MS-SCI-LS-Unit 4 -- Chapter 15- Nervous System
... dendrites, and an axon. The dendrites carry impulses toward the neuron's cell body. The axon carries impulses away from the cell body. Find the dendrites and axon in Figure 2. Nerve impulses begin in a dendrite, next move toward the cell body, and then move down the axon. A neuron can have many dend ...
... dendrites, and an axon. The dendrites carry impulses toward the neuron's cell body. The axon carries impulses away from the cell body. Find the dendrites and axon in Figure 2. Nerve impulses begin in a dendrite, next move toward the cell body, and then move down the axon. A neuron can have many dend ...
Contextual modulation and stimulus selectivity in extrastriate cortex
... modulation is used to refine existing feature representations that have been generated by other—unspecified, but presumably feedforward—circuitry. Here we review evidence suggesting that contextual modulation can do more, and actually creates neural selectivity for new and complex visual features. The ...
... modulation is used to refine existing feature representations that have been generated by other—unspecified, but presumably feedforward—circuitry. Here we review evidence suggesting that contextual modulation can do more, and actually creates neural selectivity for new and complex visual features. The ...
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
... one part of the body to another. Besides their ability to conduct nerve impulses, neurons have some other special characteristics: 1. They have extreme longevity. Given good nutrition, neurons can function optimally for a lifetime (over 100 years). 2. They are amitotic. As neurons assume their roles ...
... one part of the body to another. Besides their ability to conduct nerve impulses, neurons have some other special characteristics: 1. They have extreme longevity. Given good nutrition, neurons can function optimally for a lifetime (over 100 years). 2. They are amitotic. As neurons assume their roles ...
1 - Projeto Andar de Novo
... Glucose is brain´s most important energy source. Glycogen stores are present in neurons and glial cells during development and could be recruited during intense and acute demands. Animals submitted to malnutrition during a restricted period of their development presented alterations on the expressio ...
... Glucose is brain´s most important energy source. Glycogen stores are present in neurons and glial cells during development and could be recruited during intense and acute demands. Animals submitted to malnutrition during a restricted period of their development presented alterations on the expressio ...
Changes in GABA Modulation During a Theta Cycle May Be
... inhibitory interneuron; W, the strength of recurrent excitatory connections from a2 to a2 and a3 to a3 ; W 0 , the strength of excitatory connections from a2 and a3 to the interneuron; −H, the strength of the inhibitory connections from this interneuron to a2 and a3 ; h, activation of the model inte ...
... inhibitory interneuron; W, the strength of recurrent excitatory connections from a2 to a2 and a3 to a3 ; W 0 , the strength of excitatory connections from a2 and a3 to the interneuron; −H, the strength of the inhibitory connections from this interneuron to a2 and a3 ; h, activation of the model inte ...
Mirror neurons or emulator neurons?
... transformation between visually defined goal-states and the motor system (Rizzolatti et al., 1988; Jeannerod et al., 1995). This is essentially a goal-to-action type of computation, roughly corresponding to the internal 'inverse model' posited by computational theories of motor control (Wolpert & Gh ...
... transformation between visually defined goal-states and the motor system (Rizzolatti et al., 1988; Jeannerod et al., 1995). This is essentially a goal-to-action type of computation, roughly corresponding to the internal 'inverse model' posited by computational theories of motor control (Wolpert & Gh ...
VALUE-DEPENDENT SELECTION IN THE BRAIN: SIMULATION IN
... Specifically, the theory proposes that brain function is mediated by: (i) selectional events occurring among interacting cells in the developing embryo to form large repertoires of variant neural circuits; (ii) further selectional events occurring among populations of synapses to enhance those neuro ...
... Specifically, the theory proposes that brain function is mediated by: (i) selectional events occurring among interacting cells in the developing embryo to form large repertoires of variant neural circuits; (ii) further selectional events occurring among populations of synapses to enhance those neuro ...
A Cognitive Computation Fallacy?
... conclusion is that computation is neither necessary nor sufficient for cognition; its positive conclusion suggests that the adoption of a new metaphor may be helpful in addressing hard conceptual questions related to consciousness and understanding. Drawing on the conclusions of the two earlier arti ...
... conclusion is that computation is neither necessary nor sufficient for cognition; its positive conclusion suggests that the adoption of a new metaphor may be helpful in addressing hard conceptual questions related to consciousness and understanding. Drawing on the conclusions of the two earlier arti ...
