The Shunt Regulator
... 3. The load current is iL = VZK RL . 4. The current through the shunt resistor R is i = (VS −VZK ) R . 5. The current through the Zener diode is iZ = i − iL > 0 . We find then, that if the source voltage VS increases, the current i through shunt resistor R will likewise increase. However, this extra ...
... 3. The load current is iL = VZK RL . 4. The current through the shunt resistor R is i = (VS −VZK ) R . 5. The current through the Zener diode is iZ = i − iL > 0 . We find then, that if the source voltage VS increases, the current i through shunt resistor R will likewise increase. However, this extra ...
Dmm+lab+report+document+(2)
... The principle behind the VCO is that the VCO accepts a reference voltage and a corresponding frequency are produced on the output. The center frequency was determined by using the data sheet for the 4046 to achieve a center frequency of 100 kHz with a reference voltage of 5 volts. The 5 volts refere ...
... The principle behind the VCO is that the VCO accepts a reference voltage and a corresponding frequency are produced on the output. The center frequency was determined by using the data sheet for the 4046 to achieve a center frequency of 100 kHz with a reference voltage of 5 volts. The 5 volts refere ...
ICS874003-02.pdf
... plane through vias, and bypass capacitors should be used for each pin. To achieve optimum jitter performance, power supply isolation is required. Figure 1 illustrates how a 10Ω resistor along with a 10µF and a .01µF bypass capacitor should be connected to each VCCA pin. ...
... plane through vias, and bypass capacitors should be used for each pin. To achieve optimum jitter performance, power supply isolation is required. Figure 1 illustrates how a 10Ω resistor along with a 10µF and a .01µF bypass capacitor should be connected to each VCCA pin. ...
3. Basic Circuitry and Measurements
... • Use the multimeter to measure the voltages across the resistances and the current flowing in through the circuit – Voltage Measurement: Connect the multimeter in parallel. Use the Rightmost HI and the rightmost LO terminals. Push the DC V button – Current Measurement: Use Ohm’s Law – It is usually ...
... • Use the multimeter to measure the voltages across the resistances and the current flowing in through the circuit – Voltage Measurement: Connect the multimeter in parallel. Use the Rightmost HI and the rightmost LO terminals. Push the DC V button – Current Measurement: Use Ohm’s Law – It is usually ...
Basic Circuitry and Measurements Lab 3 1
... • Use the multimeter to measure the voltages across the resistances and the current flowing in through the circuit – Voltage Measurement: Connect the multimeter in parallel. Use the Rightmost HI and the rightmost LO terminals. Push the DC V button – Current Measurement: Use Ohm’s Law – It is usually ...
... • Use the multimeter to measure the voltages across the resistances and the current flowing in through the circuit – Voltage Measurement: Connect the multimeter in parallel. Use the Rightmost HI and the rightmost LO terminals. Push the DC V button – Current Measurement: Use Ohm’s Law – It is usually ...
DCR3000
... Depending on the output transmission loop configuration of a sensor instrument, the following caution should be observed. (1) Where the loop load resistance is less than an allowable level for communication ・If the loop load resistance is less than 50Ω in the 50Ω communication mode. ・If the loop loa ...
... Depending on the output transmission loop configuration of a sensor instrument, the following caution should be observed. (1) Where the loop load resistance is less than an allowable level for communication ・If the loop load resistance is less than 50Ω in the 50Ω communication mode. ・If the loop loa ...
Electrical Circuits Review - Purdue College of Engineering
... current flowing through the component Ichunk . For most materials, the current in a component made in this way would be proportional to the voltage. The ratio Vchunk / Ichunk is R, the component’s resistance, and is measured in ohms (symbol: Ω), named after Georg Simon Ohm (1787–1854). The equation ...
... current flowing through the component Ichunk . For most materials, the current in a component made in this way would be proportional to the voltage. The ratio Vchunk / Ichunk is R, the component’s resistance, and is measured in ohms (symbol: Ω), named after Georg Simon Ohm (1787–1854). The equation ...
BDTIC www.BDTIC.com/infineon Industrial and Multimarket LED Controller IC
... generator for switch-off determination (together with the feedback voltage), internally. Moreover, short-winding protection is realised by monitoring the voltage Vcs during on-time of the main power switch. GD (Gate Drive Output) ...
... generator for switch-off determination (together with the feedback voltage), internally. Moreover, short-winding protection is realised by monitoring the voltage Vcs during on-time of the main power switch. GD (Gate Drive Output) ...
Power Electronics Viva
... normal thyristors, are fully controllable switches which can be turned on and off by their GATE lead. Q8: Difference between SCR and GTO? A8: Thyristors (SCR) can only be turned ON and cannot be turned OFF. Thyristors are switched ON by a gate signal, but even after the gate signal is removed, the t ...
