Portland Community College, Sylvania Campus
... of singular and plural usage because these mistakes will count as spelling errors. Absences: You cannot miss more than two labs and still pass the course. Also you can only attend another instructor’s class once during the quarter. This must be approved by both instructors. If you attend another ins ...
... of singular and plural usage because these mistakes will count as spelling errors. Absences: You cannot miss more than two labs and still pass the course. Also you can only attend another instructor’s class once during the quarter. This must be approved by both instructors. If you attend another ins ...
The Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter
... that are responsible for sensation (sensory functions) and for the response (motor functions). But there is a third function that needs to be included. Sensory input needs to be integrated with other sensations, as well as with memories, emotional state, or learning (cognition). Some regions of the ...
... that are responsible for sensation (sensory functions) and for the response (motor functions). But there is a third function that needs to be included. Sensory input needs to be integrated with other sensations, as well as with memories, emotional state, or learning (cognition). Some regions of the ...
Physiology
... An action potential is a very rapid change in membrane potential that occurs when a nerve cell membrane is stimulated. Specifically, the membrane potential goes from the resting potential (typically -70 mV) to some positive value (typically about +30 mV) in a very short period of time (just a few mi ...
... An action potential is a very rapid change in membrane potential that occurs when a nerve cell membrane is stimulated. Specifically, the membrane potential goes from the resting potential (typically -70 mV) to some positive value (typically about +30 mV) in a very short period of time (just a few mi ...
Nerve activates contraction
... Information Is Transferred from a Neuron to Its Target Targets: another neuron, muscle cell, or gland Synapse: special junction between axon terminus and target cell Synaptic transmission – Process of transmission of impulse from sending (presynaptic neuron) across synaptic cleft to receiving ...
... Information Is Transferred from a Neuron to Its Target Targets: another neuron, muscle cell, or gland Synapse: special junction between axon terminus and target cell Synaptic transmission – Process of transmission of impulse from sending (presynaptic neuron) across synaptic cleft to receiving ...
Spinal nerves
... • Direct transfer of stimulus from sensory neuron to motor neuron (sometimes with an interneuron in between) allows for rapid response to stimuli. • May be: – Inborn (intrinsic) • Example – maintain posture, control visceral activities • Can be modified by learning and conscious effort --Learned (ac ...
... • Direct transfer of stimulus from sensory neuron to motor neuron (sometimes with an interneuron in between) allows for rapid response to stimuli. • May be: – Inborn (intrinsic) • Example – maintain posture, control visceral activities • Can be modified by learning and conscious effort --Learned (ac ...
Nerve Cells and Nerve Impulses
... • Sensory neurons carry nerve impulses from sense organs and internal organs to the central nervous system. • Motor neurons carry nerve impulses from the central nervous system to organs, glands, and muscles—the ...
... • Sensory neurons carry nerve impulses from sense organs and internal organs to the central nervous system. • Motor neurons carry nerve impulses from the central nervous system to organs, glands, and muscles—the ...
... learned about mechanisms regulating secretion of classical neurotransmitters, far less is known about those regulating secretion of neuropeptides and hormones. Classical neurotransmitters are packaged in synaptic vesicles (SVs), which are clustered at active zones. Neuropeptides are packaged into la ...
The comparative electrobiology of gelatinous
... is very tightly coupled and slow changes in resting potential, such as those that are produced by the endogenous pacemaker, occur synchronously throughout the entire population. However, it is possible to stimulate one cell so that an action potential occurs in it first and then spreads to others. S ...
... is very tightly coupled and slow changes in resting potential, such as those that are produced by the endogenous pacemaker, occur synchronously throughout the entire population. However, it is possible to stimulate one cell so that an action potential occurs in it first and then spreads to others. S ...
action potential
... postsynaptic cell A single neurotransmitter may have more than a dozen different receptors Acetylcholine is a common neurotransmitter in both invertebrates and vertebrates ...
... postsynaptic cell A single neurotransmitter may have more than a dozen different receptors Acetylcholine is a common neurotransmitter in both invertebrates and vertebrates ...
Massage Helps Relieve Muscular Pain
... strokes. He immediately serves the ball. A couple of minutes into the game, as he reaches hard for an out-of-reach ball, he feels a sharp pain in the right side of his neck. He has torn his tight levator scapula muscle. After a few more hits, the pain increases to the point he has to leave the court ...
... strokes. He immediately serves the ball. A couple of minutes into the game, as he reaches hard for an out-of-reach ball, he feels a sharp pain in the right side of his neck. He has torn his tight levator scapula muscle. After a few more hits, the pain increases to the point he has to leave the court ...
The Special Senses
... • Adaptation – the loss of sensitivity after continuous stimulation – Tonic receptors are always active – Phasic receptors only relay changes in the conditions they are monitoring ...
... • Adaptation – the loss of sensitivity after continuous stimulation – Tonic receptors are always active – Phasic receptors only relay changes in the conditions they are monitoring ...
Medical Gross Anatomy - University of Michigan
... structures by the most efficient path for the given region of the body. Postsynaptic sympathetic nerves have several possible routes depending on the location of their target organs. Many postsynaptic sympathetic fibers re-enter the spinal nerve via gray rami communicantes and get distributed to the ...
... structures by the most efficient path for the given region of the body. Postsynaptic sympathetic nerves have several possible routes depending on the location of their target organs. Many postsynaptic sympathetic fibers re-enter the spinal nerve via gray rami communicantes and get distributed to the ...
Proprioceptive Eye Position Signals Are Still Missing a Sensory
... 8), or whether palisade ending innervation should be subdivided into two separate groups. Despite thorough immunohistochemical examination, palisade endings remain surprisingly difficult to classify. Molecular features, such as positive CGRP reactivity, support the notion that palisade endings are a ...