Cognitive neuroscience of self-regulation failure
... goals, cravings and so forth implicitly [36,37]. Even if people are somewhat aware of cues around them, they are unaware of the process by which exposure to those cues implicitly activates cognitive processes that determine behavior [38]. A recent meta-analysis of 75 articles found that implicit cog ...
... goals, cravings and so forth implicitly [36,37]. Even if people are somewhat aware of cues around them, they are unaware of the process by which exposure to those cues implicitly activates cognitive processes that determine behavior [38]. A recent meta-analysis of 75 articles found that implicit cog ...
view pdf - Columbia University
... immediately upon issuing from the foramen spinosum, with the anterior division of the posterior ramus appearing to be the larger. The anterior and posterior branches of the anterior ramus divide approximately at the sylvian region, suggesting a pattern most like type IV. This description is thus som ...
... immediately upon issuing from the foramen spinosum, with the anterior division of the posterior ramus appearing to be the larger. The anterior and posterior branches of the anterior ramus divide approximately at the sylvian region, suggesting a pattern most like type IV. This description is thus som ...
Expectation of reward modulates cognitive signals in the basal ganglia
... of the subject is assumed to be the same no matter which stimulus (or stimulus feature) represents the correct response. This model is therefore ideal for investigating the cognitive aspect of action or attention, but not the motivational aspect. Action is controlled by both cognition and motivation ...
... of the subject is assumed to be the same no matter which stimulus (or stimulus feature) represents the correct response. This model is therefore ideal for investigating the cognitive aspect of action or attention, but not the motivational aspect. Action is controlled by both cognition and motivation ...
Encoding Information in Neuronal Activity
... In one example the correlated firing between two neurons during the GO tasks was highest during the first second after the onset of the stimulus and lower during the next second. During the NO- GO tasks the pattern of correlated firing was reversed. The correlation was low in the first second and hi ...
... In one example the correlated firing between two neurons during the GO tasks was highest during the first second after the onset of the stimulus and lower during the next second. During the NO- GO tasks the pattern of correlated firing was reversed. The correlation was low in the first second and hi ...
Disruption of the Blood-Brain Barrier and Neuronal Cell Death in
... using experimental codes. The coding was such that animal treatments were not known during the measurement; however, sections that came from the same animal were identified. All measurements were performed using a Nikon E600 microscope equipped with an eyepiece grid. At a magnification of 400⫻ (usin ...
... using experimental codes. The coding was such that animal treatments were not known during the measurement; however, sections that came from the same animal were identified. All measurements were performed using a Nikon E600 microscope equipped with an eyepiece grid. At a magnification of 400⫻ (usin ...
A Self-Organizing Neural Model for Multimedia Information Fusion
... text and images. However, text annotations are not always available. In addition, images are different from text in nature after all. So simply converting the multimedia association problem into pure text clustering is not a sound solution. Therefore, on top of clustering based on textual features, ...
... text and images. However, text annotations are not always available. In addition, images are different from text in nature after all. So simply converting the multimedia association problem into pure text clustering is not a sound solution. Therefore, on top of clustering based on textual features, ...
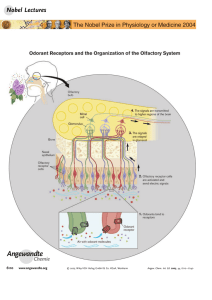
Scents and Sensibility: A Molecular Logic of Olfactory Perception
... own laboratory in 1974, Michael Wigler, my first graduate student along with Sol Silverstein, a Professor at Columbia, developed novel procedures that allowed DNA-mediated transformation of mammalian cells. Michael, even at this very early stage in his career, was conceptually and technically master ...
... own laboratory in 1974, Michael Wigler, my first graduate student along with Sol Silverstein, a Professor at Columbia, developed novel procedures that allowed DNA-mediated transformation of mammalian cells. Michael, even at this very early stage in his career, was conceptually and technically master ...
Optic Glomeruli and Their Inputs inDrosophilaShare an
... Hemisection through the brain labeled with anti-␣-tubulin and anti-GFP, showing the ensemble of type Col A LCN neurons in the lobula Animal preparation. Our animal setup (Fig. with converging axons to its corresponding Col A glomerulus. This lies ventral and medial to a glomerulus receiving terminal ...
... Hemisection through the brain labeled with anti-␣-tubulin and anti-GFP, showing the ensemble of type Col A LCN neurons in the lobula Animal preparation. Our animal setup (Fig. with converging axons to its corresponding Col A glomerulus. This lies ventral and medial to a glomerulus receiving terminal ...
