Behavioral Neuroscience: The NeuroPsychological approach
... One main finding was that each hemisphere controls (efferent nerves) and gets sensory inputs (afferent nerves) from the contralateral side of the body. How is it linked to language? ...
... One main finding was that each hemisphere controls (efferent nerves) and gets sensory inputs (afferent nerves) from the contralateral side of the body. How is it linked to language? ...
Brain Anatomy
... However, other major changes were noticed as a result of the accident. Gage, a usually friendly and normal person, suddenly began to swear frequently, ...
... However, other major changes were noticed as a result of the accident. Gage, a usually friendly and normal person, suddenly began to swear frequently, ...
Chapter 7: Structure of Nervous System
... Chapter 7: Structure of Nervous System Is divided into: Central nervous system (CNS) = brain and spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) = cranial and spinal nerves Consists of 2 kinds of cells: Neurons and supporting cells (glial cells). Neurons are ______________________ units of N ...
... Chapter 7: Structure of Nervous System Is divided into: Central nervous system (CNS) = brain and spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) = cranial and spinal nerves Consists of 2 kinds of cells: Neurons and supporting cells (glial cells). Neurons are ______________________ units of N ...
Neural Basis of Motor Control
... reversing the depolarization. Also at about this time, sodium channels start to close. This causes the action potential to go back toward -70 mV (a repolarization). Gradually, the ion concentrations go back to resting levels and the cell returns to -70 mV. ...
... reversing the depolarization. Also at about this time, sodium channels start to close. This causes the action potential to go back toward -70 mV (a repolarization). Gradually, the ion concentrations go back to resting levels and the cell returns to -70 mV. ...
fahime_sheikhzadeh
... Computational models Why should one use computational models to address questions in neuroscience? • Dealing with complexity • Checking conceptual models and revealing assumptions • Comparing and discovering hypotheses • Suggesting fruitful areas for new experiments ...
... Computational models Why should one use computational models to address questions in neuroscience? • Dealing with complexity • Checking conceptual models and revealing assumptions • Comparing and discovering hypotheses • Suggesting fruitful areas for new experiments ...
Learning Skill
... This process demands synthesis of new proteins in “some” nerve cells to modify their ability to be activated by other nerves and thereby create a new patterns of activation. ...
... This process demands synthesis of new proteins in “some” nerve cells to modify their ability to be activated by other nerves and thereby create a new patterns of activation. ...
Autism And Mirror Neurons
... Humans are normally able to do this quite well once fully developed- BUT autistic people seem to have a lack of ...
... Humans are normally able to do this quite well once fully developed- BUT autistic people seem to have a lack of ...
myelin sheath
... emergence of cell assemblies in a small network of 69 neurons. They found that everything became active in their network. • They decided that they needed to include inhibitory synapses. This worked and cell assemblies did, indeed, form. • This was later confirmed in real brain circuitry. ...
... emergence of cell assemblies in a small network of 69 neurons. They found that everything became active in their network. • They decided that they needed to include inhibitory synapses. This worked and cell assemblies did, indeed, form. • This was later confirmed in real brain circuitry. ...
Document
... emergence of cell assemblies in a small network of 69 neurons. They found that everything became active in their network. • They decided that they needed to include inhibitory synapses. This worked and cell assemblies did, indeed, form. • This was later confirmed in real brain circuitry. ...
... emergence of cell assemblies in a small network of 69 neurons. They found that everything became active in their network. • They decided that they needed to include inhibitory synapses. This worked and cell assemblies did, indeed, form. • This was later confirmed in real brain circuitry. ...
Cortical Stimulation Mapping www.AssignmentPoint.com Cortical
... under general anesthesia. If the patient is under general anesthesia, the depth of the anesthesia can affect the outcome because if the levels of muscle relaxation are too high due to neuromuscular blocking drugs, then the results from the mapping can be incorrect. For the awake procedure there are ...
... under general anesthesia. If the patient is under general anesthesia, the depth of the anesthesia can affect the outcome because if the levels of muscle relaxation are too high due to neuromuscular blocking drugs, then the results from the mapping can be incorrect. For the awake procedure there are ...