... 8), or whether palisade ending innervation should be subdivided into two separate groups. Despite thorough immunohistochemical examination, palisade endings remain surprisingly difficult to classify. Molecular features, such as positive CGRP reactivity, support the notion that palisade endings are a ...
Memory from the dynamics of intrinsic membrane currents
... Sustained neuronal activity in response to a brief stimulus has been proposed to underlie some short-term memory tasks (see other papers in this colloquium). For many years, the assumption was made that such sustained activity resulted from reverberating activity through excitatory feedback loops. H ...
... Sustained neuronal activity in response to a brief stimulus has been proposed to underlie some short-term memory tasks (see other papers in this colloquium). For many years, the assumption was made that such sustained activity resulted from reverberating activity through excitatory feedback loops. H ...
Spinal Cord - Study Windsor
... reticulospinal tract. Loss of these upper motor neurons deprives the anterior horn cells, i.e., lower motor neurons, of the impulses which generate contraction of skeletal muscle, hence, weakness (paresis) or paralysis. Hypertonia and hyperreflexia appear to result from loss of the inhibitory effe ...
... reticulospinal tract. Loss of these upper motor neurons deprives the anterior horn cells, i.e., lower motor neurons, of the impulses which generate contraction of skeletal muscle, hence, weakness (paresis) or paralysis. Hypertonia and hyperreflexia appear to result from loss of the inhibitory effe ...
Ch33 nervous system reading essentials
... in the brain and spinal cord. They receive the signals sent by the sensory neurons. Interneurons also send signals to the motor neurons. The motor neurons are located in your glands and mucles and cause movement. When you stub your toe, sensory neurons in your foot send impulses to the interneurons. ...
... in the brain and spinal cord. They receive the signals sent by the sensory neurons. Interneurons also send signals to the motor neurons. The motor neurons are located in your glands and mucles and cause movement. When you stub your toe, sensory neurons in your foot send impulses to the interneurons. ...
7-1 The Special Senses
... about our surroundings Grouped into two major categories: - general senses - special senses ...
... about our surroundings Grouped into two major categories: - general senses - special senses ...
Spinal Sensorimotor System: An Overview
... Signals from different types of sensors are conveyed to the dorsal horn via fibers with different propagation velocities by sensory neurons of different types. Figure 8 tabulates the spectrum of different sensory signal-carrying elements (and also includes the three motor fibers that carry action po ...
... Signals from different types of sensors are conveyed to the dorsal horn via fibers with different propagation velocities by sensory neurons of different types. Figure 8 tabulates the spectrum of different sensory signal-carrying elements (and also includes the three motor fibers that carry action po ...
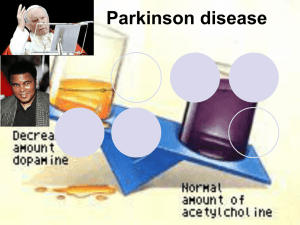
Parkinson disease
... trihexyphenedyl are used. They are less effective than dopaminergic drugs. they are more effective in reducing tremor than the other symptoms. They are useful in treatment of early and advanced parkinson disease, they can reduce parkinsonian symptoms caused by dopamine receptor antagonists eg ...
... trihexyphenedyl are used. They are less effective than dopaminergic drugs. they are more effective in reducing tremor than the other symptoms. They are useful in treatment of early and advanced parkinson disease, they can reduce parkinsonian symptoms caused by dopamine receptor antagonists eg ...
NeuralNets
... Na channels have 2 types of gating mechanisms: • Activation during depolarization open Na Channels • Inactivation after depolarization close Na Channels ...
... Na channels have 2 types of gating mechanisms: • Activation during depolarization open Na Channels • Inactivation after depolarization close Na Channels ...
Basal Ganglia
... cerebral cortex. They receive information from the frontal cortex about behavior that is being planned for a particular situation. In turn, the basal ganglia affect activity in the frontal cortex through a series of neural projections that ultimately go back up to the same cortical areas from which ...
... cerebral cortex. They receive information from the frontal cortex about behavior that is being planned for a particular situation. In turn, the basal ganglia affect activity in the frontal cortex through a series of neural projections that ultimately go back up to the same cortical areas from which ...
Neuromuscular junction

A neuromuscular junction (sometimes called a myoneural junction) is a junction between nerve and muscle; it is a chemical synapse formed by the contact between the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron and the postsynaptic membrane of a muscle fiber. It is at the neuromuscular junction that a motor neuron is able to transmit a signal to the muscle fiber, causing muscle contraction.Muscles require innervation to function—and even just to maintain muscle tone, avoiding atrophy. Synaptic transmission at the neuromuscular junction begins when an action potential reaches the presynaptic terminal of a motor neuron, which activates voltage-dependent calcium channels to allow calcium ions to enter the neuron. Calcium ions bind to sensor proteins (synaptotagmin) on synaptic vesicles, triggering vesicle fusion with the cell membrane and subsequent neurotransmitter release from the motor neuron into the synaptic cleft. In vertebrates, motor neurons release acetylcholine (ACh), a small molecule neurotransmitter, which diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) on the cell membrane of the muscle fiber, also known as the sarcolemma. nAChRs are ionotropic receptors, meaning they serve as ligand-gated ion channels. The binding of ACh to the receptor can depolarize the muscle fiber, causing a cascade that eventually results in muscle contraction.Neuromuscular junction diseases can be of genetic and autoimmune origin. Genetic disorders, such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy, can arise from mutated structural proteins that comprise the neuromuscular junction, whereas autoimmune diseases, such as myasthenia gravis, occur when antibodies are produced against nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on the sarcolemma.