Anomalous Prefrontal-Subcortical Activation in
... have underlying abnormalities in the regulation of prefrontal-subcortical circuits. Further functional magnetic resonance imaging studies of attention and mood with greater sample sizes are needed. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2004;61:781-792 ...
... have underlying abnormalities in the regulation of prefrontal-subcortical circuits. Further functional magnetic resonance imaging studies of attention and mood with greater sample sizes are needed. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2004;61:781-792 ...
Two Phylogenetic Specializations in the Human Brain
... The spindle cells may serve to augment and relay the error-correcting information to other parts of the brain. The spindle cells are located in layer 5, which typically relays the output of cortical processing to other cortical areas and subcortical structures. The axons of the spindle cells are kno ...
... The spindle cells may serve to augment and relay the error-correcting information to other parts of the brain. The spindle cells are located in layer 5, which typically relays the output of cortical processing to other cortical areas and subcortical structures. The axons of the spindle cells are kno ...
Competitive Dynamics in Cortical Responses to Visual Stimuli
... network operated in what we termed normalization mode. If the strength of the inhibition was increased, the network entered an oscillatory mode in which the two pools were alternately active (Fig. 3B). At high inhibitory strength, the network operated in a winner-take-all mode in which only one pool ...
... network operated in what we termed normalization mode. If the strength of the inhibition was increased, the network entered an oscillatory mode in which the two pools were alternately active (Fig. 3B). At high inhibitory strength, the network operated in a winner-take-all mode in which only one pool ...
Diagnostic History of Traumatic Axonal Injury in Patients with
... lesion is not diffuse but multifocal) and underline the etiology of the axonal injury in trauma instead of DAI [23,24]. On the other hand, since the 1980’s, many researchers, including Povlishock, have used the term “TAI” in their histopathological studies [23,25,26,39]. Patients with the traditiona ...
... lesion is not diffuse but multifocal) and underline the etiology of the axonal injury in trauma instead of DAI [23,24]. On the other hand, since the 1980’s, many researchers, including Povlishock, have used the term “TAI” in their histopathological studies [23,25,26,39]. Patients with the traditiona ...
Preprint
... retrieval structures to facilitate the retrieval of information stored in LTM. [...] [R]etrieval structures are used strategically to encode information in LTM with cues that can be later regenerated to retrieve the stored information efficiently without a lengthy search.” This approach has been app ...
... retrieval structures to facilitate the retrieval of information stored in LTM. [...] [R]etrieval structures are used strategically to encode information in LTM with cues that can be later regenerated to retrieve the stored information efficiently without a lengthy search.” This approach has been app ...
Bidirectional propagation of Action potentials
... different functions to make the nervous system work. We can classify neurons in three functional categories: sensory neurons, motor neurons and interneurons. While sensory neurons convey signals from the body’s periphery to the nervous system, motor neurons communicate commands and decisions form th ...
... different functions to make the nervous system work. We can classify neurons in three functional categories: sensory neurons, motor neurons and interneurons. While sensory neurons convey signals from the body’s periphery to the nervous system, motor neurons communicate commands and decisions form th ...
PDF file
... from the field of view randomly, but rather, they move continuously across the field of view, given their motion is not too fast for the brain to respond. At the pixel level, views are very discontinuous as image patches sweep across the field of view. Motivated by cerebral cortex, our model explore ...
... from the field of view randomly, but rather, they move continuously across the field of view, given their motion is not too fast for the brain to respond. At the pixel level, views are very discontinuous as image patches sweep across the field of view. Motivated by cerebral cortex, our model explore ...
Encoding and decoding in fMRI
... individual voxels that described the information about natural scenes represented by the voxel activity. To model voxels they first mapped the stimuli into an over-complete nonlinear basis consisting of many phase-invariant Gabor wavelets that varied in location, orientation, and spatial frequency. T ...
... individual voxels that described the information about natural scenes represented by the voxel activity. To model voxels they first mapped the stimuli into an over-complete nonlinear basis consisting of many phase-invariant Gabor wavelets that varied in location, orientation, and spatial frequency. T ...
Child and Time - Lapsco - Université Blaise Pascal
... strategies because they are well aware of the inaccurate nature of their temporal estimates in most situations. To summarize, because the majority of the employed experimental conditions have used an explicit judgment of time, human subjects, and children in particular, have often been found not to ...
... strategies because they are well aware of the inaccurate nature of their temporal estimates in most situations. To summarize, because the majority of the employed experimental conditions have used an explicit judgment of time, human subjects, and children in particular, have often been found not to ...