1 How the Nervous System Works
... synapse between the axon tip of one neuron and the dendrite of another neuron. Notice that a small gap separates these two structures. For a nerve impulse to be carried along at a synapse, it must cross the gap between the axon and the next structure. The axon tips release chemicals that carry the i ...
... synapse between the axon tip of one neuron and the dendrite of another neuron. Notice that a small gap separates these two structures. For a nerve impulse to be carried along at a synapse, it must cross the gap between the axon and the next structure. The axon tips release chemicals that carry the i ...
Motor Function_2 - bloodhounds Incorporated
... • Basal Ganglia modulates the Thalamic excitability by an inhibitory loop ...
... • Basal Ganglia modulates the Thalamic excitability by an inhibitory loop ...
Nervous System - IB BiologyMr. Van Roekel Salem High School
... • Motor neurons also have long axons and transmit nerve impulses from the central nervous system to effectors (muscles and glands) all over the body. • Interneurons (also called connector neurons or relay neurons) are usually much smaller cells, with many interconnections. • When many individual neu ...
... • Motor neurons also have long axons and transmit nerve impulses from the central nervous system to effectors (muscles and glands) all over the body. • Interneurons (also called connector neurons or relay neurons) are usually much smaller cells, with many interconnections. • When many individual neu ...
Brain
... Efferent neurons Stimulate and control effectors somatic motor neurons visceral motor neurons Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) • Sympathetic • Parasympathetic They both control the same effectors (with few exceptions) but have opposite responses in the effectors ...
... Efferent neurons Stimulate and control effectors somatic motor neurons visceral motor neurons Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) • Sympathetic • Parasympathetic They both control the same effectors (with few exceptions) but have opposite responses in the effectors ...
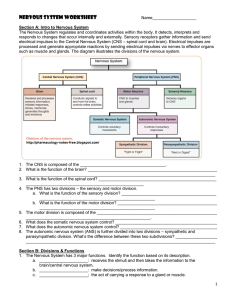
Nervous System Worksheet - Jackson County Faculty Sites!
... 1. What are the 3 types of neurons? ______________________________________________________ 2. What is the function of the afferent neurons? ______________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 3. What is the function of int ...
... 1. What are the 3 types of neurons? ______________________________________________________ 2. What is the function of the afferent neurons? ______________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 3. What is the function of int ...
Nervous System
... of nerve fibers (axons) through which impulses travel between the CNS and the other parts of the body. A message from the brain travels down the spinal cord, then along the axon of a motor neuron inside a nerve to the muscle. The message makes the muscle contract. ...
... of nerve fibers (axons) through which impulses travel between the CNS and the other parts of the body. A message from the brain travels down the spinal cord, then along the axon of a motor neuron inside a nerve to the muscle. The message makes the muscle contract. ...
Anatomical Terminology
... i. Most sensory receptors (generalized) b. Complex i. Special senses (vision, audition, olfaction, gustation) 4. Generalized sensory receptors a. Free dendritic endings (unencapsulated) i. Free ii. Merkel discs iii. Root hair plexus b. Encapsulated i. Meisner’s corpuscles—low frequency vibration) ii ...
... i. Most sensory receptors (generalized) b. Complex i. Special senses (vision, audition, olfaction, gustation) 4. Generalized sensory receptors a. Free dendritic endings (unencapsulated) i. Free ii. Merkel discs iii. Root hair plexus b. Encapsulated i. Meisner’s corpuscles—low frequency vibration) ii ...
Japan-Canada Joint Health Research Program – U
... We employed the corticospinal motor evoked potential (D-wave) as a monitoring index of motor function. Direct cortical stimulation revealed that if one electrode was placed on the posterior half of the precentral gyrus, the D-wave could be recorded even with 10 mm-distant bipolar cortical stimulatio ...
... We employed the corticospinal motor evoked potential (D-wave) as a monitoring index of motor function. Direct cortical stimulation revealed that if one electrode was placed on the posterior half of the precentral gyrus, the D-wave could be recorded even with 10 mm-distant bipolar cortical stimulatio ...
LEARNING OBJECTIVE 7: Explain hemisphere dominance.
... Angell, Marcia. May 26, 1994. After Quinlan: The dilemma of the persistent vegetative state. New England Journal of Medicine, vol. 330. Karen Quinlan spent nine years in a persistent vegetative state. Brain analysis reveals that the causative defect was in Quinlan’s thalamus. Changeux, Jean-Pierre. ...
