2.1 Current Voltage Resistance and Power Word Document
... The E24 Series of resistor values If you look in a component suppliers’ catalogues for resistors e.g. Rapid Electronics, you will find that resistors are available in the range from 1Ω to 10 MΩ. Clearly there are 10 million resistor values in between these two values, and it would be completely impr ...
... The E24 Series of resistor values If you look in a component suppliers’ catalogues for resistors e.g. Rapid Electronics, you will find that resistors are available in the range from 1Ω to 10 MΩ. Clearly there are 10 million resistor values in between these two values, and it would be completely impr ...
Title CMOS voltage reference based on gate
... for the series resistors R2/(R1 R2) was used. A small negative temperature dependence that is not well expressed by quadratic regression equations remained, due to the small temperature dependence of R1/R2 ratio for temperatures below 25 C. Temperature coefficient of the reference voltage measured u ...
... for the series resistors R2/(R1 R2) was used. A small negative temperature dependence that is not well expressed by quadratic regression equations remained, due to the small temperature dependence of R1/R2 ratio for temperatures below 25 C. Temperature coefficient of the reference voltage measured u ...
Electricity Lab (Virtual) Part 1. To investigate Ohm`s Law V= I R V
... When connect to 120 V, which filament has the largest electrical current? A or B Which filament will glow brightest in your home? ...
... When connect to 120 V, which filament has the largest electrical current? A or B Which filament will glow brightest in your home? ...
Introduction to Electrical Theory
... Multimeter: an electrical test instrument that can measure several values, usually voltage, current, and resistance. Ohm’s law: a law in electricity that states that the current (amps expressed as I) in a circuit is proportional to the potential difference (voltage, expressed as E) divided by the re ...
... Multimeter: an electrical test instrument that can measure several values, usually voltage, current, and resistance. Ohm’s law: a law in electricity that states that the current (amps expressed as I) in a circuit is proportional to the potential difference (voltage, expressed as E) divided by the re ...
ISL65426 - Intersil
... internal synchronous power MOSFET switches. The average voltage of this node is equal to the regulator output voltage. ...
... internal synchronous power MOSFET switches. The average voltage of this node is equal to the regulator output voltage. ...
min i mum drop out volt age on a se rial pnp tran sis tor
... tor’s dropout voltage significantly increases, it may not be anymore suitable for the supply of battery powered devices or high-performance microprocessors, due to the notably increased dissipation or even decrease of output voltage below the acceptable limit. In this paper the results related to th ...
... tor’s dropout voltage significantly increases, it may not be anymore suitable for the supply of battery powered devices or high-performance microprocessors, due to the notably increased dissipation or even decrease of output voltage below the acceptable limit. In this paper the results related to th ...
5/24/2011 Chapter 27 ...
... In our circuit this potential is equal to the emf E of the battery. The three resistors have different currents The other two will come from KLR: If we traverse the left loop (bad) starting at b and going in the counterclockwise direction we get: KLR/loop bad: E1 − i1R1 + i3 R3 = 0 (eqs.2) Now we go ...
... In our circuit this potential is equal to the emf E of the battery. The three resistors have different currents The other two will come from KLR: If we traverse the left loop (bad) starting at b and going in the counterclockwise direction we get: KLR/loop bad: E1 − i1R1 + i3 R3 = 0 (eqs.2) Now we go ...
Resistivity of a Superconductor
... enough to avoid sample heating. Considering the 600 ohm source resistance of the oscillator, the current will be at most, I = V/R = 2 V/600 Ω ~ 3 mA. The fairly high oscillator frequency will ensure that significantly many sine wave cycles will be averaged in a reasonable amount of time. For example ...
... enough to avoid sample heating. Considering the 600 ohm source resistance of the oscillator, the current will be at most, I = V/R = 2 V/600 Ω ~ 3 mA. The fairly high oscillator frequency will ensure that significantly many sine wave cycles will be averaged in a reasonable amount of time. For example ...
CM8870 - Bilim Teknik
... the minimum signal duration to be recognized by the receiver. A value for C of 0.1µF is recommended for most applications, leaving R to be selected by the designer. For example, a suitable value of R for a tREC of 40ms would be 300K. A typical circuit using this steering configuration is shown in Fi ...
... the minimum signal duration to be recognized by the receiver. A value for C of 0.1µF is recommended for most applications, leaving R to be selected by the designer. For example, a suitable value of R for a tREC of 40ms would be 300K. A typical circuit using this steering configuration is shown in Fi ...
