CSS - CBSE Guess
... When each one of them is separately connected across alternating voltage Eosinωt Q.24> Derive the average power dissipated in a LCR circuit. Explain “Power factor” Q.25> Describe the construction and working of a A.C. Generator. Q.26> Explain the construction and working of motor starter. Q.27> Usin ...
... When each one of them is separately connected across alternating voltage Eosinωt Q.24> Derive the average power dissipated in a LCR circuit. Explain “Power factor” Q.25> Describe the construction and working of a A.C. Generator. Q.26> Explain the construction and working of motor starter. Q.27> Usin ...
1 Gate-Defined Quantum Dots on Carbon Nanotubes MJ
... consistent with the interpretation that the interaction between the two dots is due to tunnel coupling. If we assume that tunneling rates through the outer barriers, ΓBL and ΓBR, are equal and remain roughly constant in the three coupling regimes (these rates do change somewhat as indicated by a var ...
... consistent with the interpretation that the interaction between the two dots is due to tunnel coupling. If we assume that tunneling rates through the outer barriers, ΓBL and ΓBR, are equal and remain roughly constant in the three coupling regimes (these rates do change somewhat as indicated by a var ...
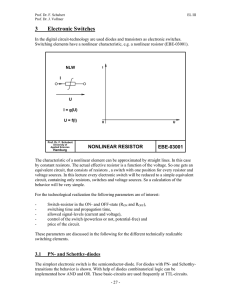
3 Electronic Switches
... means, that in the ON-state is made by a switch a connection with the supply-voltage (e.g. GND). In the OFF-state the switch is blocked. This blocking behaviour will not be reached inertia-less. So this will limit the maximum frequency of the system. Using two phases or push-pull switches is possibl ...
... means, that in the ON-state is made by a switch a connection with the supply-voltage (e.g. GND). In the OFF-state the switch is blocked. This blocking behaviour will not be reached inertia-less. So this will limit the maximum frequency of the system. Using two phases or push-pull switches is possibl ...
Current Electricity
... with a power supply of 1.3-V. What is the resistance in the circuit? 1. A current of 400mA runs through a bulb that is connected to two 15-Ω resistors. What is the voltage in the circuit? 1. A light bulb has a resistance of 10-Ω in a circuit powered by three 0.5-V batteries. What is the current runn ...
... with a power supply of 1.3-V. What is the resistance in the circuit? 1. A current of 400mA runs through a bulb that is connected to two 15-Ω resistors. What is the voltage in the circuit? 1. A light bulb has a resistance of 10-Ω in a circuit powered by three 0.5-V batteries. What is the current runn ...
AP Physics Free Response Practice – Circuits – ANSWERS 1976B3
... b. i./ii. The resistances are unchanged = 480 and 360 . The total resistance in series is 480 + 360 = 840 making the total current I = V/R = 0.14 A which is the same value for both resistors in series c. The bulbs are brightest in parallel, where they provide their labeled values of 40 W an ...
... b. i./ii. The resistances are unchanged = 480 and 360 . The total resistance in series is 480 + 360 = 840 making the total current I = V/R = 0.14 A which is the same value for both resistors in series c. The bulbs are brightest in parallel, where they provide their labeled values of 40 W an ...
Frequently Asked Questions Solid-State Relays Frequently Asked
... A: The LED emits light onto a PV stack which acts as a power source for the MOSFET switches. In case of fully integrated SSRs, the part already consists of a pair of integrated MOSFETs on the output. Vishay also offers stand-alone MOSFET drivers to allow the designer to build up a customized SSR mod ...
... A: The LED emits light onto a PV stack which acts as a power source for the MOSFET switches. In case of fully integrated SSRs, the part already consists of a pair of integrated MOSFETs on the output. Vishay also offers stand-alone MOSFET drivers to allow the designer to build up a customized SSR mod ...
AND8303/D Generating a 1.2 V Voltage Supply using the NCP102
... The minimum output voltage is limited by the voltage reference. The pass transistor is selected to achieve the desired input voltage and output current. Stability of linear regulators is very critical as with any feedback system. The main contributors to the stability of a linear regulator are the e ...
