DB4301594597
... huge mobile applications on a single device for long in Fig (1.1). period also a reason to reduce power consumption of The basic Dual Mode Logic (DML) gate the devices. In VLSI designs power, speed and area architecture is composed of a standard CMOS gate are the most often used measures for determi ...
... huge mobile applications on a single device for long in Fig (1.1). period also a reason to reduce power consumption of The basic Dual Mode Logic (DML) gate the devices. In VLSI designs power, speed and area architecture is composed of a standard CMOS gate are the most often used measures for determi ...
Design_Considerations_for_High_Step
... losses. But for practical applications, efficiency measurements can provide better indications, when comparing one fet as compared to another. One of the main drawback of using conventional model is that it does not take into account the effect of source and drain inductances. These are package rela ...
... losses. But for practical applications, efficiency measurements can provide better indications, when comparing one fet as compared to another. One of the main drawback of using conventional model is that it does not take into account the effect of source and drain inductances. These are package rela ...
Building virtual circuit worksheet
... Run the circuit. What is the ammeter reading for that part of the circuit? ___________ amps Shift the ammeter to the other side of the circuit. Run the circuit. What is the ammeter reading for that part of the circuit? ___________ amps Has the lamp affected how fast the electrons move? ...
... Run the circuit. What is the ammeter reading for that part of the circuit? ___________ amps Shift the ammeter to the other side of the circuit. Run the circuit. What is the ammeter reading for that part of the circuit? ___________ amps Has the lamp affected how fast the electrons move? ...
Objective : Equipments Needed : Theory
... will increase I. This increase in I will be absorbed by the Zener diode without affecting IL. This increase in Vin will be dropped across R thereby keeping Vout constant. Conversely, if supply voltage Vin falls, the diode takes a smaller current and voltagedrop across R is reduced, thus again keepin ...
... will increase I. This increase in I will be absorbed by the Zener diode without affecting IL. This increase in Vin will be dropped across R thereby keeping Vout constant. Conversely, if supply voltage Vin falls, the diode takes a smaller current and voltagedrop across R is reduced, thus again keepin ...
ZXGD3112N7 Description Applications Features Mechanical Data
... Diodes Incorporated products are specifically not authorized for use as critical components in life support devices or systems without the express written approval of the Chief Executive Officer of Diodes Incorporated. As used herein: A. Life support devices or systems are devices or systems which: ...
... Diodes Incorporated products are specifically not authorized for use as critical components in life support devices or systems without the express written approval of the Chief Executive Officer of Diodes Incorporated. As used herein: A. Life support devices or systems are devices or systems which: ...
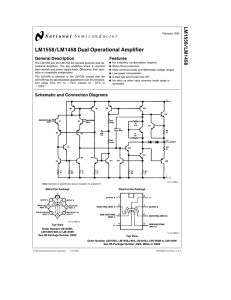
LM1558/LM1458 Dual Operational Amplifier
... bias network and power supply leads. Otherwise, their operation is completely independent. The LM1458 is identical to the LM1558 except that the LM1458 has its specifications guaranteed over the temperature range from 0§ C to a 70§ C instead of b55§ C to a 125§ C. ...
... bias network and power supply leads. Otherwise, their operation is completely independent. The LM1458 is identical to the LM1558 except that the LM1458 has its specifications guaranteed over the temperature range from 0§ C to a 70§ C instead of b55§ C to a 125§ C. ...
Topic 4: Digital Circuits
... • For each logic IC place a small capacitor (0.01uF tp 0.1uF) across Vcc and ground in close proximity to the IC • Reduces transient effect of switching on power supply, particularly when supply source is connected via long circuit path (resistive and inductive effects). Essentially each capacitor p ...
... • For each logic IC place a small capacitor (0.01uF tp 0.1uF) across Vcc and ground in close proximity to the IC • Reduces transient effect of switching on power supply, particularly when supply source is connected via long circuit path (resistive and inductive effects). Essentially each capacitor p ...
6C33C-B (RU) – 6S33S-V
... - data of actual valves may deviate because of manufacturing tolerances, ageing, transport damage or unannounced variations in product specification or execution by the manufacturer(s). The author does not accept any responsibility and/or liability for damage or injury inflicted on any party based o ...
... - data of actual valves may deviate because of manufacturing tolerances, ageing, transport damage or unannounced variations in product specification or execution by the manufacturer(s). The author does not accept any responsibility and/or liability for damage or injury inflicted on any party based o ...
Lab 2: Circuit Simulation - Electrical and Computer Engineering
... 8. Place the source on your schematic page by left-clicking on the spot that you want to place it. To stop placing sources, right click and select End Mode. Parts can be moved by simply highlighting and dragging. 9. Now type R into the ‘Place Part’ window to start putting down resistors. Another way ...
... 8. Place the source on your schematic page by left-clicking on the spot that you want to place it. To stop placing sources, right click and select End Mode. Parts can be moved by simply highlighting and dragging. 9. Now type R into the ‘Place Part’ window to start putting down resistors. Another way ...
Notes
... We also know that in the above case we have two paths for the current to pass through and that the current will divide between the two paths. The current will not necessarily divide in half. The division of the current depends on the resistance of the resistor. The biggest part of the current will m ...
... We also know that in the above case we have two paths for the current to pass through and that the current will divide between the two paths. The current will not necessarily divide in half. The division of the current depends on the resistance of the resistor. The biggest part of the current will m ...
resistance questions
... You have only 4 resistors. Design a combination circuit that has a total resistance of 10 . You have only 3 resistors. Design a combination circuit that has a total resistance of 2 . You have only 5 resistors. Design a combination circuit that has a total resistance of 11.25 . You have resi ...
... You have only 4 resistors. Design a combination circuit that has a total resistance of 10 . You have only 3 resistors. Design a combination circuit that has a total resistance of 2 . You have only 5 resistors. Design a combination circuit that has a total resistance of 11.25 . You have resi ...
SEL-9501 AND SEL-9502
... SEL-9502 1. Use the supplied bracket to mount the SEL-9502 to any available surface close to the protected contact, keeping the leads as short as possible. 2. Connect the SEL-9502 across the contact, routing the connection to the negative terminal of the contact through the hole in the SEL-9502 (in ...
... SEL-9502 1. Use the supplied bracket to mount the SEL-9502 to any available surface close to the protected contact, keeping the leads as short as possible. 2. Connect the SEL-9502 across the contact, routing the connection to the negative terminal of the contact through the hole in the SEL-9502 (in ...
(Kirchhoff`s Voltage Law).
... conductor. Current is measured in (A) amperes or amps. ( E ) Voltage is the difference in electrical potential between two points in a circuit. It's the push or pressure behind current flow through a circuit, and is measured in (V) volts. ( R ) Resistance determines how much current will flow throug ...
... conductor. Current is measured in (A) amperes or amps. ( E ) Voltage is the difference in electrical potential between two points in a circuit. It's the push or pressure behind current flow through a circuit, and is measured in (V) volts. ( R ) Resistance determines how much current will flow throug ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.