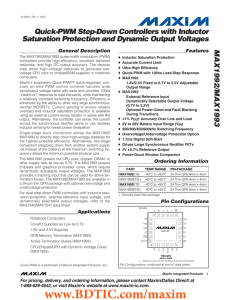
OPA3684 Low-Power, Triple Current-Feedback OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER With Disable FEATURES
... headroom requirement is complemented by a similar 1.2V input stage headroom giving exceptional capability for single +5V operation. The OPA3684’s low 1.7mA/ch supply current is precisely trimmed at 25°C. This trim, along with low shift over temperature and supply voltage, gives a very robust design ...
... headroom requirement is complemented by a similar 1.2V input stage headroom giving exceptional capability for single +5V operation. The OPA3684’s low 1.7mA/ch supply current is precisely trimmed at 25°C. This trim, along with low shift over temperature and supply voltage, gives a very robust design ...
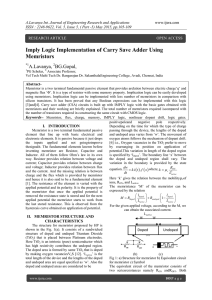
MAX1992/MAX1993 Quick-PWM Step-Down Controllers with Inductor Saturation Protection and Dynamic Output Voltages
... V+ to AGND............................................................-0.3V to +30V VCC to AGND............................................................-0.3V to +6V VDD to PGND............................................................-0.3V to +6V PGOOD, ILIM, SKIP, SHDN to AGND ................ ...
... V+ to AGND............................................................-0.3V to +30V VCC to AGND............................................................-0.3V to +6V VDD to PGND............................................................-0.3V to +6V PGOOD, ILIM, SKIP, SHDN to AGND ................ ...
Leakage Current Reduction in CMOS VLSI Circuits by Input Vector
... ways to do this, but in all of them some process technology modification is necessary. However, this may not be always possible. Another approach is to use high-threshold voltage devices on non-critical paths so as to reduce the leakage power while using low-threshold devices on critical paths so th ...
... ways to do this, but in all of them some process technology modification is necessary. However, this may not be always possible. Another approach is to use high-threshold voltage devices on non-critical paths so as to reduce the leakage power while using low-threshold devices on critical paths so th ...
+ R - Purdue Physics
... An ammeter must be inserted into the circuit in series with the circuit element whose current you want to measure. An ammeter must have a very small resistance, so as not to alter significantly the circuit in which it has been inserted. ...
... An ammeter must be inserted into the circuit in series with the circuit element whose current you want to measure. An ammeter must have a very small resistance, so as not to alter significantly the circuit in which it has been inserted. ...
Chapter 4. Switch Realization
... A majority-carrier device: fast switching speed Typical switching frequencies: tens and hundreds of kHz On-resistance increases rapidly with rated blocking voltage Easy to drive The device of choice for blocking voltages less than 500V 1000V devices are available, but are useful only at low power le ...
... A majority-carrier device: fast switching speed Typical switching frequencies: tens and hundreds of kHz On-resistance increases rapidly with rated blocking voltage Easy to drive The device of choice for blocking voltages less than 500V 1000V devices are available, but are useful only at low power le ...
LOW-DISTORTION, HIGH-SPEED, RAIL-TO-RAIL OUTPUT OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS THS4221, THS4225 THS4222, THS4226
... maximum conditions for extended periods may degrade device reliability. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those specified is not implied. (2) The maximum junction temperature for continuous operation is limited by package co ...
... maximum conditions for extended periods may degrade device reliability. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those specified is not implied. (2) The maximum junction temperature for continuous operation is limited by package co ...
Atmel LED Drivers MSL2160/MSL2161
... For video applications, the PWM LED drive signals synchronize to the LCD’s video frame timing via the PHI input, and to the LCD’s pixel timing via the GSC input. This synchronization eliminates beating artifacts. Suitability for LED backlight architectures is shown in Table 1. Area LED dimming for d ...
... For video applications, the PWM LED drive signals synchronize to the LCD’s video frame timing via the PHI input, and to the LCD’s pixel timing via the GSC input. This synchronization eliminates beating artifacts. Suitability for LED backlight architectures is shown in Table 1. Area LED dimming for d ...
AD5282 数据手册DataSheet下载
... positions. R-DNL measures the relative step change from ideal between successive tap positions. Parts are guaranteed monotonic. ...
... positions. R-DNL measures the relative step change from ideal between successive tap positions. Parts are guaranteed monotonic. ...
leakage power analysis and reduction for nanoscale circuits
... changing Vth to reduce leakFigure 5. A dual Vth CMOS circuit (a), and a path distribution of dual Vth and single Vth CMOS (b). age when maximum performance is not needed. In active mode, the operating temperature same critical delay as the single low-Vth increases because of the transistors’ switchi ...
... changing Vth to reduce leakFigure 5. A dual Vth CMOS circuit (a), and a path distribution of dual Vth and single Vth CMOS (b). age when maximum performance is not needed. In active mode, the operating temperature same critical delay as the single low-Vth increases because of the transistors’ switchi ...
LT3090 – 36V, 600mA Negative Linear
... current or spread heat on surface mounted boards. Designed with a precision current reference followed by a high performance rail-to-rail voltage buffer, this regulator finds use in applications requiring precision output, high current with no heat sink, output adjustability to zero and low dropout ...
... current or spread heat on surface mounted boards. Designed with a precision current reference followed by a high performance rail-to-rail voltage buffer, this regulator finds use in applications requiring precision output, high current with no heat sink, output adjustability to zero and low dropout ...
DAC161S997 16-bit SPI Programmable DAC for 4
... analog output current over an industry standard 4-20 mA current loop. The DAC161S997 has a simple 4wire SPI for data transfer and configuration of the DAC functions. To reduce power and component count in compact loop-powered applications, the DAC161S997 contains an internal ultra-low power voltage ...
... analog output current over an industry standard 4-20 mA current loop. The DAC161S997 has a simple 4wire SPI for data transfer and configuration of the DAC functions. To reduce power and component count in compact loop-powered applications, the DAC161S997 contains an internal ultra-low power voltage ...
DESIGN, MODELLING AND SIMULATION OF A FUEL CELL
... converter consists of two traditional boost converters interleaved together; as a result its steady state equations are similar to the steady state equations of the traditional boost converter. L2 ...
... converter consists of two traditional boost converters interleaved together; as a result its steady state equations are similar to the steady state equations of the traditional boost converter. L2 ...
TLV431 Description Pin Assignments
... In a conventional shunt regulator application (Figure 1), an external series resistor (R3) is connected between the supply voltage, VIN, and the TLV431. R3 determines the current that flows through the load (IL) and the TLV431 (IK). The TLV431 will adjust how much current it sinks or “shunts” to mai ...
... In a conventional shunt regulator application (Figure 1), an external series resistor (R3) is connected between the supply voltage, VIN, and the TLV431. R3 determines the current that flows through the load (IL) and the TLV431 (IK). The TLV431 will adjust how much current it sinks or “shunts” to mai ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.