... The minimum output voltage is limited by the voltage reference. The pass transistor is selected to achieve the desired input voltage and output current. Stability of linear regulators is very critical as with any feedback system. The main contributors to the stability of a linear regulator are the e ...
Latest Technology PT IGBTs vs. Power MOSFETs
... Second, a convenient comparison to note is that the ID rating of the APT6010B2LL (continuous conduction with the case at 25 °C) is similar to the IC2 rating of the APT30GP60B (continuous conduction with the case at 110 °C), 54 and 49 Amps respectively. These two current ratings are similar, and the ...
... Second, a convenient comparison to note is that the ID rating of the APT6010B2LL (continuous conduction with the case at 25 °C) is similar to the IC2 rating of the APT30GP60B (continuous conduction with the case at 110 °C), 54 and 49 Amps respectively. These two current ratings are similar, and the ...
Simple Way to Achieve Changeable Holding Current of DRV8x
... Output of Holding State................................................................................................... 4 Normal Operation Waveform .......................................................................................... 4 Holding State Waveform ................................. ...
... Output of Holding State................................................................................................... 4 Normal Operation Waveform .......................................................................................... 4 Holding State Waveform ................................. ...
EE3310_classnotes_fl..
... 2) Most of the depletion region around the gate is in the n-side of the junction. This is because the density of the n-side is much lower than the p+-side. Because the total charge inside the junction must be zero, more of the junction must be on the n-side. 3) If there is a small bias between the s ...
... 2) Most of the depletion region around the gate is in the n-side of the junction. This is because the density of the n-side is much lower than the p+-side. Because the total charge inside the junction must be zero, more of the junction must be on the n-side. 3) If there is a small bias between the s ...
Nodal Analysis
... 2. Label the voltage at the other nodes 3. Label the currents flowing through each of the components in the circuit 4. Use Kirchhoff’s Current Law 5. Use Ohm’s Law to relate the voltages at each node to the currents flowing in and out of them. 6. Solve for the node voltage 7. Once the node voltages ...
... 2. Label the voltage at the other nodes 3. Label the currents flowing through each of the components in the circuit 4. Use Kirchhoff’s Current Law 5. Use Ohm’s Law to relate the voltages at each node to the currents flowing in and out of them. 6. Solve for the node voltage 7. Once the node voltages ...
Data Sheet General Description Features
... The AP3605 is a step-up DC/DC converter based on 1.5x charge pump current source, it is specially designed for LED supplies in backlight display. ...
... The AP3605 is a step-up DC/DC converter based on 1.5x charge pump current source, it is specially designed for LED supplies in backlight display. ...
Driving LEDs with a PIC Microcontroller Application Note
... The multiplexer can be digitally controlled by the microcontroller. Each LED is assigned an address which allows it to be selected by the PIC, in order to determine the current passing through the diode for current regulation or to assist in failure recognition. ...
... The multiplexer can be digitally controlled by the microcontroller. Each LED is assigned an address which allows it to be selected by the PIC, in order to determine the current passing through the diode for current regulation or to assist in failure recognition. ...
Solution - University of California, Berkeley
... The L-units represent positive latches clocked by . L has a setup time of 150 psec and a delay of 250 psec (td-q when latch is transparent). Tc-q is 100 psec and thold is 100 psec. The clock has a period T and is high for a duration of Ton. The duty cycle of the clock hence equals 100 Ton/T %. a) ...
... The L-units represent positive latches clocked by . L has a setup time of 150 psec and a delay of 250 psec (td-q when latch is transparent). Tc-q is 100 psec and thold is 100 psec. The clock has a period T and is high for a duration of Ton. The duty cycle of the clock hence equals 100 Ton/T %. a) ...
Blackstart of An Induction Motor in An Autonomous Microgrid
... using Voltage-Sourced Converter (VSC) interfaced source in an autonomous microgrid. This paper provides procedures and techniques for controlling the VSC. First, a dynamic model of a microgrid is analyzed to provide a designing criteria of VSC’s controller. Vector control is implemented to control t ...
... using Voltage-Sourced Converter (VSC) interfaced source in an autonomous microgrid. This paper provides procedures and techniques for controlling the VSC. First, a dynamic model of a microgrid is analyzed to provide a designing criteria of VSC’s controller. Vector control is implemented to control t ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.