BrainMechanismsofUnconsciousInference2011
... Neuronal Structure and Function • Neurons combine excitatory and inhibitory signals obtained from other neurons. • They signal to other neurons primarily via ‘spikes’ or action potentials. ...
... Neuronal Structure and Function • Neurons combine excitatory and inhibitory signals obtained from other neurons. • They signal to other neurons primarily via ‘spikes’ or action potentials. ...
Lab07 Brain - Tacoma Community College
... Note that the surface of the cerebral hemispheres has ridges of tissue called gyri (singular gyrus) separated by grooves called sulci (singular sulcus). Deeper sulci are referred to as fissures that se ...
... Note that the surface of the cerebral hemispheres has ridges of tissue called gyri (singular gyrus) separated by grooves called sulci (singular sulcus). Deeper sulci are referred to as fissures that se ...
Brain Computer Interface Boulevard of Smarter Thoughts
... (UWSOM), Seattle [2]. A monkey was used as the subject where he successfully deflected a biofeedback meter measuring arm with the intervention of his neural activity. Another subsequent research used the same subject, but in numbers to announce the voluntary control of solo and multiple neurons in t ...
... (UWSOM), Seattle [2]. A monkey was used as the subject where he successfully deflected a biofeedback meter measuring arm with the intervention of his neural activity. Another subsequent research used the same subject, but in numbers to announce the voluntary control of solo and multiple neurons in t ...
Perception
... Grandmother cell: according to Lettvin is a neuron that responds only to a specific stimulus ...
... Grandmother cell: according to Lettvin is a neuron that responds only to a specific stimulus ...
Hormonal Control
... function to support the neurons in various ways. Neurons have a cell body or cyton, where the nucleus is found, and several processes or extensions off this cell body. The processes that conduct the impulse toward the cell body are called dendrites, while the one very long extension that conducts th ...
... function to support the neurons in various ways. Neurons have a cell body or cyton, where the nucleus is found, and several processes or extensions off this cell body. The processes that conduct the impulse toward the cell body are called dendrites, while the one very long extension that conducts th ...
Linear associator
... system. We know if a tone is consistently presented at the same time as food, the dog will eventually become conditioned to respond by salivating to the tone alone. In the previous lab, we hypothesized that this may have been due to neurons of the auditory system forming synapses directly onto the c ...
... system. We know if a tone is consistently presented at the same time as food, the dog will eventually become conditioned to respond by salivating to the tone alone. In the previous lab, we hypothesized that this may have been due to neurons of the auditory system forming synapses directly onto the c ...
Divisions of the Nervous System
... – controls subconscious actions: contractions of smooth muscle and cardiac muscle and ...
... – controls subconscious actions: contractions of smooth muscle and cardiac muscle and ...
Your Brain
... radio waves disorients the atoms momentarily. When the atoms return to their normal spin they release detectable signals, which are processed into computer-generated images of the concentrations of these atoms. The result is a detailed picture of the brain’s soft tissues. For example, MRI scans reve ...
... radio waves disorients the atoms momentarily. When the atoms return to their normal spin they release detectable signals, which are processed into computer-generated images of the concentrations of these atoms. The result is a detailed picture of the brain’s soft tissues. For example, MRI scans reve ...
Lesson Overview - Diman Regional
... communication link between the brain and the rest of the body. It carries thousands of signals at once between the central and peripheral nervous systems. ...
... communication link between the brain and the rest of the body. It carries thousands of signals at once between the central and peripheral nervous systems. ...
Music and the Brain: Areas and Networks
... Beyond the auditory cortices, musical sounds activate distributed grey matter throughout the brain. Researchers have proposed various functional networks or pathways beyond the level of the primary auditory cortex. These functional networks subserve language and generalized auditory processing as we ...
... Beyond the auditory cortices, musical sounds activate distributed grey matter throughout the brain. Researchers have proposed various functional networks or pathways beyond the level of the primary auditory cortex. These functional networks subserve language and generalized auditory processing as we ...
Human Physiology/The Nervous System
... a neuron can vary in size from 4 to 100 micrometers in diameter. The soma (cell body) is the central part of the neuron. It contains the nucleus of the cell, and therefore is where most protein synthesis occurs. The nucleus ranges from 3 to 18 micrometers in diameter. The dendrites of a neuron are c ...
... a neuron can vary in size from 4 to 100 micrometers in diameter. The soma (cell body) is the central part of the neuron. It contains the nucleus of the cell, and therefore is where most protein synthesis occurs. The nucleus ranges from 3 to 18 micrometers in diameter. The dendrites of a neuron are c ...
The Function & Anatomy of Neurons What is a Neuron?
... What is a Neuron? It is the cell of nerve tissue that is responsive and conducts impulses within the Nervous System at high rates of speed. They are the primary structural and functional unit of the nervous system. ...
... What is a Neuron? It is the cell of nerve tissue that is responsive and conducts impulses within the Nervous System at high rates of speed. They are the primary structural and functional unit of the nervous system. ...
The Cells of the Nervous System Lab
... dragging the mouse to rotate. The purkinje cell axons, not shown here, are inhibitory, and provide the entire output of the cerebellar cortex. Excitatory neurons Neurons in the same brain region may also have very different morphologies reflecting their unique function in the brain. In the cerebral ...
... dragging the mouse to rotate. The purkinje cell axons, not shown here, are inhibitory, and provide the entire output of the cerebellar cortex. Excitatory neurons Neurons in the same brain region may also have very different morphologies reflecting their unique function in the brain. In the cerebral ...
