Quantification of the Effect of Different Levels of IOP in the Astroglia
... Corresponding author: José M. Ramírez, Instituto de Investigaciones Oftalmológicas Ramón Castroviejo. School of Medicine, Complutense University, 28040 Madrid, Spain; [email protected]. ...
... Corresponding author: José M. Ramírez, Instituto de Investigaciones Oftalmológicas Ramón Castroviejo. School of Medicine, Complutense University, 28040 Madrid, Spain; [email protected]. ...
Mild Traumatic Brain Injury
... Diffuse Axonal Injury Brain injury does not require a direct head impact. During rapid acceleration of the head, some parts of the brain can move separately from other parts. This type of motion creates shear forces that can destroy axons necessary for brain functioning. These shear forces can stre ...
... Diffuse Axonal Injury Brain injury does not require a direct head impact. During rapid acceleration of the head, some parts of the brain can move separately from other parts. This type of motion creates shear forces that can destroy axons necessary for brain functioning. These shear forces can stre ...
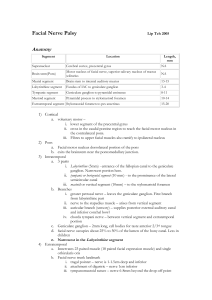
Facial Nerve Palsy
... i. 15cm, distal branches can be used for pes anserinus 2) Results not as good as with primary repair (more incomplete reinnervation of facial divisions, decreased voluntary contractions, and more severe synkinesis) Cross facial nerve graft Smith and Scaramella, working independently (1971) ...
... i. 15cm, distal branches can be used for pes anserinus 2) Results not as good as with primary repair (more incomplete reinnervation of facial divisions, decreased voluntary contractions, and more severe synkinesis) Cross facial nerve graft Smith and Scaramella, working independently (1971) ...
Lecture 1
... Myelinated axons: sheath of Schwann and myelin sheath one Schwann cell myelinates a single axon multiple Schwann cells needed to cover entire length of an axon ...
... Myelinated axons: sheath of Schwann and myelin sheath one Schwann cell myelinates a single axon multiple Schwann cells needed to cover entire length of an axon ...
Neuroscience and Behavior (The Brain)
... • There has also been a cortical area identified that specializes in receiving information from the skin senses and from the movement of body parts • Sensory cortex- the area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body sensations • Stimulate a part of the cortex and a person ...
... • There has also been a cortical area identified that specializes in receiving information from the skin senses and from the movement of body parts • Sensory cortex- the area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body sensations • Stimulate a part of the cortex and a person ...
Taste and Smell - Liberty Hill High School
... • Smell not as good as animals • Humans can distinguish 10,000 or so chemicals • Olfactory fatigue or adaptation • Old people lose sense of smell • What we really smell is pain: ex. chili, ammonia, menthol (cold) ...
... • Smell not as good as animals • Humans can distinguish 10,000 or so chemicals • Olfactory fatigue or adaptation • Old people lose sense of smell • What we really smell is pain: ex. chili, ammonia, menthol (cold) ...
P416 COMPARATIVE ANIMAL PHYSIOLOGY
... – Longitudinally oriented tracts of neurons, with lateral commissures ...
... – Longitudinally oriented tracts of neurons, with lateral commissures ...
Nervous System - Serrano High School AP Biology
... which relays signals to other dendrites of other neurons thorough chemical messengers called neurotransmitters. The space between the synaptic terminal and the dendrite of the other neuron is called the SYNAPSE. A synapse between a neuron and a muscle cell is a neuromuscular junction. A synapse betw ...
... which relays signals to other dendrites of other neurons thorough chemical messengers called neurotransmitters. The space between the synaptic terminal and the dendrite of the other neuron is called the SYNAPSE. A synapse between a neuron and a muscle cell is a neuromuscular junction. A synapse betw ...
Somatosensory system
... mechanical, chemical or thermal stimulation received into receptor potentials • Action potential peripheral axon soma in dorsal root ganglion proximal axon in spinal cord via axons white matter brain • The diameter of the axons, the degree of axonal myelination, and the number of synapse in th ...
... mechanical, chemical or thermal stimulation received into receptor potentials • Action potential peripheral axon soma in dorsal root ganglion proximal axon in spinal cord via axons white matter brain • The diameter of the axons, the degree of axonal myelination, and the number of synapse in th ...
bulbar pseudobulbar
... On the other hand, unilateral lower motor neuron lesions may cause paralysis. This occurs because the lower motor neurons are the final common pathway for neural messages travelling to the muscles of the body. At the level of the lower motor neurons, there is no alternative route which will allow me ...
... On the other hand, unilateral lower motor neuron lesions may cause paralysis. This occurs because the lower motor neurons are the final common pathway for neural messages travelling to the muscles of the body. At the level of the lower motor neurons, there is no alternative route which will allow me ...
POWERPOINT VERSION ()
... • controls visceral activities • regulates smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands • efferent fibers typically lead to ganglia outside CNS ...
... • controls visceral activities • regulates smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands • efferent fibers typically lead to ganglia outside CNS ...
