Resistance and Ohm`s Law
... since water plays a role of conductor. Therefore, if you grab the probes of multimeter, you can find out your resistance change. For the application, if you know your volume and weight, you could calculate your muscle or ...
... since water plays a role of conductor. Therefore, if you grab the probes of multimeter, you can find out your resistance change. For the application, if you know your volume and weight, you could calculate your muscle or ...
Experiment IV: Magnetic Fields and Inductance
... Conservation of energy, and Kirchhoff’s Laws, require that VIN = VL + VR. For the resistor, Ohm’s Law allows us to make the substitution VR = IR . Using the definition of inductance we can write and thus come up with a first-order differential equation that describes the current in the circuit as a ...
... Conservation of energy, and Kirchhoff’s Laws, require that VIN = VL + VR. For the resistor, Ohm’s Law allows us to make the substitution VR = IR . Using the definition of inductance we can write and thus come up with a first-order differential equation that describes the current in the circuit as a ...
Document
... An induced current’s magnetic field opposes the original change in flux • Always tries to keep magnetic field inside loop constant. • Use right-hand rule to predict direction of current. ...
... An induced current’s magnetic field opposes the original change in flux • Always tries to keep magnetic field inside loop constant. • Use right-hand rule to predict direction of current. ...
I - אתר מורי הפיזיקה
... V a. How is the total resistance related to the individual resistances? Explain what you think is happening. b. Look up the mathematical relationship for finding total resistance in a parallel circuit. Show that your data fits the equation. c. Imagine you and your friends are running in the neighbor ...
... V a. How is the total resistance related to the individual resistances? Explain what you think is happening. b. Look up the mathematical relationship for finding total resistance in a parallel circuit. Show that your data fits the equation. c. Imagine you and your friends are running in the neighbor ...
Transistor TIP120 - Mechanical Engineering
... Like the single transistors, there are physical limits for the Darlington pair. The collector characteristic has three important regions: the cutoff region, the active linear region, the saturation region. The cutoff region is the region in which the collector and base currents are oppose each other ...
... Like the single transistors, there are physical limits for the Darlington pair. The collector characteristic has three important regions: the cutoff region, the active linear region, the saturation region. The cutoff region is the region in which the collector and base currents are oppose each other ...
There are several ways to save electricity at
... Voltage (V) It is the force that causes the electrons to move in an electrical circuit. Just as water needs some pressure to force it through a pipe, electrical current needs some force to make it flow. Voltage is typically supplied by either a generator or a battery. Voltage is measured in Volts ...
... Voltage (V) It is the force that causes the electrons to move in an electrical circuit. Just as water needs some pressure to force it through a pipe, electrical current needs some force to make it flow. Voltage is typically supplied by either a generator or a battery. Voltage is measured in Volts ...
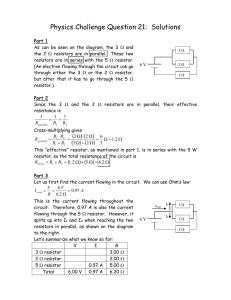
Physics Challenge Question 1: Solutions
... since the 3 and the 2 resistors are in parallel with each other, they both have the same potential difference. Vseries V1 V2 V2 Vseries V1 6.00 V 4.84 V 1.16 V Now that we know the voltage over the two remaining resistors, we can use Ohm’s law to find the current through each ...
... since the 3 and the 2 resistors are in parallel with each other, they both have the same potential difference. Vseries V1 V2 V2 Vseries V1 6.00 V 4.84 V 1.16 V Now that we know the voltage over the two remaining resistors, we can use Ohm’s law to find the current through each ...
Methods of Analysis and Selected Topics (dc)
... A node is defined as a junction of two or more branches. If we now define one node of any network as a reference (that is, a point of zero potential or ground), the remaining nodes of the network will all have a fixed potential relative to this reference. For a network of N nodes, therefore, there w ...
... A node is defined as a junction of two or more branches. If we now define one node of any network as a reference (that is, a point of zero potential or ground), the remaining nodes of the network will all have a fixed potential relative to this reference. For a network of N nodes, therefore, there w ...
Passive-Optical Person Detector
... millivolts, essentially independent of the absolute level at which this relative change occurs. ...
... millivolts, essentially independent of the absolute level at which this relative change occurs. ...
1./ RANGE OF APPLICATIONS: 2./ BUILD, INSTALLATION and
... solid; as for their material: metal and non metal: plastic, glass, wood, water, organic, dry feed, processed materials, etc. The proximity switch can differentiate between liquids based on their pollution or quality. (It will be suitable for separating oil, water or oily water, for instance → see wa ...
... solid; as for their material: metal and non metal: plastic, glass, wood, water, organic, dry feed, processed materials, etc. The proximity switch can differentiate between liquids based on their pollution or quality. (It will be suitable for separating oil, water or oily water, for instance → see wa ...
ENT161LAB3 - UniMAP Portal
... The sum of the currents through each path is equal to the total current that flows from the source. If one path is drawing 1 amp and the other is drawing 1 amp then the total is 2 amps at the source. If there are 4 branches in this same 2 amp circuit, then one path may draw 1/4A (.25A), the next 1/4 ...
... The sum of the currents through each path is equal to the total current that flows from the source. If one path is drawing 1 amp and the other is drawing 1 amp then the total is 2 amps at the source. If there are 4 branches in this same 2 amp circuit, then one path may draw 1/4A (.25A), the next 1/4 ...
RT9302 - Richtek
... to 5.5V. An input capacitor at the VIN pin could reduce ripple voltage. It is recommended to use a ceramic 1μF or larger capacitance as the input capacitor. This IC provides an under voltage lockout (UVLO) function to prevent it from unstable issue when startup. The UVLO threshold of input falling v ...
... to 5.5V. An input capacitor at the VIN pin could reduce ripple voltage. It is recommended to use a ceramic 1μF or larger capacitance as the input capacitor. This IC provides an under voltage lockout (UVLO) function to prevent it from unstable issue when startup. The UVLO threshold of input falling v ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.