1 EXPERIMENT Ohm’s Law
... It is important to understand just what is meant by these quantities. The current (I) is a measure of how many electrons are flowing past a give point during a set amount of time. The current flows because of the electrical potential (V), sometimes referred to as the voltage applied to a circuit. I ...
... It is important to understand just what is meant by these quantities. The current (I) is a measure of how many electrons are flowing past a give point during a set amount of time. The current flows because of the electrical potential (V), sometimes referred to as the voltage applied to a circuit. I ...
AND8256/D Control of the Output Voltage Range in NCP1653
... Two second order effects were not taken into account in the study: − The PFC stage efficiency: we generally consider the variation over the output power range while the output voltage actually depends on the input power. − The output voltage ripple that is seen by the low gain regulator. Practically ...
... Two second order effects were not taken into account in the study: − The PFC stage efficiency: we generally consider the variation over the output power range while the output voltage actually depends on the input power. − The output voltage ripple that is seen by the low gain regulator. Practically ...
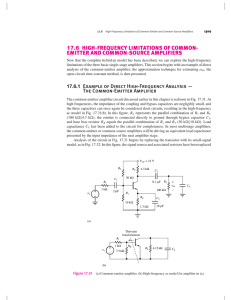
17.6 high-frequency limitations of common- emitter
... Now that the complete hybrid-pi model has been described, we can explore the high-frequency limitations of the three basic single-stage amplifiers. This section begins with an example of direct analysis of the common-emitter amplifier; the approximation technique for estimating ω H , the open-circui ...
... Now that the complete hybrid-pi model has been described, we can explore the high-frequency limitations of the three basic single-stage amplifiers. This section begins with an example of direct analysis of the common-emitter amplifier; the approximation technique for estimating ω H , the open-circui ...
Solution Tutorial 1
... - conditions that essentially prevents current through the diode. - Positive terminal of VBIAS is connected to n region while the negative terminal is connected to p region of diode. - Because unlike charges attract, the positive side of the bias-voltage source ‘pulls’ the free-electrons away the pn ...
... - conditions that essentially prevents current through the diode. - Positive terminal of VBIAS is connected to n region while the negative terminal is connected to p region of diode. - Because unlike charges attract, the positive side of the bias-voltage source ‘pulls’ the free-electrons away the pn ...
MAX1448 10-Bit, 80Msps, Single 3.0V, Low-Power ADC with Internal Reference General Description
... differential signal path. The ADC is optimized for lowpower, high dynamic performance in imaging and digital communications applications. The converter operates from a single 2.7V to 3.6V supply, consuming only 120mW while delivering a 59dB (typ) signal-tonoise ratio (SNR) at a 20MHz input frequency ...
... differential signal path. The ADC is optimized for lowpower, high dynamic performance in imaging and digital communications applications. The converter operates from a single 2.7V to 3.6V supply, consuming only 120mW while delivering a 59dB (typ) signal-tonoise ratio (SNR) at a 20MHz input frequency ...
Operational amplifier

An operational amplifier (""op-amp"") is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output. In this configuration, an op-amp produces an output potential (relative to circuit ground) that is typically hundreds of thousands of times larger than the potential difference between its input terminals.Operational amplifiers had their origins in analog computers, where they were used to do mathematical operations in many linear, non-linear and frequency-dependent circuits. The popularity of the op-amp as a building block in analog circuits is due to its versatility. Due to negative feedback, the characteristics of an op-amp circuit, its gain, input and output impedance, bandwidth etc. are determined by external components and have little dependence on temperature coefficients or manufacturing variations in the op-amp itself.Op-amps are among the most widely used electronic devices today, being used in a vast array of consumer, industrial, and scientific devices. Many standard IC op-amps cost only a few cents in moderate production volume; however some integrated or hybrid operational amplifiers with special performance specifications may cost over $100 US in small quantities. Op-amps may be packaged as components, or used as elements of more complex integrated circuits.The op-amp is one type of differential amplifier. Other types of differential amplifier include the fully differential amplifier (similar to the op-amp, but with two outputs), the instrumentation amplifier (usually built from three op-amps), the isolation amplifier (similar to the instrumentation amplifier, but with tolerance to common-mode voltages that would destroy an ordinary op-amp), and negative feedback amplifier (usually built from one or more op-amps and a resistive feedback network).



![Low Pin Count, Low VIN [3.0V to 5.5V] Synchronous Buck DC-to](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006453823_1-99ea647aae0c603d083eeed480046ac6-300x300.png)