2300_QU2_Shattuck_Fall2002
... The device shown in the figure below was connected to a voltmeter. The voltmeter had a 200[V] full-scale voltage, and a meter resistance of 100[k]. The voltmeter read vD = 124[V] when connected to the device. Then, the device was disconnected from the voltmeter, and was connected to an ammeter. Th ...
... The device shown in the figure below was connected to a voltmeter. The voltmeter had a 200[V] full-scale voltage, and a meter resistance of 100[k]. The voltmeter read vD = 124[V] when connected to the device. Then, the device was disconnected from the voltmeter, and was connected to an ammeter. Th ...
LM3448 Phase Dimmable Offline LED Driver with
... angle" and may be stated in degrees or radians. The off-time represents the delay caused by the RC circuit feeding the TRIAC. The off-time can be referred to as the "firing angle" and is simply (180° - θ). Figure 16(c) shows a waveform from a reverse phase dimmer, sometimes referred to as an electro ...
... angle" and may be stated in degrees or radians. The off-time represents the delay caused by the RC circuit feeding the TRIAC. The off-time can be referred to as the "firing angle" and is simply (180° - θ). Figure 16(c) shows a waveform from a reverse phase dimmer, sometimes referred to as an electro ...
Normalized calculation of impulse current circuits for given impulse
... change the circuit elements C, L, and R in such a manner that a certain new current impulse with a desired amplitude or duration is obtained. To simplify this task, the change of impulse characteristics (amplitude and front or time to half-value) were determined in conjunction with the change of onl ...
... change the circuit elements C, L, and R in such a manner that a certain new current impulse with a desired amplitude or duration is obtained. To simplify this task, the change of impulse characteristics (amplitude and front or time to half-value) were determined in conjunction with the change of onl ...
REF200 Dual Current Source and Current Sink (Rev. B)
... Applications for the REF200 are limitless. Application Bulletin AB-165 (SBOA046) shows additional REF200 circuits as well as other related current source techniques. In this section, a collection of circuits are shown to illustrate some techniques. If the current sources are subjected to reverse vol ...
... Applications for the REF200 are limitless. Application Bulletin AB-165 (SBOA046) shows additional REF200 circuits as well as other related current source techniques. In this section, a collection of circuits are shown to illustrate some techniques. If the current sources are subjected to reverse vol ...
TSM9634F - Silicon Labs
... and to keep the physical size of RSENSE small. If the external RSENSE is allowed to dissipate significant power, then its inherent temperature coefficient may alter its design center value, thereby reducing load current measurement accuracy. Precisely because the TSM9634F’s input stage was designed ...
... and to keep the physical size of RSENSE small. If the external RSENSE is allowed to dissipate significant power, then its inherent temperature coefficient may alter its design center value, thereby reducing load current measurement accuracy. Precisely because the TSM9634F’s input stage was designed ...
Chapter 27-Circuits Multi-Resistor Single Loop Circuits Q1. A battery
... Q14. A capacitor in an RC circuit is charged to 85% of its maximum value in 2.4 s. What is the time constant of this circuit?Ans:1.3 s Q15. A 4.00 micro-F capacitor is charged to 24.0 V. Find the charge on the capacitor 4.00 milli-seconds after it is connected across a 200-Ohm resistor.Ans:0.647 mic ...
... Q14. A capacitor in an RC circuit is charged to 85% of its maximum value in 2.4 s. What is the time constant of this circuit?Ans:1.3 s Q15. A 4.00 micro-F capacitor is charged to 24.0 V. Find the charge on the capacitor 4.00 milli-seconds after it is connected across a 200-Ohm resistor.Ans:0.647 mic ...
5A EXPERIMENT RC Circuits
... Because the two plates have different charge, there is a net electric field between the two plates. Hence, there is a voltage difference between the plates. If, sometime later, we connect the plates again, this time with a light bulb in place of the battery, the plates will discharge: the electrons ...
... Because the two plates have different charge, there is a net electric field between the two plates. Hence, there is a voltage difference between the plates. If, sometime later, we connect the plates again, this time with a light bulb in place of the battery, the plates will discharge: the electrons ...
Sample Investigation
... measurements, they learn that voltage drops in a circuit as work is done (lighting a bulb) while current does not change in the same circuit. ...
... measurements, they learn that voltage drops in a circuit as work is done (lighting a bulb) while current does not change in the same circuit. ...
IA = Ica - Engineering.com
... SEL Relay neutral and ground, zoomed out. No significant change in In from before, during after… suspect In is garbage data. What about IG… where does this dc come from? ...
... SEL Relay neutral and ground, zoomed out. No significant change in In from before, during after… suspect In is garbage data. What about IG… where does this dc come from? ...
Evaluates: MAX686 MAX686 Evaluation Kit General Description ____________________________Features
... LCDON can be used to turn on a positive LCD bias voltage when VBATT is above the desired threshold. A resistor-divider (R16-R17) from VBATT to POK controls the open-drain output LCDON, which pulls low when VPOK > 1.125V. LCDON can drive an external PNP transistor, Q1, switching a positive VOUT to th ...
... LCDON can be used to turn on a positive LCD bias voltage when VBATT is above the desired threshold. A resistor-divider (R16-R17) from VBATT to POK controls the open-drain output LCDON, which pulls low when VPOK > 1.125V. LCDON can drive an external PNP transistor, Q1, switching a positive VOUT to th ...
TDA2050 - STMicroelectronics
... An overload on the output (even if it is permanent), or an above-limit ambient temperature can be easily tolerated since Tj cannot be higher than 150 °C. ...
... An overload on the output (even if it is permanent), or an above-limit ambient temperature can be easily tolerated since Tj cannot be higher than 150 °C. ...
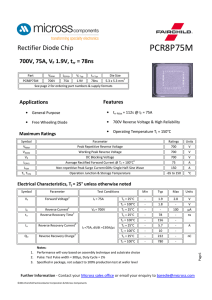
PCR8P75M - Micross Components
... LIFE SUPPORT POLICY FAIRCHILD’S PRODUCTS ARE NOT AUTHORIZED FOR USE AS CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN LIFE SUPPORT DEVICES OR SYSTEMS WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN APPROVAL OF FAIRCHILD SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION. As used here in: ...
... LIFE SUPPORT POLICY FAIRCHILD’S PRODUCTS ARE NOT AUTHORIZED FOR USE AS CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN LIFE SUPPORT DEVICES OR SYSTEMS WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN APPROVAL OF FAIRCHILD SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION. As used here in: ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.