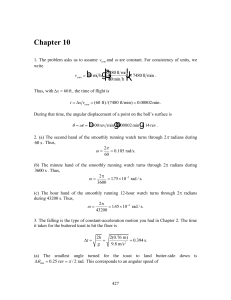
1 Definition of Physics
... The standard SI unit for length is the meter. Originally, the definition of the meter was the distance between two scratches on a length of metal. The standard length of metal was stored in a secure vault under controlled conditions of temperature, pressure, and humidity. Most countries had their ow ...
... The standard SI unit for length is the meter. Originally, the definition of the meter was the distance between two scratches on a length of metal. The standard length of metal was stored in a secure vault under controlled conditions of temperature, pressure, and humidity. Most countries had their ow ...
Optimizing OFETs properties for spintronics applications
... Résumé de thèse Cette thèse a conduit à l’étude du transport des porteurs de charge de plusieurs dispositifs afin d’identifier les propriétés spécifiques permettant la réalisation de vannes à spin organique de géométrie latérale. En effet, cette thèse a porté sur deux domaines de recherche principau ...
... Résumé de thèse Cette thèse a conduit à l’étude du transport des porteurs de charge de plusieurs dispositifs afin d’identifier les propriétés spécifiques permettant la réalisation de vannes à spin organique de géométrie latérale. En effet, cette thèse a porté sur deux domaines de recherche principau ...
Modern Physics for Science and Engineering (eval).
... mechanics are easily managed with this approach through the introduction of operator algebra and with the occasional use of one of the five definite integrals provided in Appendix A. This reduced mathematical emphasis allows students to concentrate on the more important underlying physical concepts an ...
... mechanics are easily managed with this approach through the introduction of operator algebra and with the occasional use of one of the five definite integrals provided in Appendix A. This reduced mathematical emphasis allows students to concentrate on the more important underlying physical concepts an ...
Physics 120 Lab 3: Modeling Motion of Cart on Track: no force
... will undergo oscillation and so we expect the cart to move between the left and right ends of the track. Therefore, we pick the center of the track to be the position of the mass when the spring is at its natural length. Conveniently, the center of the track is the origin, and so the amount of stret ...
... will undergo oscillation and so we expect the cart to move between the left and right ends of the track. Therefore, we pick the center of the track to be the position of the mass when the spring is at its natural length. Conveniently, the center of the track is the origin, and so the amount of stret ...
Classical Mechanics and Human Movement
... Mathematica, published in 1687, Sir Isaac Newton presented these laws in mathematical language. The laws of motion can be summarized as follows: A body in our universe is subjected to a multitude of forces exerted by other bodies. The forces exchanged between any two bodies are equal in magnitude bu ...
... Mathematica, published in 1687, Sir Isaac Newton presented these laws in mathematical language. The laws of motion can be summarized as follows: A body in our universe is subjected to a multitude of forces exerted by other bodies. The forces exchanged between any two bodies are equal in magnitude bu ...
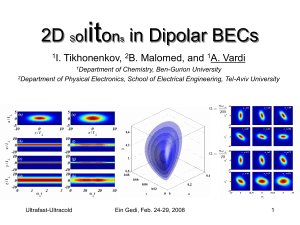
Microwave Spectroscopy of Two-Dimensional Electrons in Tilted Magnetic Field
... 174) because at low ν the energy curves of the two types of states can come so close to each other that a small error in the estimation can vastly affect the prediction. There have also been propositions (15, 16, 79, 113, 170) that correlations responsible for the FQHE’s can still be relevant for th ...
... 174) because at low ν the energy curves of the two types of states can come so close to each other that a small error in the estimation can vastly affect the prediction. There have also been propositions (15, 16, 79, 113, 170) that correlations responsible for the FQHE’s can still be relevant for th ...
Theory on the scattering of light and surface plasmon polaritons by
... The price we pay is that the modal expansion formalism is approximate and relies on the SIBCs, whereas the Green dyadic method is virtually exact. The implementation of modal expansion calculations usually faces another source of inaccuracy. The required overlaps between plane waves and waveguide mo ...
... The price we pay is that the modal expansion formalism is approximate and relies on the SIBCs, whereas the Green dyadic method is virtually exact. The implementation of modal expansion calculations usually faces another source of inaccuracy. The required overlaps between plane waves and waveguide mo ...
Second Order QED Processes in an Intense
... the program of renormalisation was developed [Tom46, Tea47, Tom48, Sch48a, Sch48b]. In this view wave functions develop from one space-like surface to another resulting in equations which are covariant at each stage of calculation. This is known as the proper time method. The second reformulation of ...
... the program of renormalisation was developed [Tom46, Tea47, Tom48, Sch48a, Sch48b]. In this view wave functions develop from one space-like surface to another resulting in equations which are covariant at each stage of calculation. This is known as the proper time method. The second reformulation of ...
Lecture 37 - USU Department of Physics
... Light from a single slit is split by passing through two slits, resulting in two light waves in phase with each other. The two waves will interfere constructively or destructively, depending on a difference in the path length. If the two waves travel equal distances to the screen, they interfere ...
... Light from a single slit is split by passing through two slits, resulting in two light waves in phase with each other. The two waves will interfere constructively or destructively, depending on a difference in the path length. If the two waves travel equal distances to the screen, they interfere ...
mechanics of material forces
... and curl^ respectively. The latter two operations are applied to a vector xL where x is the position vector. This procedure has been successfully used in elastostatics in material space (cf. [4]), leading to the pathindependent integral commonly known as J , M and L. Thus it appeared intriguing to i ...
... and curl^ respectively. The latter two operations are applied to a vector xL where x is the position vector. This procedure has been successfully used in elastostatics in material space (cf. [4]), leading to the pathindependent integral commonly known as J , M and L. Thus it appeared intriguing to i ...
Semiconductor Physics Sectional Programme Overview
... mid-infrared (MIR) QCLs, THz QCLs remain difficult to fabricate. The tolerances in alloy composition, layer thickness, and doping are lower for THz QCLs than their MIR counterparts. Processing of GaAs QC lasers at THz frequencies isin spite of the relaxed dimensions, still a demanding task. This is ...
... mid-infrared (MIR) QCLs, THz QCLs remain difficult to fabricate. The tolerances in alloy composition, layer thickness, and doping are lower for THz QCLs than their MIR counterparts. Processing of GaAs QC lasers at THz frequencies isin spite of the relaxed dimensions, still a demanding task. This is ...
General Relativistic Radiative Transfer
... important. Strong gravity modifies the observable properties of the light emitted by an object. A photon no longer travels in straight lines, and its frequency is shifted as it propagates. Gravitational lensing may make multiple images of the emitter, further modifying the temporal and spectral prop ...
... important. Strong gravity modifies the observable properties of the light emitted by an object. A photon no longer travels in straight lines, and its frequency is shifted as it propagates. Gravitational lensing may make multiple images of the emitter, further modifying the temporal and spectral prop ...
Photonic-crystal slabs with a triangular lattice of triangular holes
... in this work兲, the matrix H is complex Hermitian. Line and point defects can be treated by introducing a supercell in one or two directions, respectively, like in 2D plane-wave calculations. The formalism presented here refers to the most general case of an asymmetric PhC slab. If the structure is ...
... in this work兲, the matrix H is complex Hermitian. Line and point defects can be treated by introducing a supercell in one or two directions, respectively, like in 2D plane-wave calculations. The formalism presented here refers to the most general case of an asymmetric PhC slab. If the structure is ...