https://www
... Now answer the following questions 1 THROUGH 8 on the next page below b) watch these selected SEGMENTS from the following video: Time 0:00 through 5:20 (stop at Parallel circuits). Then begin at 6:35 to 7:15. Then end with 7:35 to the end. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D2monVkCkX4&list=PL3A1792F78 ...
... Now answer the following questions 1 THROUGH 8 on the next page below b) watch these selected SEGMENTS from the following video: Time 0:00 through 5:20 (stop at Parallel circuits). Then begin at 6:35 to 7:15. Then end with 7:35 to the end. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D2monVkCkX4&list=PL3A1792F78 ...
Word
... them individually, which is also half that of globe C. Hence the resistance of this arm is 3/2 times that of a single globe. Globe C will have a potential difference of 2/3 of the voltage V, and D and E will each have 1/3 V. Brightness increases with power which goes like the V2, so we can rank the ...
... them individually, which is also half that of globe C. Hence the resistance of this arm is 3/2 times that of a single globe. Globe C will have a potential difference of 2/3 of the voltage V, and D and E will each have 1/3 V. Brightness increases with power which goes like the V2, so we can rank the ...
Series Circuits
... In a series circuit, the voltage across the resistive elements will divide as the magnitude of the resistance levels. It is the ratio of resistor values that counts when it comes to voltage division. Current levels will be affected. This rule permits determining the voltage levels without first find ...
... In a series circuit, the voltage across the resistive elements will divide as the magnitude of the resistance levels. It is the ratio of resistor values that counts when it comes to voltage division. Current levels will be affected. This rule permits determining the voltage levels without first find ...
ZXCT1010 ENHANCED HIGH-SIDE CURRENT MONITOR
... The product specifications contained in this publication are issued to provide outline information only which (unless agreed by the company in writing) may not be used, applied or reproduced for any purpose or form part of any order or contract or be regarded as a representation relating to the prod ...
... The product specifications contained in this publication are issued to provide outline information only which (unless agreed by the company in writing) may not be used, applied or reproduced for any purpose or form part of any order or contract or be regarded as a representation relating to the prod ...
Direction of current flow What is DC?
... magnet, electricity is produced • http://www.wvic.com/how-gen-works.htm • this electricity is AC • the voltage depends on how much wire the coil has and how fast it is rotated. • devices called transformers can make the voltage bigger or smaller • transformers only work with AC Í ...
... magnet, electricity is produced • http://www.wvic.com/how-gen-works.htm • this electricity is AC • the voltage depends on how much wire the coil has and how fast it is rotated. • devices called transformers can make the voltage bigger or smaller • transformers only work with AC Í ...
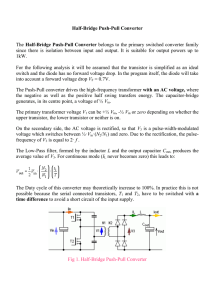
Half-Bridge Push
... The Duty cycle of this converter may theoretically increase to 100%. In practice this is not possible because the serial connected transistors, T1 and T2, have to be switched with a time difference to avoid a short circuit of the input supply. ...
... The Duty cycle of this converter may theoretically increase to 100%. In practice this is not possible because the serial connected transistors, T1 and T2, have to be switched with a time difference to avoid a short circuit of the input supply. ...
TP_101.01_Short Circuit impedance with Midas_1110
... If the transformer has a neutral on the HV-side (Yn on HV-side), do not connect any cables to the neutral, connect between the phases. Measurements between Phase and neutral are also possible, however a different formula has to be applied in order to derive the correct (%) short-circuit impedance. I ...
... If the transformer has a neutral on the HV-side (Yn on HV-side), do not connect any cables to the neutral, connect between the phases. Measurements between Phase and neutral are also possible, however a different formula has to be applied in order to derive the correct (%) short-circuit impedance. I ...
Kirchhoff`s junction law.
... 100 times more than copper). Because of this, the wires heat up and toast your bread. Resistors are used in circuits like the one below to control the amount of current and the voltages in a circuit. ...
... 100 times more than copper). Because of this, the wires heat up and toast your bread. Resistors are used in circuits like the one below to control the amount of current and the voltages in a circuit. ...
Appendix S1 Circuit with Improved Hill Function We present a
... The assumption that the output of op-amp U2 is saturated at V-sat when Vi-1 = 0 (no inhibition) means that G1G-2Vcth > 3.5 V. Using the relations between Vcth and Vth, between Vth and α, and between G1G-2 and nα, we find the restriction on the Hill coefficient n > 2.35(-V-sat − 1)/(imaxR) = 2.35(3.5 ...
... The assumption that the output of op-amp U2 is saturated at V-sat when Vi-1 = 0 (no inhibition) means that G1G-2Vcth > 3.5 V. Using the relations between Vcth and Vth, between Vth and α, and between G1G-2 and nα, we find the restriction on the Hill coefficient n > 2.35(-V-sat − 1)/(imaxR) = 2.35(3.5 ...
Word
... Part I: Voltage (V) Current (I), Resistance (R) and meters, Part A: A circuit is connected at your work table. It consists of a battery, a light bulb connected to two meters. Connect the voltage supply to the light bulb by closing the switch and record the meter readings in volts and amperes. Voltag ...
... Part I: Voltage (V) Current (I), Resistance (R) and meters, Part A: A circuit is connected at your work table. It consists of a battery, a light bulb connected to two meters. Connect the voltage supply to the light bulb by closing the switch and record the meter readings in volts and amperes. Voltag ...
TAP 117- 3: Verifying Kirchhoff`s Laws
... You should be able to find some connections between these values. What are they and why are they connected like this? Your explanation should involve the way charge flows in the circuit. (d) ...
... You should be able to find some connections between these values. What are they and why are they connected like this? Your explanation should involve the way charge flows in the circuit. (d) ...
M IN Overview:
... control the air conditioner units through low voltage signals. (1) In the Service Type Window, Mini-PCS automatically detects and displays the type of Power the RV is connected to. When "30A" is illuminated, the owner can press the (3) "Select" button and toggle between 30A and 20A service. (2) The ...
... control the air conditioner units through low voltage signals. (1) In the Service Type Window, Mini-PCS automatically detects and displays the type of Power the RV is connected to. When "30A" is illuminated, the owner can press the (3) "Select" button and toggle between 30A and 20A service. (2) The ...
Robust High Voltage Over-The-Top Op Amps Maintain High Input
... input voltages and over temperature. Input Topology—Theory of Operation An Over-The-Top input stage is shown in Figure 1. At low common modes, the PNPs Q1 and Q2 form a conventional precision differential pair with tail current provided by I1. The diff pair forwards its collector currents into the f ...
... input voltages and over temperature. Input Topology—Theory of Operation An Over-The-Top input stage is shown in Figure 1. At low common modes, the PNPs Q1 and Q2 form a conventional precision differential pair with tail current provided by I1. The diff pair forwards its collector currents into the f ...
A. Use of current limited power supply (Topward TPS
... Experiment: Use a circuit similar to example D above to measure the input impedance of the multimeter. Adjust R1 until the measured voltage is half of the supply voltage. If the voltage drop is the same then they have to have the same impedance (i.e. the meter input impedance is the same as R1). Err ...
... Experiment: Use a circuit similar to example D above to measure the input impedance of the multimeter. Adjust R1 until the measured voltage is half of the supply voltage. If the voltage drop is the same then they have to have the same impedance (i.e. the meter input impedance is the same as R1). Err ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.