What is memory? How does the brain perceive the outside
... Schwann cells (PNS): Prevents abnormal communication between neurons Contain myelin and wraps around neuronal axons to boost communications, up to 200 mph! ...
... Schwann cells (PNS): Prevents abnormal communication between neurons Contain myelin and wraps around neuronal axons to boost communications, up to 200 mph! ...
Organization of Nervous System
... As it turns out, there are also receptors on the bouton itself. These receptors modulate the release of neurotransmitters. Adenosine is a neurotransmitter that acts on the presynaptic receptor. It inhibits the release of glutamate. ...
... As it turns out, there are also receptors on the bouton itself. These receptors modulate the release of neurotransmitters. Adenosine is a neurotransmitter that acts on the presynaptic receptor. It inhibits the release of glutamate. ...
The Brain
... o Video: through plasticity, Sharron(who had hydrocephalus) can regain all functions, despite having half a brain o Note: plasticity takes time, it wouldn’t be the same as if an adult were to have it CSF Summary • Produced from blood by the choroid plexi (all ventricles) • Full replacement ev ...
... o Video: through plasticity, Sharron(who had hydrocephalus) can regain all functions, despite having half a brain o Note: plasticity takes time, it wouldn’t be the same as if an adult were to have it CSF Summary • Produced from blood by the choroid plexi (all ventricles) • Full replacement ev ...
PSYCH 2 StudyGuide
... experience sensations of falling. Stage 2 is a deeper stage of sleep and is characterized by sleep spindles. Stage 3 is transitional while Stage 4 emits large, slow delta waves (also apparent in stage 3). After the first cycle you return to REM- in between 2 and 1. Heart rate rises and breathing bec ...
... experience sensations of falling. Stage 2 is a deeper stage of sleep and is characterized by sleep spindles. Stage 3 is transitional while Stage 4 emits large, slow delta waves (also apparent in stage 3). After the first cycle you return to REM- in between 2 and 1. Heart rate rises and breathing bec ...
Malleable vs. Fixed Intelligence
... Neurons have three main parts: 1. The soma (a.k.a cell body) 2. The axon 3. The dendrites ...
... Neurons have three main parts: 1. The soma (a.k.a cell body) 2. The axon 3. The dendrites ...
HW CH 5 PSY 2513 Submit your answers on canvas
... the areas of the brain are strongly committed to specific functions, and there is a high capacity for learning. b. if a part of the cortex is damaged, other parts can take over the tasks it would have handled. c. spatial skills develop more rapidly than language skills and are easier to recover afte ...
... the areas of the brain are strongly committed to specific functions, and there is a high capacity for learning. b. if a part of the cortex is damaged, other parts can take over the tasks it would have handled. c. spatial skills develop more rapidly than language skills and are easier to recover afte ...
Final Exam Review, Pt. 3
... • Motivated Forgetting - Inability to encode or retrieve memories due to anxiety. • Retrieval Failure * • Inability to bring information into working memory ...
... • Motivated Forgetting - Inability to encode or retrieve memories due to anxiety. • Retrieval Failure * • Inability to bring information into working memory ...
explain-bio-factors-and-memory-handout
... four days of exposure. The good news is it appears that it would take several days of stresses like major surgery or severe psychological trauma in order for cortisol to produce memory impairment. And after a one-week wash-out period, memory performance returned to the untreated levels." The cortiso ...
... four days of exposure. The good news is it appears that it would take several days of stresses like major surgery or severe psychological trauma in order for cortisol to produce memory impairment. And after a one-week wash-out period, memory performance returned to the untreated levels." The cortiso ...
Unit 3 Notes
... Dendrite: a neuron’s bushy, branching extensions that receive messages and conduct impulses toward the cell body. Axon: the neuron extension that passes messages through its branches to other neurons or to muscles or glands. ...
... Dendrite: a neuron’s bushy, branching extensions that receive messages and conduct impulses toward the cell body. Axon: the neuron extension that passes messages through its branches to other neurons or to muscles or glands. ...
“Put that in the Form of a Question, Please!”
... In terms of sensory receptors, _____respond to variations in light, but ______respond to changes in temperature. ...
... In terms of sensory receptors, _____respond to variations in light, but ______respond to changes in temperature. ...
Document
... messages like a telephone wire. Sensory nerves send messages to the brain and generally connect to the brain to all the muscles and glands in the body. When neurons are stimulated by heat, cold, touch, sound vibration, or some other message it begins to generate a tiny electric pulse. This electrici ...
