PPT
... CheckPoint The magnitude of the angular momentum of a freely rotating disk around its center is L. You toss a heavy block onto the disk along the direction shown. Friction acts between the disk and the block so that eventually the block is at rest on the disk and rotates with it. What is the magnit ...
... CheckPoint The magnitude of the angular momentum of a freely rotating disk around its center is L. You toss a heavy block onto the disk along the direction shown. Friction acts between the disk and the block so that eventually the block is at rest on the disk and rotates with it. What is the magnit ...
[2015 solutions]
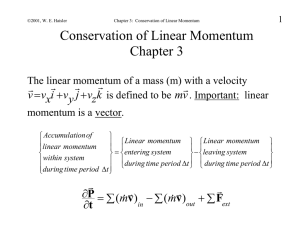
... (1) (a) Show that angular momentum is conserved by calculating Torque. (b) We have L2 mṙ2 Veff = ...
... (1) (a) Show that angular momentum is conserved by calculating Torque. (b) We have L2 mṙ2 Veff = ...
Word
... momentum moving the other direction. If the car was at perfect rest, it’s momentum would be zero, so that’s not allowed.” “Wait a minute,” Frank said, “I’m not so sure about that. Suppose you set up the spring car against the wall of the classroom. After the explosion, wouldn’t the wall still be at ...
... momentum moving the other direction. If the car was at perfect rest, it’s momentum would be zero, so that’s not allowed.” “Wait a minute,” Frank said, “I’m not so sure about that. Suppose you set up the spring car against the wall of the classroom. After the explosion, wouldn’t the wall still be at ...
Properties of electrons scattered on a strong plane electromagnetic
... packet moves along the trajectory obeying the classical equations of motion (the Lorentz equation) with the electromagnetic field representing a superposition of the external field and the field created by an electron wave packet. If the wave packet is localized enough (as we have assumed), the stan ...
... packet moves along the trajectory obeying the classical equations of motion (the Lorentz equation) with the electromagnetic field representing a superposition of the external field and the field created by an electron wave packet. If the wave packet is localized enough (as we have assumed), the stan ...
Linear Momentum
... Impulse and Bouncing • Impulses are greater when bouncing takes place. • The impulse required to bring an object to a stop and then throw it back again is greater than the impulse required to bring an object to a stop. ...
... Impulse and Bouncing • Impulses are greater when bouncing takes place. • The impulse required to bring an object to a stop and then throw it back again is greater than the impulse required to bring an object to a stop. ...
Physics Year Long Plan
... describe the difference between "physics work" and every day work describe the relationship between force, displacement and the angle at which the force is applied use the work equation to calculate work done on an object use the different equations to determine power, force, work, time, average vel ...
... describe the difference between "physics work" and every day work describe the relationship between force, displacement and the angle at which the force is applied use the work equation to calculate work done on an object use the different equations to determine power, force, work, time, average vel ...
Chapter_4_08
... Astronomy is the attempt to gather information from cosmic objects through the detection of particles (photons, leptons, hadrons, neutrinos etc.), emitted or affected by them. Astrophysics is the attempt to use our knowledge of the physical laws such as we know them on the Earth to propose theories ...
... Astronomy is the attempt to gather information from cosmic objects through the detection of particles (photons, leptons, hadrons, neutrinos etc.), emitted or affected by them. Astrophysics is the attempt to use our knowledge of the physical laws such as we know them on the Earth to propose theories ...
Red-Electrostatics Protons have what type of charge? Electrons
... Can mechanical waves travel through a vacuum? The number of cycles per time is called what? Frequency is measured in what units? The time it takes for one wave to pass a point is called what? Do waves transfer energy, matter, or both? Waves are caused by what? What type of relationship exists betwee ...
... Can mechanical waves travel through a vacuum? The number of cycles per time is called what? Frequency is measured in what units? The time it takes for one wave to pass a point is called what? Do waves transfer energy, matter, or both? Waves are caused by what? What type of relationship exists betwee ...
Coriolis force, geometric phase, and spin
... momentum of a particle. Mediated by a spin-orbit coupling in the valence band, this perturbation leads to spin rotation that may affect the coherent transport properties of a charge carrier and cause a spin precession in zero magnetic fields. These effects may be also interpreted as a manifestation ...
... momentum of a particle. Mediated by a spin-orbit coupling in the valence band, this perturbation leads to spin rotation that may affect the coherent transport properties of a charge carrier and cause a spin precession in zero magnetic fields. These effects may be also interpreted as a manifestation ...
Vocabulary Quiz Exam 1 - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... We can reason either of two ways at this point: Either momentum is not conserved at high speeds or mass is not conserved. Conservation of momentum follows from position symmetry (Noether’s theorem). This makes it very solid. Mass, as it turns out, is not conserved by itself. Instead it is conserve ...
... We can reason either of two ways at this point: Either momentum is not conserved at high speeds or mass is not conserved. Conservation of momentum follows from position symmetry (Noether’s theorem). This makes it very solid. Mass, as it turns out, is not conserved by itself. Instead it is conserve ...








![[2015 solutions]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008881821_1-1b74810f90a341f17acc5dd8ebcca870-300x300.png)













