template - TeacherWeb
... This is much greater than the ¼IV from before. The power for B is 1/3I(1/3V) or 1/9IV. As can be seen, the power for A is 4 times that for B and that the power for B has decreased greatly from when the switch was open. ...
... This is much greater than the ¼IV from before. The power for B is 1/3I(1/3V) or 1/9IV. As can be seen, the power for A is 4 times that for B and that the power for B has decreased greatly from when the switch was open. ...
Today’s Topics - Department of Electrical Engineering
... In power systems there are so many different elements such as Motors, Generators and Transformers with very different sizes and nominal values. To be able to compare the performances of a big and a small element, per unit system is used. In per unit system, each electric quantity is measured as a de ...
... In power systems there are so many different elements such as Motors, Generators and Transformers with very different sizes and nominal values. To be able to compare the performances of a big and a small element, per unit system is used. In per unit system, each electric quantity is measured as a de ...
review copy not for distribution - Iramis
... junction oscillates periodically at the Bloch frequency fB = I/2e [1]. Such an experiment, which would provide a direct link between time and current units, would be of fundamental interest for electrical metrology. However, current-biasing a junction over a large frequency range by embedding it in ...
... junction oscillates periodically at the Bloch frequency fB = I/2e [1]. Such an experiment, which would provide a direct link between time and current units, would be of fundamental interest for electrical metrology. However, current-biasing a junction over a large frequency range by embedding it in ...
Link - thephysicsteacher.ie
... low). You will probably find that this reading is about 0.2 ohms above the other readings. This is because the multimeter is also taking into account the resistance of the electrical leads. Can you figure out how to correct for this? Notes 1. It may be helpful to throw out the very first reading; t ...
... low). You will probably find that this reading is about 0.2 ohms above the other readings. This is because the multimeter is also taking into account the resistance of the electrical leads. Can you figure out how to correct for this? Notes 1. It may be helpful to throw out the very first reading; t ...
File
... Circuit – a complete path from the high to low potential which includes a load between the two potentials If there’s no load - only direct connection from high to low - then it’s called a short (circuit) – dangerous… If there’s a switch: open = no flow; closed = flow There are only “one way st ...
... Circuit – a complete path from the high to low potential which includes a load between the two potentials If there’s no load - only direct connection from high to low - then it’s called a short (circuit) – dangerous… If there’s a switch: open = no flow; closed = flow There are only “one way st ...
SW60 Single Pole Single Throw Normally Open (Part of
... The SW60 is a miniature series single pole contactor - free standing and compact it is designed to fill the gap between 30 ampere relays and 100 ampere contactors. Devised for both interrupted and uninterrupted loads, the SW60 is suitable for switching Resistive, Capacitive and Inductive loads. Typi ...
... The SW60 is a miniature series single pole contactor - free standing and compact it is designed to fill the gap between 30 ampere relays and 100 ampere contactors. Devised for both interrupted and uninterrupted loads, the SW60 is suitable for switching Resistive, Capacitive and Inductive loads. Typi ...
01 EXPERIMENT 02 SCR PHASE CONTROL Objective 1
... There are many forms of phase control possible with the thyristor, as shown in Fig. 8-1. The simplest form is the half-wave control of Fig. 8-1(a) which uses one SCR for control of current flow in one direction only. This circuit is used for loads which require power control from zero to one-half of ...
... There are many forms of phase control possible with the thyristor, as shown in Fig. 8-1. The simplest form is the half-wave control of Fig. 8-1(a) which uses one SCR for control of current flow in one direction only. This circuit is used for loads which require power control from zero to one-half of ...
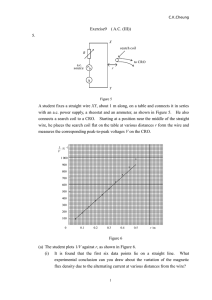
Exercise 9 Revision on A.C(III)
... screen was only 20 mV. Hence, estimate the value of the other C.R.O. input component [(1) or (2)], briefly explaining your reasoning. (9 marks) 83 IIB ...
... screen was only 20 mV. Hence, estimate the value of the other C.R.O. input component [(1) or (2)], briefly explaining your reasoning. (9 marks) 83 IIB ...
P21 Homework Set #7
... Assess: Using reactance is just like using resistance in Ohm’s law. This, however, does not apply to instantaneous values of current and voltage. ...
... Assess: Using reactance is just like using resistance in Ohm’s law. This, however, does not apply to instantaneous values of current and voltage. ...
EUP3010/A 1.5MHz,1A Synchronous Step-Down Converter with Soft Start
... the power transferred to the load each cycle using PWM comparator. The duty cycle is controlled by three weighted differential signals: the output of error amplifier, the main switch sense voltage and the slope-compensation ramp. It modulates output power by adjusting the inductor-peak current durin ...
... the power transferred to the load each cycle using PWM comparator. The duty cycle is controlled by three weighted differential signals: the output of error amplifier, the main switch sense voltage and the slope-compensation ramp. It modulates output power by adjusting the inductor-peak current durin ...
Probing Transistors at the Contact Level in Integrated Circuits
... An SEM/FIB is typically optimized for low mechanical and electrical noise, which is necessary to achieve sub-nanometer resolution images. Ambient conditions which commonly affect AFM systems, such as thermal fluctuations and air drafts, are thus eliminated by the controlled environment of the SEM or ...
... An SEM/FIB is typically optimized for low mechanical and electrical noise, which is necessary to achieve sub-nanometer resolution images. Ambient conditions which commonly affect AFM systems, such as thermal fluctuations and air drafts, are thus eliminated by the controlled environment of the SEM or ...
Electrical Measurements and Instruments
... bulb filament. 6. Compare your result in (5) with your measurement in (3). Are they the same? If not, can ...
... bulb filament. 6. Compare your result in (5) with your measurement in (3). Are they the same? If not, can ...
ECE 201 Exam #2 Review
... analysis methodology, but allows scaling of current/voltage values • Leads to superposition: “In any linear circuit containing multiple independent sources, the current or voltage at any point in the circuit may be calculated as the algebraic sum of the individual contributions of each source acting ...
... analysis methodology, but allows scaling of current/voltage values • Leads to superposition: “In any linear circuit containing multiple independent sources, the current or voltage at any point in the circuit may be calculated as the algebraic sum of the individual contributions of each source acting ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.