... messages like a telephone wire. Sensory nerves send messages to the brain and generally connect to the brain to all the muscles and glands in the body. When neurons are stimulated by heat, cold, touch, sound vibration, or some other message it begins to generate a tiny electric pulse. This electrici ...
Pharmacology - The reward pathway
... and time, and the amygdala, which records the emotional colour, the intensity of our experiences. The dopamine pathways communicate between the limbic system and the cortex. The cortex, and particularly the prefrontal cortex, is associated with thinking, and planning, and deciding. It gives us a sen ...
... and time, and the amygdala, which records the emotional colour, the intensity of our experiences. The dopamine pathways communicate between the limbic system and the cortex. The cortex, and particularly the prefrontal cortex, is associated with thinking, and planning, and deciding. It gives us a sen ...
AP PSych Cum Test Ch 1-7 - Mater Academy Lakes High School
... have actually received a potentially memory-enhancing drug and which have received a placebo. This investigation involves the use of a. naturalistic observation. b. the hindsight bias. c. random sampling. d. the double-blind procedure. e. replication. ____ 117. Which of the following is true for tho ...
... have actually received a potentially memory-enhancing drug and which have received a placebo. This investigation involves the use of a. naturalistic observation. b. the hindsight bias. c. random sampling. d. the double-blind procedure. e. replication. ____ 117. Which of the following is true for tho ...
Nervous System - Science
... 1. Stimuli comes into the brain through the five senses. The nerves that bring stimuli into the body are SENSORY neurons. 2. The impulse travels through INTERNEURONS. 3. When the impulse reaches the MOTOR neuron, the response occurs. ...
... 1. Stimuli comes into the brain through the five senses. The nerves that bring stimuli into the body are SENSORY neurons. 2. The impulse travels through INTERNEURONS. 3. When the impulse reaches the MOTOR neuron, the response occurs. ...
memory - Haiku
... blackboard with an endless supply of chalk and erasers.” --Elizabeth Loftus and ...
... blackboard with an endless supply of chalk and erasers.” --Elizabeth Loftus and ...
Types of LTM - Beauchamp Psychology
... These are memories relating to knowledge about the world, such as facts learnt at school. Semantic memories may relate to things such as functions of objects, what behaviour is appropriate (e.g. social customs) but also to abstract ideas such as knowledge of Mathematical rules. These memories begin ...
... These are memories relating to knowledge about the world, such as facts learnt at school. Semantic memories may relate to things such as functions of objects, what behaviour is appropriate (e.g. social customs) but also to abstract ideas such as knowledge of Mathematical rules. These memories begin ...
Slide ()
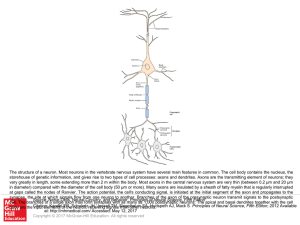
... The structure of a neuron. Most neurons in the vertebrate nervous system have several main features in common. The cell body contains the nucleus, the storehouse of genetic information, and gives rise to two types of cell processes: axons and dendrites. Axons are the transmitting element of neurons; ...
... The structure of a neuron. Most neurons in the vertebrate nervous system have several main features in common. The cell body contains the nucleus, the storehouse of genetic information, and gives rise to two types of cell processes: axons and dendrites. Axons are the transmitting element of neurons; ...
Neural Networks.Chap..
... convey information to brain. Effectors: Convert electrical impulses generated by brain into discernible responses as system outputs. ...
... convey information to brain. Effectors: Convert electrical impulses generated by brain into discernible responses as system outputs. ...
2016-2017_1stSemester_Exam2_180117_final
... GABAergic interneuron establishing axo-axonic synapses ...
... GABAergic interneuron establishing axo-axonic synapses ...
nervous quiz RG
... __________ 6. What is the function of the neurotransmitter Dopamine? a. fight or \flight b. provides a barrier to prevent the uptake of neurotransmitters. c. is a pleasure neurotransmitter d. increases electrical activity in the brain. __________ 7. What is a synapse? a. a gap between neurons b. a g ...
... __________ 6. What is the function of the neurotransmitter Dopamine? a. fight or \flight b. provides a barrier to prevent the uptake of neurotransmitters. c. is a pleasure neurotransmitter d. increases electrical activity in the brain. __________ 7. What is a synapse? a. a gap between neurons b. a g ...