... normal thyristors, are fully controllable switches which can be turned on and off by their GATE lead. Q8: Difference between SCR and GTO? A8: Thyristors (SCR) can only be turned ON and cannot be turned OFF. Thyristors are switched ON by a gate signal, but even after the gate signal is removed, the t ...
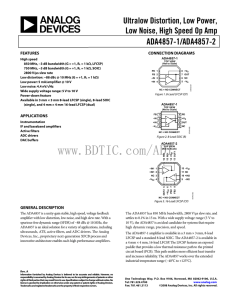
NOT FOR NEW DESIGNS
... bias circuit. This pin has no internal bonding; therefore, this pin can be connected to output pin 7, connected to the ground plane, or not connected. Slight tuning of the output match may be required due to stray capacitance of the pin. RF output and power supply for final stage. This is the unmatc ...
... bias circuit. This pin has no internal bonding; therefore, this pin can be connected to output pin 7, connected to the ground plane, or not connected. Slight tuning of the output match may be required due to stray capacitance of the pin. RF output and power supply for final stage. This is the unmatc ...
Word 2000 format
... test voltage means that (a) the polarity of the electrolytic does not matter when it is connected to the instrument and (b) the ESR meter can be used for accurate in circuit testing of capacitors because no semiconductor junctions will be turned on. So with nothing connected to the test terminals, t ...
... test voltage means that (a) the polarity of the electrolytic does not matter when it is connected to the instrument and (b) the ESR meter can be used for accurate in circuit testing of capacitors because no semiconductor junctions will be turned on. So with nothing connected to the test terminals, t ...
High-Efficiency, 8A, Current-Mode Synchronous Step-Down Switching Regulator MAX15108 General Description Features
... power switches delivers up to 8A of output current. The regulator operates from 2.7V to 5.5V and provides an output voltage from 0.6V up to 95% of the input voltage, making the device ideal for distributed power systems, portable devices, and preregulation applications. The IC utilizes a current-mod ...
... power switches delivers up to 8A of output current. The regulator operates from 2.7V to 5.5V and provides an output voltage from 0.6V up to 95% of the input voltage, making the device ideal for distributed power systems, portable devices, and preregulation applications. The IC utilizes a current-mod ...
Performance Characteristics of Sensors and Actuators
... It may specify the range of voltages under which the device should operate (say 2 to 12V), range of current, power dissipation, maximum excitation as a function of temperature and sometimes frequency. Part of the data sheet for the device Together with other specifications it defines the norma ...
... It may specify the range of voltages under which the device should operate (say 2 to 12V), range of current, power dissipation, maximum excitation as a function of temperature and sometimes frequency. Part of the data sheet for the device Together with other specifications it defines the norma ...
Impedance - Learn About Electronics
... Impedance matching of inputs and outputs is necessary because the gain of a single amplifier is often insufficient for a given purpose. For this reason several stages of amplification are used, which involves feeding the output of one amplifier into the input of another. This is called connecting th ...
... Impedance matching of inputs and outputs is necessary because the gain of a single amplifier is often insufficient for a given purpose. For this reason several stages of amplification are used, which involves feeding the output of one amplifier into the input of another. This is called connecting th ...
NCP102MBGEVB NCP102 4 W Motherboard Evaluation Board User's Manual
... of output capacitors (such as electrolytic and ceramic), zeros at different frequencies are generated. The external pass transistor contributes a zero and affects the poles of the system. The frequency response from VDRV to Vout is given by Equation 4. ...
... of output capacitors (such as electrolytic and ceramic), zeros at different frequencies are generated. The external pass transistor contributes a zero and affects the poles of the system. The frequency response from VDRV to Vout is given by Equation 4. ...
Operational amplifier

An operational amplifier (""op-amp"") is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output. In this configuration, an op-amp produces an output potential (relative to circuit ground) that is typically hundreds of thousands of times larger than the potential difference between its input terminals.Operational amplifiers had their origins in analog computers, where they were used to do mathematical operations in many linear, non-linear and frequency-dependent circuits. The popularity of the op-amp as a building block in analog circuits is due to its versatility. Due to negative feedback, the characteristics of an op-amp circuit, its gain, input and output impedance, bandwidth etc. are determined by external components and have little dependence on temperature coefficients or manufacturing variations in the op-amp itself.Op-amps are among the most widely used electronic devices today, being used in a vast array of consumer, industrial, and scientific devices. Many standard IC op-amps cost only a few cents in moderate production volume; however some integrated or hybrid operational amplifiers with special performance specifications may cost over $100 US in small quantities. Op-amps may be packaged as components, or used as elements of more complex integrated circuits.The op-amp is one type of differential amplifier. Other types of differential amplifier include the fully differential amplifier (similar to the op-amp, but with two outputs), the instrumentation amplifier (usually built from three op-amps), the isolation amplifier (similar to the instrumentation amplifier, but with tolerance to common-mode voltages that would destroy an ordinary op-amp), and negative feedback amplifier (usually built from one or more op-amps and a resistive feedback network).