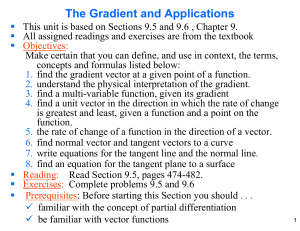
Kinesiology 201 Solutions Kinetics
... the wheel to the whole system. Another way of saying this is that a torque impulse is applied to the wheel to stop it rotating about its longitudinal axis. It therefore exerts an equal and opposite torque impulse on the subject and hence the whole system (the subject, the wheel and the top plate of ...
... the wheel to the whole system. Another way of saying this is that a torque impulse is applied to the wheel to stop it rotating about its longitudinal axis. It therefore exerts an equal and opposite torque impulse on the subject and hence the whole system (the subject, the wheel and the top plate of ...
Spin Hall Magnetoresistance Induced by a Nonequilibrium Proximity Effect
... plane. This additional electric current due to the combination of SHE and ISHE is always parallel to the original one; electric currents measured in a thin film with spin-orbit interaction inevitably include this additional contribution. We may now control this process by putting an electrically ins ...
... plane. This additional electric current due to the combination of SHE and ISHE is always parallel to the original one; electric currents measured in a thin film with spin-orbit interaction inevitably include this additional contribution. We may now control this process by putting an electrically ins ...
Momentum - eduBuzz.org
... Explosions and Newton’s third law Explosions Explosions are treated in the same way as collisions, in that total momentum is conserved. For example, in the case of a bullet being fired from a gun, the total momentum before firing is zero, since nothing is moving. After firing, the bullet has momentu ...
... Explosions and Newton’s third law Explosions Explosions are treated in the same way as collisions, in that total momentum is conserved. For example, in the case of a bullet being fired from a gun, the total momentum before firing is zero, since nothing is moving. After firing, the bullet has momentu ...
File
... a) In relation to a sprinter describe what is meant by the term impulse and how it can be shown on a force time graph. (4 marks) b) Draw and label a force – time graph to show the impulse of an accelerating sprinter. (3 marks) a) • An impulse (force x time) is a force acting over a period of time. ...
... a) In relation to a sprinter describe what is meant by the term impulse and how it can be shown on a force time graph. (4 marks) b) Draw and label a force – time graph to show the impulse of an accelerating sprinter. (3 marks) a) • An impulse (force x time) is a force acting over a period of time. ...
09._SystemsOfParticles
... Example 9.6. Fighting a Fire A firefighter directs a stream of water to break the window of a burning building. The hose delivers water at a rate of 45 kg/s, hitting the window horizontally at 32 m/s. After hitting the window, the water drops horizontally. What horizontal force does the water exert ...
... Example 9.6. Fighting a Fire A firefighter directs a stream of water to break the window of a burning building. The hose delivers water at a rate of 45 kg/s, hitting the window horizontally at 32 m/s. After hitting the window, the water drops horizontally. What horizontal force does the water exert ...
Momentum Class Notes - Hicksville Public Schools
... station at 2 m/s. How fast must he throw his wrench so that he can stop floating away? ...
... station at 2 m/s. How fast must he throw his wrench so that he can stop floating away? ...
THE FIELD OF A STEP–LIKE ACCELERATED POINT CHARGE
... and similarly for Jz (x, κy , κz , ω) = vq(x, κy , κz , ω). After the substitution into (65) and integration with respect to x′ and κz one obtains for temporal frequency spectra Φ(r, ω) and Az (r, ω) the formula ...
... and similarly for Jz (x, κy , κz , ω) = vq(x, κy , κz , ω). After the substitution into (65) and integration with respect to x′ and κz one obtains for temporal frequency spectra Φ(r, ω) and Az (r, ω) the formula ...
Rotational Motion
... of one side. On what side of the bread will the toast land if it falls from a table 0.5 m high? If it falls from a table 1.0 m high? Assume l = 0.10 m, and ignore air resistance. When a turntable rotating at 33 rev/min is turned off, it comes to rest in 26 s. Assuming constant angular acceleration ...
... of one side. On what side of the bread will the toast land if it falls from a table 0.5 m high? If it falls from a table 1.0 m high? Assume l = 0.10 m, and ignore air resistance. When a turntable rotating at 33 rev/min is turned off, it comes to rest in 26 s. Assuming constant angular acceleration ...
2. Energy loss in Matter
... We will first concentrate on electromagnetic forces since a combination of their strength and range make them the primary responsible for energy loss in matter. For neutrons, hadrons generally and neutrinos strong and weak interactions enter in addition. 2.1 Heavy charged particles Heavy charged par ...
... We will first concentrate on electromagnetic forces since a combination of their strength and range make them the primary responsible for energy loss in matter. For neutrons, hadrons generally and neutrinos strong and weak interactions enter in addition. 2.1 Heavy charged particles Heavy charged par ...
Tesla Healing Technology - Breakthru
... Advances in quantum mechanics and the seemingly unrelated field of radio astronomy began to remove some of the conceptual barriers that impeded understanding and acceptance of earlier electrotherapeutic discoveries. In one account of new insights from these advances it was declared that: “Each human ...
... Advances in quantum mechanics and the seemingly unrelated field of radio astronomy began to remove some of the conceptual barriers that impeded understanding and acceptance of earlier electrotherapeutic discoveries. In one account of new insights from these advances it was declared that: “Each human ...
Gravity-centripetal acceleration
... The force that brings about this acceleration is called the centripetal force. Its direction is also towards the center of the circular path. Centripetal means "center seeking". The centripetal force changes the direction of the object’s velocity vector. Without it, there would be no circular path. ...
... The force that brings about this acceleration is called the centripetal force. Its direction is also towards the center of the circular path. Centripetal means "center seeking". The centripetal force changes the direction of the object’s velocity vector. Without it, there would be no circular path. ...
Laser cooling and trapping of neutral atoms 1 - ENS-phys
... For the simple case of an atom in a plane running wave, the dissipative force corresponds to the usual radiation pressure; it is due to the absorption of one laser photon of momentum tifL and the spontaneous emission of one fluorescence photon of momentum tiks. The corresponding average change in at ...
... For the simple case of an atom in a plane running wave, the dissipative force corresponds to the usual radiation pressure; it is due to the absorption of one laser photon of momentum tifL and the spontaneous emission of one fluorescence photon of momentum tiks. The corresponding average change in at ...