board. The load supply terminal, VBB, should be decoupled with an electrolytic capacitor (>47 µF is recommended) placed as close to the device as possible. To avoid problems due to capacitive coupling of the high dv/dt switching transients, route the bridge-outpu ...
Automatic 9V Battery Charger»Automatic 9V battery charger
... A pulse width modulation signal is used to drive the MOSFET, which controls the power flow from the input to the output of the converter. Two main components are used to model the PWM: a triangle wave and a comparator. Pspice does not have a triangle wave generator/source, but a triangle wave can be ...
... A pulse width modulation signal is used to drive the MOSFET, which controls the power flow from the input to the output of the converter. Two main components are used to model the PWM: a triangle wave and a comparator. Pspice does not have a triangle wave generator/source, but a triangle wave can be ...
Operational amplifier

An operational amplifier (""op-amp"") is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output. In this configuration, an op-amp produces an output potential (relative to circuit ground) that is typically hundreds of thousands of times larger than the potential difference between its input terminals.Operational amplifiers had their origins in analog computers, where they were used to do mathematical operations in many linear, non-linear and frequency-dependent circuits. The popularity of the op-amp as a building block in analog circuits is due to its versatility. Due to negative feedback, the characteristics of an op-amp circuit, its gain, input and output impedance, bandwidth etc. are determined by external components and have little dependence on temperature coefficients or manufacturing variations in the op-amp itself.Op-amps are among the most widely used electronic devices today, being used in a vast array of consumer, industrial, and scientific devices. Many standard IC op-amps cost only a few cents in moderate production volume; however some integrated or hybrid operational amplifiers with special performance specifications may cost over $100 US in small quantities. Op-amps may be packaged as components, or used as elements of more complex integrated circuits.The op-amp is one type of differential amplifier. Other types of differential amplifier include the fully differential amplifier (similar to the op-amp, but with two outputs), the instrumentation amplifier (usually built from three op-amps), the isolation amplifier (similar to the instrumentation amplifier, but with tolerance to common-mode voltages that would destroy an ordinary op-amp), and negative feedback amplifier (usually built from one or more op-amps and a resistive feedback network).