Nervous System
... The neuron transmits electric signals like an electric wire. The perikaryon (cell body) is the neuron central part. Dendrites, short branches, extend from the neuron. These input channels receive information from other neurons or sensory cells (cells that receive information from the environment). A ...
... The neuron transmits electric signals like an electric wire. The perikaryon (cell body) is the neuron central part. Dendrites, short branches, extend from the neuron. These input channels receive information from other neurons or sensory cells (cells that receive information from the environment). A ...
Reading_Nervous_System
... The neuron transmits electric signals like an electric wire. The perikaryon (cell body) is the neuron central part. Dendrites, short branches, extend from the neuron. These input channels receive information from other neurons or sensory cells (cells that receive information from the environment). A ...
... The neuron transmits electric signals like an electric wire. The perikaryon (cell body) is the neuron central part. Dendrites, short branches, extend from the neuron. These input channels receive information from other neurons or sensory cells (cells that receive information from the environment). A ...
The Autonomic Nervous System
... The entire sensory cortex is arranged in columns of cortical neurons with each column representing a building block of sensory perception – The thalamus projects fibers (sorted out by sensation type) to the primary somatosensory cortex and to sensory association areas – First to those restricted to ...
... The entire sensory cortex is arranged in columns of cortical neurons with each column representing a building block of sensory perception – The thalamus projects fibers (sorted out by sensation type) to the primary somatosensory cortex and to sensory association areas – First to those restricted to ...
Childhood Experience and the Expression of Genetic Potential
... while others will not. Again, this process appears to have genetic and environmental determinants. Neurons that make synaptic connections with others and have an adequate level of activation will survive; neurons with little activity resorb. This is one example of a general principle of activity-dep ...
... while others will not. Again, this process appears to have genetic and environmental determinants. Neurons that make synaptic connections with others and have an adequate level of activation will survive; neurons with little activity resorb. This is one example of a general principle of activity-dep ...
Skeletal System
... The entire sensory cortex is arranged in columns of cortical neurons with each column representing a building block of sensory perception – The thalamus projects fibers (sorted out by sensation type) to the primary somatosensory cortex and to sensory association areas – First to those restricted to ...
... The entire sensory cortex is arranged in columns of cortical neurons with each column representing a building block of sensory perception – The thalamus projects fibers (sorted out by sensation type) to the primary somatosensory cortex and to sensory association areas – First to those restricted to ...
Molecular Identification and the Immunolocalization of Purinergic Signaling Receptors in... Mammalian Vomeronasal Organ
... Information about the external world is conveyed through the nervous system via specialized sensory organs such as the vomeronasal organ (VNO). The VNO is crucial for pheromone detection and the regulation of social behavior in many mammals. Recent research has shown that purinergic signaling pathwa ...
... Information about the external world is conveyed through the nervous system via specialized sensory organs such as the vomeronasal organ (VNO). The VNO is crucial for pheromone detection and the regulation of social behavior in many mammals. Recent research has shown that purinergic signaling pathwa ...
File
... he died in 1955, showed that the parietal lobes, which are linked to math ability, appear 15% wider than normal. But the size of his brain was a little smaller than average. • We may be the smartest creatures on the planet, but others have bigger brains. Larger brains are needed partly to control la ...
... he died in 1955, showed that the parietal lobes, which are linked to math ability, appear 15% wider than normal. But the size of his brain was a little smaller than average. • We may be the smartest creatures on the planet, but others have bigger brains. Larger brains are needed partly to control la ...
Neurons
... Unlike other body cells, neurons stop reproducing shortly after birth. Because of this, some parts of the brain have more neurons at birth than later in life because neurons die but are not replaced. While neurons do not reproduce, research has shown that new connections between neurons form through ...
... Unlike other body cells, neurons stop reproducing shortly after birth. Because of this, some parts of the brain have more neurons at birth than later in life because neurons die but are not replaced. While neurons do not reproduce, research has shown that new connections between neurons form through ...
Open Document - Clinton Community College
... Complexities occurring even with simplest function ◦ Example ...
... Complexities occurring even with simplest function ◦ Example ...
Abstracts - Yale School of Medicine
... Brain size during adulthood is a function of two processes: brain growth and brain shrinkage. Brain growth determines the maximum size an individual’s brain achieves, usually during early adolescence. Brain shrinkage begins late in the second or early in the third decade of life and continues over t ...
... Brain size during adulthood is a function of two processes: brain growth and brain shrinkage. Brain growth determines the maximum size an individual’s brain achieves, usually during early adolescence. Brain shrinkage begins late in the second or early in the third decade of life and continues over t ...
The Mirror Mechanism: A Mechanism for Understanding Others
... the mirror mechanism in social cognition. I will discuss this issue and will show that, although there are several mechanisms through which one can understand the behaviour of others, the parieto-frontal mechanism is the only one that allows understanding others’ actions from the inside giving the o ...
... the mirror mechanism in social cognition. I will discuss this issue and will show that, although there are several mechanisms through which one can understand the behaviour of others, the parieto-frontal mechanism is the only one that allows understanding others’ actions from the inside giving the o ...
Optogenetics: Molecular and Optical Tools for Controlling Life with
... Over the last several years we and our colleagues have developed a toolbox of fully genetically encoded molecules that, when expressed in neurons, enable the electrical potentials of the neurons to be controlled in a temporally precise fashion by brief pulses of light. Some of the molecules enable t ...