Doktryna neuronu
... of ion flow between the cells. This bridging of the cells is facilitated by a narrowing of the normal intercellular space (20 nm) to only 3.5 nm at the gap junction Electron micrograph: The array of channels shown here was isolated from the membrane of a rat liver. Each channel appears hexagonal in ...
... of ion flow between the cells. This bridging of the cells is facilitated by a narrowing of the normal intercellular space (20 nm) to only 3.5 nm at the gap junction Electron micrograph: The array of channels shown here was isolated from the membrane of a rat liver. Each channel appears hexagonal in ...
Exam Questions - NEVR2030 - Autumn 2012
... 16. Name the structure in the developing brain from which the interneurons in the cortex originate. (1) 17. During the formation of the neural tube, a number of embryonic cells differentiate into the so‐called neural crest. Name two derivatives of neural crest cells. (2) 18. The prosencephalo ...
... 16. Name the structure in the developing brain from which the interneurons in the cortex originate. (1) 17. During the formation of the neural tube, a number of embryonic cells differentiate into the so‐called neural crest. Name two derivatives of neural crest cells. (2) 18. The prosencephalo ...
11-5_TheMulti-CenterAspectOfMotorControl. _NagyD
... THE BASAL GANGLIA As their name suggests, the basal ganglia consist of a set of neural structures buried deep inside the cerebrum. The main basal ganglia are the caudate nucleus, the putamen, and the globus pallidus. These ganglia, or clusters of nerve cells, are tightly interconnected. They also re ...
... THE BASAL GANGLIA As their name suggests, the basal ganglia consist of a set of neural structures buried deep inside the cerebrum. The main basal ganglia are the caudate nucleus, the putamen, and the globus pallidus. These ganglia, or clusters of nerve cells, are tightly interconnected. They also re ...
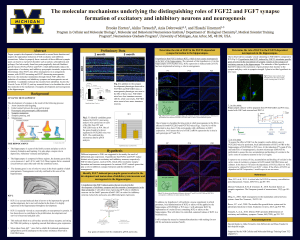
Abstract Background Preliminary Data Hypothesis
... Abstract Proper synaptic development is fundamental to normal brain function and requires the appropriate induction of both excitatory and inhibitory connections. Failure to properly form a network of these different synaptic types can lead to a myriad of disorders such as autism, schizophrenia and ...
... Abstract Proper synaptic development is fundamental to normal brain function and requires the appropriate induction of both excitatory and inhibitory connections. Failure to properly form a network of these different synaptic types can lead to a myriad of disorders such as autism, schizophrenia and ...
New Autism Research
... Pineda, who also works on a number of brain-computer interface projects, says that the mu rhythm is one that we most readily learn to control. "We can learn to increase or decrease the strength of the mu signal at will. By imagining action, subjects are able to move a paddle in a computer game of 'P ...
... Pineda, who also works on a number of brain-computer interface projects, says that the mu rhythm is one that we most readily learn to control. "We can learn to increase or decrease the strength of the mu signal at will. By imagining action, subjects are able to move a paddle in a computer game of 'P ...
Chapter 18
... PET scan on the left shows two areas of the brain (red and yellow) that become particularly active when volunteers read words on a video screen: the primary visual cortex and an additional part of the visual system, both in the back of the left hemisphere. Other brain regions become especially activ ...
... PET scan on the left shows two areas of the brain (red and yellow) that become particularly active when volunteers read words on a video screen: the primary visual cortex and an additional part of the visual system, both in the back of the left hemisphere. Other brain regions become especially activ ...
From autism to ADHD: computational simulations
... • MNS: observing action elicits similar motor activations as if it had been performed by oneself; visuo-motor neurons. • This helps to understand actions of others, modeling behavior via embodied simulation of their actions, intentions, and emotions. • MNS theory of autism (Williams et al, 2001): di ...
... • MNS: observing action elicits similar motor activations as if it had been performed by oneself; visuo-motor neurons. • This helps to understand actions of others, modeling behavior via embodied simulation of their actions, intentions, and emotions. • MNS theory of autism (Williams et al, 2001): di ...