... Angell, Marcia. May 26, 1994. After Quinlan: The dilemma of the persistent vegetative state. New England Journal of Medicine, vol. 330. Karen Quinlan spent nine years in a persistent vegetative state. Brain analysis reveals that the causative defect was in Quinlan’s thalamus. Changeux, Jean-Pierre. ...
chapter30_Sensory Perception(1
... • Different types of sensory neurons respond to different specific stimuli by producing action potentials • Types of sensory receptors include, chemoreceptors, thermoreceptors, pain receptors, mechanoreceptors, and ...
... • Different types of sensory neurons respond to different specific stimuli by producing action potentials • Types of sensory receptors include, chemoreceptors, thermoreceptors, pain receptors, mechanoreceptors, and ...
Neural Basis of Motor Control
... muscles fiber (neuromuscular junction) – At this junction is where nerve impulses are transmitted to the muscle fiber producing muscle contraction – When alpha motor neuron activates, all the muscle fibers to which it connects contracts. – Greater the number of motor units activated (recruitment) ...
... muscles fiber (neuromuscular junction) – At this junction is where nerve impulses are transmitted to the muscle fiber producing muscle contraction – When alpha motor neuron activates, all the muscle fibers to which it connects contracts. – Greater the number of motor units activated (recruitment) ...
MR Imaging of Perineural Spread of Malignancy - SCBT-MR
... Cases/Conclusion: Five patients with gadolinium contrast pelvic MRI and perineural malignancy on a sciatic nerve biopsy were reviewed (Table). All patients had MR neural enhancement patterns suggesting an infiltrative process. Four of the five patients had ipsilateral perirectal fascial thickening w ...
... Cases/Conclusion: Five patients with gadolinium contrast pelvic MRI and perineural malignancy on a sciatic nerve biopsy were reviewed (Table). All patients had MR neural enhancement patterns suggesting an infiltrative process. Four of the five patients had ipsilateral perirectal fascial thickening w ...
Zoran Đogaš
... and larger neurons will fire later (larger twitch tension). • V = IR: Small neurons have a higher resistance, which means they will show a stronger depolarization (V) for the same current (I). • That's why they fire first. This is the opposite of external stimulation, ...
... and larger neurons will fire later (larger twitch tension). • V = IR: Small neurons have a higher resistance, which means they will show a stronger depolarization (V) for the same current (I). • That's why they fire first. This is the opposite of external stimulation, ...
Answers to Test Your Knowledge questions for
... over working muscle fibres, the extrafusal fibres, by means of alpha motor neurons. Note that, as shown here, the 'state of muscle' is information fed back to perceptual systems. This derives from muscle spindles and sensory neurons that detect proprioceptive information. (Though the section focused ...
... over working muscle fibres, the extrafusal fibres, by means of alpha motor neurons. Note that, as shown here, the 'state of muscle' is information fed back to perceptual systems. This derives from muscle spindles and sensory neurons that detect proprioceptive information. (Though the section focused ...
Nervous system - Nayland College
... (CNS), and the nerves supplying the rest of the body. Neurons and white tissue are most likely to be attacked in MS. During periods of MS activity white blood cells (leukocytes) are drawn to regions of the white matter. These initiate and take part in what is known as the inflammatory response. The ...
... (CNS), and the nerves supplying the rest of the body. Neurons and white tissue are most likely to be attacked in MS. During periods of MS activity white blood cells (leukocytes) are drawn to regions of the white matter. These initiate and take part in what is known as the inflammatory response. The ...
Neuropsychologia, 47, 1621-6
... design. Specifically, participants pointed to visual targets projected onto the glabrous (palm) or hairy (back) side of their actual left hand or onto the palm or back of the fake left hand. The four hand-skin conditions, real-glabrous, real-hairy, fake-glabrous, and fake-hairy, were presented in eig ...
... design. Specifically, participants pointed to visual targets projected onto the glabrous (palm) or hairy (back) side of their actual left hand or onto the palm or back of the fake left hand. The four hand-skin conditions, real-glabrous, real-hairy, fake-glabrous, and fake-hairy, were presented in eig ...
8-Nervous tissue
... • The classification of neurons: • According to the number of process The shape of the cell body is dependent on the number of processes arising from it. The most common type of neuron gives off several processes from the cell body is, therefore, multipolar. Some neurons have only one axon and one ...