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) PNS – all neural structures
... -Axon and myelin sheath distal to injury disintegrate due to lack of nutrients from the cell body (Wallerian degeneration) -Neurilemma remains intact -Schwann cells proliferate and migrate to injury site and form a regeneration tube that guide axon ...
... -Axon and myelin sheath distal to injury disintegrate due to lack of nutrients from the cell body (Wallerian degeneration) -Neurilemma remains intact -Schwann cells proliferate and migrate to injury site and form a regeneration tube that guide axon ...
Nervous System Notes
... 3. Oligodendrocytes – resemble astrocytes but w/fewer processes; form myelin sheath in CNS ...
... 3. Oligodendrocytes – resemble astrocytes but w/fewer processes; form myelin sheath in CNS ...
12-13 LIFE SCI E10 11
... Unit Statement: In this unit the student will explore the structures and functions of the nervous system, the endocrine system and the reproductive system at both the cellular and organismal level. The student will also make comparisons between the endocrine and nervous systems in how they control b ...
... Unit Statement: In this unit the student will explore the structures and functions of the nervous system, the endocrine system and the reproductive system at both the cellular and organismal level. The student will also make comparisons between the endocrine and nervous systems in how they control b ...
important ascending tracts
... Pseudounipolar neurons in the dorsal root ganglion have axons that lead from the skin into the dorsal spinal cord where they ascend or descend one or two vertebral levels via Lissauer's tract and then synapse with secondary neurons in either the substantia gelatinosa of Rolando or the nucleus propri ...
... Pseudounipolar neurons in the dorsal root ganglion have axons that lead from the skin into the dorsal spinal cord where they ascend or descend one or two vertebral levels via Lissauer's tract and then synapse with secondary neurons in either the substantia gelatinosa of Rolando or the nucleus propri ...
Funkcje ruchowe
... The cerebellum influences the motor systems by evaluating disparities between intention and action and by adjusting the operation of motor centers in the cortex and brain stem while a movement is in progress as well as during repetitions of the same movement. Three aspects of the cerebellum's organi ...
... The cerebellum influences the motor systems by evaluating disparities between intention and action and by adjusting the operation of motor centers in the cortex and brain stem while a movement is in progress as well as during repetitions of the same movement. Three aspects of the cerebellum's organi ...
BIOL241connective6aJUL2012
... • Sheets of spindle-shaped cells with central nuclei that have no striations • Found in the walls of hollow organs ...
... • Sheets of spindle-shaped cells with central nuclei that have no striations • Found in the walls of hollow organs ...
Nervous System - Discovery Education
... cord and through the peripheral nerve to your arm. This is a voluntary action that is controlled by conscious thought. This is referred to as the somatic nervous system. There are other actions that are not voluntary or under conscious control. This part of the peripheral nervous system is called t ...
... cord and through the peripheral nerve to your arm. This is a voluntary action that is controlled by conscious thought. This is referred to as the somatic nervous system. There are other actions that are not voluntary or under conscious control. This part of the peripheral nervous system is called t ...
48nervous
... Networks of neurons either intricate connections form nervous systems • Neuron Structure and Synapses. – The neuron is the structural and functional unit of the nervous system. ...
... Networks of neurons either intricate connections form nervous systems • Neuron Structure and Synapses. – The neuron is the structural and functional unit of the nervous system. ...
Fascia Iliaca Block
... Hip fractures are painful and the provision of appropriate pain relief should be a priority in the ED. Conventional pain relief in this population is often associated with undesirable side-effects and not always effective. In particular, bolus narcotics may cause respiratory depression, hypotension, ...
... Hip fractures are painful and the provision of appropriate pain relief should be a priority in the ED. Conventional pain relief in this population is often associated with undesirable side-effects and not always effective. In particular, bolus narcotics may cause respiratory depression, hypotension, ...
Activity Overview - Teacher Enrichment Initiatives
... 1. Explain that “Motor Neurons” carry messages away from the brain to the muscles and other structures in the body. 2. For the simulation, all “Motor Neurons” must work together to send a message from the “Brain” to the “Foot”. 3. Explain to students that their left hand = the dendrite, their body=c ...
... 1. Explain that “Motor Neurons” carry messages away from the brain to the muscles and other structures in the body. 2. For the simulation, all “Motor Neurons” must work together to send a message from the “Brain” to the “Foot”. 3. Explain to students that their left hand = the dendrite, their body=c ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 13.1 Ectodermis subdivided into
... FIGURE 13.1 Ectodermis subdivided into different fates during gastrulation. Shown is a crosssectional side view, and top view of an amphibian embryo before (blastula-stage) and after gastrulation (neural plate-stage). During gastrulation, the gray and green (dorsal mesoderm) regions of the blastula ...
... FIGURE 13.1 Ectodermis subdivided into different fates during gastrulation. Shown is a crosssectional side view, and top view of an amphibian embryo before (blastula-stage) and after gastrulation (neural plate-stage). During gastrulation, the gray and green (dorsal mesoderm) regions of the blastula ...