... Over the last several years we and our colleagues have developed a toolbox of fully genetically encoded molecules that, when expressed in neurons, enable the electrical potentials of the neurons to be controlled in a temporally precise fashion by brief pulses of light. Some of the molecules enable t ...
Chapter 2
... During the development of the nervous system, large numbers of neurons are created, though not all of them survive. In fact, it has been estimated that between 20 per cent and 80 per cent of neurons may die in various locations in the nervous system (Toates, 2006). In order to survive, a neuron must ...
... During the development of the nervous system, large numbers of neurons are created, though not all of them survive. In fact, it has been estimated that between 20 per cent and 80 per cent of neurons may die in various locations in the nervous system (Toates, 2006). In order to survive, a neuron must ...
Slide () - AccessAnesthesiology
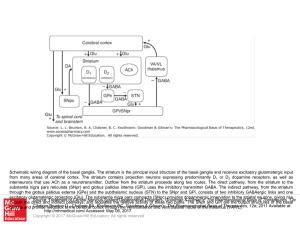
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
The neuronal representation of information in the human brain
... and primates including humans, is that rat hippocampal neurons represent the place where the rat is located (O’Keefe, 1979), whereas a population of neurons in the macaque hippocampus and parahippocampal cortex has been discovered that represents a spatial view of a scene with its landmarks independ ...
... and primates including humans, is that rat hippocampal neurons represent the place where the rat is located (O’Keefe, 1979), whereas a population of neurons in the macaque hippocampus and parahippocampal cortex has been discovered that represents a spatial view of a scene with its landmarks independ ...
Biology 2401 Anatomy and Physiology I notes
... Schwann cells - in peripheral ns only; form myelin sheath and neurolemma around axons of neurons outside of brain and spinal cord. (more on myelin sheaths later) *List five types of glial cells and tell what the function is of each. *Which glial cells are only in the central nervous system (brain a ...
... Schwann cells - in peripheral ns only; form myelin sheath and neurolemma around axons of neurons outside of brain and spinal cord. (more on myelin sheaths later) *List five types of glial cells and tell what the function is of each. *Which glial cells are only in the central nervous system (brain a ...
Lund University Publications
... learning to activity within these cells (42). Thus, by combining genetic targeting for high spatial resolution of defined cells with in vivo light illumination for their activation enables definition of neuronal subtypes for their participation in behavioral events. As optogenetics al ...
... learning to activity within these cells (42). Thus, by combining genetic targeting for high spatial resolution of defined cells with in vivo light illumination for their activation enables definition of neuronal subtypes for their participation in behavioral events. As optogenetics al ...
Synapse Formation
... • Axon grows to target – differentiates into the presynaptic terminal • Target cell also changes – into postsynaptic terminal • Both already carrying the components to form the synapse Æ contact is trigger ...
... • Axon grows to target – differentiates into the presynaptic terminal • Target cell also changes – into postsynaptic terminal • Both already carrying the components to form the synapse Æ contact is trigger ...
BRAIN GLUCOSE-SENSING: AGE- AND ENERGY
... and lectured in some of the world’s top universities. Working with a multidisciplinary team of collaborators, Spanswick is primarily attempting to understand how nerve cells interpret the enormous volume of hormonal and nutrient signals they receive, and how their function changes as a result of fac ...
... and lectured in some of the world’s top universities. Working with a multidisciplinary team of collaborators, Spanswick is primarily attempting to understand how nerve cells interpret the enormous volume of hormonal and nutrient signals they receive, and how their function changes as a result of fac ...
IBM Research Report - Dharmendra S Modha`s Brain
... Since the final submission of our work on the Compass scalable simulator for the IBM TrueNorth Cognitive Computing architecture [1], we have simulated an unprecedented 2.084 billion neurosynaptic cores containing 53 × 1010 neurons and 1.37 × 1014 synapses running at only 1542× slower than real time. ...
... Since the final submission of our work on the Compass scalable simulator for the IBM TrueNorth Cognitive Computing architecture [1], we have simulated an unprecedented 2.084 billion neurosynaptic cores containing 53 × 1010 neurons and 1.37 × 1014 synapses running at only 1542× slower than real time. ...
Slides - Indiana University Bloomington
... requirement of NMDA receptors that glutamate bind them and that the cell be hypopolarized, the binding opens the channel and the hypopolarization displaces Mg++ that blocks the channel lumen. Also required is that the pre-and post-synaptic cells both be active at the same time. This property is term ...
... requirement of NMDA receptors that glutamate bind them and that the cell be hypopolarized, the binding opens the channel and the hypopolarization displaces Mg++ that blocks the channel lumen. Also required is that the pre-and post-synaptic cells both be active at the same time. This property is term ...
Chapter 10
... perception of sensation Phasic receptors rapidly adapting Tonic receptors slow adapting or do not adapt ...
... perception of sensation Phasic receptors rapidly adapting Tonic receptors slow adapting or do not adapt ...
List of Research Projects and Faculty 2017
... Memory refers to the storage of information across time. Historically, information storage in a biological system has been seen as requiring either a persistent structural or functional change at the cellular level. Whether a memory relies on a structural or functional alteration in neurons is a dif ...
... Memory refers to the storage of information across time. Historically, information storage in a biological system has been seen as requiring either a persistent structural or functional change at the cellular level. Whether a memory relies on a structural or functional alteration in neurons is a dif ...