... • The classification of neurons: • According to the number of process The shape of the cell body is dependent on the number of processes arising from it. The most common type of neuron gives off several processes from the cell body is, therefore, multipolar. Some neurons have only one axon and one ...
Hearing and Equilibrium Human Ear Major questions Anatomy of
... • Hearing: our perception of the energy in these waves • Travel in all directions (344 m/sec in air) and energy dissipates • Frequency determines pitch • Amplitude determines intensity (loudness) ...
... • Hearing: our perception of the energy in these waves • Travel in all directions (344 m/sec in air) and energy dissipates • Frequency determines pitch • Amplitude determines intensity (loudness) ...
I. Functions and Divisions of the Nervous System A. The nervous
... of Na+ that at least equals the amount of efflux of K+. 7. Action potentials are all-or-none phenomena: they either happen completely, in the case of a threshold stimulus, or not at all, in the event of a subthreshold stimulus. 8. Stimulus intensity is coded in the frequency of action potentials. ...
... of Na+ that at least equals the amount of efflux of K+. 7. Action potentials are all-or-none phenomena: they either happen completely, in the case of a threshold stimulus, or not at all, in the event of a subthreshold stimulus. 8. Stimulus intensity is coded in the frequency of action potentials. ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM CNS-Central Nervous System PNS
... 1. Pesticides can affect the nervous system. A) Explain how. B) What symptoms did the uncle have that could indicate pesticides as the cause for his hospitalization). 2. Food-poisoning can affect the nervous system. A) Explain how. B) What symptoms did the uncle have that could indicate Botulism as ...
... 1. Pesticides can affect the nervous system. A) Explain how. B) What symptoms did the uncle have that could indicate pesticides as the cause for his hospitalization). 2. Food-poisoning can affect the nervous system. A) Explain how. B) What symptoms did the uncle have that could indicate Botulism as ...
NEURAL CONTROL AND COORDINATION
... The nerve fibres of the PNS are of two types •Afferent fibres(sensory) •Efferent fibres(motor) The sensory or afferent nerve fibres transmit or convey impulses from the sensory receptors to the CNS and efferent fibres(motor) carry impulses from the CNS to effector organs, the muscles and glands. Th ...
... The nerve fibres of the PNS are of two types •Afferent fibres(sensory) •Efferent fibres(motor) The sensory or afferent nerve fibres transmit or convey impulses from the sensory receptors to the CNS and efferent fibres(motor) carry impulses from the CNS to effector organs, the muscles and glands. Th ...
Visual Prostheses: Current Progress and Challenges
... surgical challenge. As to epi-retinal versus sub-retinal, the epiretinal approach is easier form a surgical point of view but the mechanical anchoring of the implant to the epi-retinal surface is difficult[2]. This can be partially alleviated by placing the device subretinally[3], though the surgery ...
... surgical challenge. As to epi-retinal versus sub-retinal, the epiretinal approach is easier form a surgical point of view but the mechanical anchoring of the implant to the epi-retinal surface is difficult[2]. This can be partially alleviated by placing the device subretinally[3], though the surgery ...
Body Systems Test Study guide
... 8. How many chromosomes are found in human sex cells? 9. Blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart are called __________________. 10. What is the main function of the excretory system? 11. What are the 3 functions of the digestive system? 12. Which organ of the digestive system absorbs nutr ...
... 8. How many chromosomes are found in human sex cells? 9. Blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart are called __________________. 10. What is the main function of the excretory system? 11. What are the 3 functions of the digestive system? 12. Which organ of the digestive system absorbs nutr ...
Microneurography

Microneurography is a neurophysiological method employed by scientists to visualize and record the normal traffic of nerve impulses that are conducted in peripheral nerves of waking human subjects. The method has been successfully employed to reveal functional properties of a number of neural systems, e.g. sensory systems related to touch, pain, and muscle sense as well as sympathetic activity controlling the constriction state of blood vessels. To study nerve impulses of an identified neural system, a fine tungsten needle electrode is inserted into the nerve and connected to a high gain recording amplifier. The exact position of the electrode tip within the nerve is then adjusted in minute steps until the electrode discriminates impulses of the neural system of interest. A unique feature and a significant strength of the microneurography method is that subjects are fully awake and able to cooperate in tests requiring mental attention, while impulses in a representative nerve fibre or set of nerve fibres are recorded, e.g. when cutaneous sense organs are stimulated or subjects perform voluntary precision movements.