The Brain - Polk School District
... • Gray matter—pinkish-gray color—contains cell bodies, dendrites, and axon terminals of neurons…so this is where all the synapses are; nonmyelinated axons. – Cerebral cortex – Specialized regions of the brain involved in computation, thinking, memory storage, muscle control, sensory perceptions, suc ...
... • Gray matter—pinkish-gray color—contains cell bodies, dendrites, and axon terminals of neurons…so this is where all the synapses are; nonmyelinated axons. – Cerebral cortex – Specialized regions of the brain involved in computation, thinking, memory storage, muscle control, sensory perceptions, suc ...
Chapter 28
... synapse by chemical messengers called neurotransmitters. • These chemicals are packaged in tiny sacs, or vesicles, at the tip of the axon. • When a nerve impulse reaches the end of an axon, it causes the vesicles to release the neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. • Chemically-gated channels o ...
... synapse by chemical messengers called neurotransmitters. • These chemicals are packaged in tiny sacs, or vesicles, at the tip of the axon. • When a nerve impulse reaches the end of an axon, it causes the vesicles to release the neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. • Chemically-gated channels o ...
Chapter 11- 14 Integration of Nervous System Functions
... sensed by electrodes placed on the scalp • Brain wave patterns – Alpha: Resting state with eyes closed – Beta: During intense mental activity – Theta: Occur in children but also in adults experiencing frustration or brain disorders – Delta: Occur in deep sleep, infancy, and severe brain disorders ...
... sensed by electrodes placed on the scalp • Brain wave patterns – Alpha: Resting state with eyes closed – Beta: During intense mental activity – Theta: Occur in children but also in adults experiencing frustration or brain disorders – Delta: Occur in deep sleep, infancy, and severe brain disorders ...
The Nervous System http://www.gmstigers.com/apps/pages/index
... brain to all parts of your body. The messages are carried through electrical and chemical signals. Neurons are made up of three main parts, the cell body, axons, and dendrites. Axons and dendrites branch out to messages to be sent and received to all parts of the body. The spinal cord is the long bu ...
... brain to all parts of your body. The messages are carried through electrical and chemical signals. Neurons are made up of three main parts, the cell body, axons, and dendrites. Axons and dendrites branch out to messages to be sent and received to all parts of the body. The spinal cord is the long bu ...
Brain
... • Selective barrier that allows nutrients to pass freely • Is ineffective against substances that can diffuse through plasma membranes • Absent in some areas (vomiting center and the hypothalamus), allowing these areas to monitor the chemical composition of the blood • Stress increases the ability o ...
... • Selective barrier that allows nutrients to pass freely • Is ineffective against substances that can diffuse through plasma membranes • Absent in some areas (vomiting center and the hypothalamus), allowing these areas to monitor the chemical composition of the blood • Stress increases the ability o ...
File
... the dendrites along the axon to the end plates of the neuron. • Active transport and diffusion of sodium and potassium ions establish a polarized membrane. • An action potential is caused by the inflow of sodium ions. • Nerve cells exhibit an all-or-none response. • Neurotransmitters allow the nerve ...
... the dendrites along the axon to the end plates of the neuron. • Active transport and diffusion of sodium and potassium ions establish a polarized membrane. • An action potential is caused by the inflow of sodium ions. • Nerve cells exhibit an all-or-none response. • Neurotransmitters allow the nerve ...
Chapter 31.2: Parts of the brain
... – Each of the major areas of the brain- the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brain stem- are responsible for processing and relaying information – Most of the neurons that enter and leave the brain do so in a large cluster of neurons and other cells known as the spinal cord. • The spinal cord is the main c ...
... – Each of the major areas of the brain- the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brain stem- are responsible for processing and relaying information – Most of the neurons that enter and leave the brain do so in a large cluster of neurons and other cells known as the spinal cord. • The spinal cord is the main c ...
Baby`s Brain Begins Now: Conception to Age 3
... for one of the body’s key stress systems, regulating the release of cortisol and other stress hormones. The amygdala evaluates threats and triggers the body’s stress response.2,5,6 F ...
... for one of the body’s key stress systems, regulating the release of cortisol and other stress hormones. The amygdala evaluates threats and triggers the body’s stress response.2,5,6 F ...