Tango and mirror neurons
... One of the most convincing demonstrations of the existence of mirror neurons in the human brain is provided by the remarkable property of insular neurons to "feel" someone else affects, as a true basis of human empathy. •The most recent works show that parts of the mirror neuron system, including th ...
... One of the most convincing demonstrations of the existence of mirror neurons in the human brain is provided by the remarkable property of insular neurons to "feel" someone else affects, as a true basis of human empathy. •The most recent works show that parts of the mirror neuron system, including th ...
Modeling stability in neuron and network function: the role of activity
... is, neurons that are generating single spikes followed by a sustained plateau phase. Although the voltage trajectories of these three model neurons are quite similar, they vary dramatically in their conductance densities: neuron 1 has a high Naþ conductance and a low delayed rectifier Kþ conductance ...
... is, neurons that are generating single spikes followed by a sustained plateau phase. Although the voltage trajectories of these three model neurons are quite similar, they vary dramatically in their conductance densities: neuron 1 has a high Naþ conductance and a low delayed rectifier Kþ conductance ...
WELCH Notes Chapter 12
... c. Theta waves are irregular waves that are not common when awake, but may occur when concentrating or emotional stress. d. Delta waves are high amplitude waves seen during deep sleep, but indicate brain damage if observed in awake adults. 3. Brain waves change with age, sensory stimuli, brain disea ...
... c. Theta waves are irregular waves that are not common when awake, but may occur when concentrating or emotional stress. d. Delta waves are high amplitude waves seen during deep sleep, but indicate brain damage if observed in awake adults. 3. Brain waves change with age, sensory stimuli, brain disea ...
view - Queen`s University
... which form connections with the motor neurons after the synapse, and permit substantial processing of signals. But the direct projection from sensory afferents to motor neurons precludes such processing. Instead, the activity of these synapses (and other afferent synapses in the spinal cord) is regu ...
... which form connections with the motor neurons after the synapse, and permit substantial processing of signals. But the direct projection from sensory afferents to motor neurons precludes such processing. Instead, the activity of these synapses (and other afferent synapses in the spinal cord) is regu ...
Chapter 48 and 49 Name_______________________________
... Neurons are nerve cells that transfer information within the body Neurons use two types of signals to communicate: electrical signals (long-distance) and chemical signals (short-distance) 2. What are the three stages in which the nervous systems process information? Briefly describe them. Nervous sy ...
... Neurons are nerve cells that transfer information within the body Neurons use two types of signals to communicate: electrical signals (long-distance) and chemical signals (short-distance) 2. What are the three stages in which the nervous systems process information? Briefly describe them. Nervous sy ...
Motor activity induced by disinhibition of the primary motor cortex of
... the anesthesia used (ketamine) is a NMDA receptor antagonist we applied another NMDA receptor antagonist (APV) in order to block more effectively and locally the transmission through this receptor. Application of APV did not affect the spontaneous EMG activity elicited by bicuculline (Fig. 1B). Appl ...
... the anesthesia used (ketamine) is a NMDA receptor antagonist we applied another NMDA receptor antagonist (APV) in order to block more effectively and locally the transmission through this receptor. Application of APV did not affect the spontaneous EMG activity elicited by bicuculline (Fig. 1B). Appl ...
Neurons
... Sensory Neurons (a.k.a. Afferent Neurons) carry incoming information from the sense receptors to the CNS. Motor Neurons (a.k.a. Efferent Neurons) carry outgoing information from the CNS to muscles and glands. Interneurons connect the two neurons. ...
... Sensory Neurons (a.k.a. Afferent Neurons) carry incoming information from the sense receptors to the CNS. Motor Neurons (a.k.a. Efferent Neurons) carry outgoing information from the CNS to muscles and glands. Interneurons connect the two neurons. ...
They Come From the Cortex - American Association of Sleep
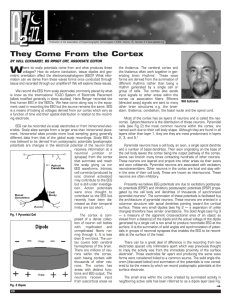
... EEG can be recorded via scalp electrodes or from intracranial electrodes. Scalp sites sample from a larger area than intracranial placement. Intracranial sites provide more local sampling giving generally different data from that of the global scalp recordings. Scalp EEG is now believed to be derive ...
... EEG can be recorded via scalp electrodes or from intracranial electrodes. Scalp sites sample from a larger area than intracranial placement. Intracranial sites provide more local sampling giving generally different data from that of the global scalp recordings. Scalp EEG is now believed to be derive ...
Nerve Tissue
... – stimulates a new wave of electrical activity in the next cell across the synapse – electrical synapses do exist ...
... – stimulates a new wave of electrical activity in the next cell across the synapse – electrical synapses do exist ...
3.2 Our Brains Control Our Thoughts, Feelings, and Behavior
... functions to coordinate voluntary movement. People who have damage to the cerebellum have difficulty walking, keeping their balance, and holding their hands steady. Consuming alcohol influences the cerebellum, which is why people who are drunk have more difficulty walking in a straight line. Also, t ...
... functions to coordinate voluntary movement. People who have damage to the cerebellum have difficulty walking, keeping their balance, and holding their hands steady. Consuming alcohol influences the cerebellum, which is why people who are drunk have more difficulty walking in a straight line. Also, t ...