NCP5006 Compact Backlight LED Boost Driver
... than the Over Voltage Protection threshold (OVP) the device comes back to shutdown mode. To restart the chip, one must either send a Low to High sequence on Pin EN, or switch off the Vbat supply. A capacitor must be used on the output voltage to avoid false triggering of the OVP circuit. This capaci ...
... than the Over Voltage Protection threshold (OVP) the device comes back to shutdown mode. To restart the chip, one must either send a Low to High sequence on Pin EN, or switch off the Vbat supply. A capacitor must be used on the output voltage to avoid false triggering of the OVP circuit. This capaci ...
A Novel Electric Shock Protection System Based on Contact
... conductors (usually phase and neutral) serving a load is monitored. If the difference exceeds a predetermined level, it is assumed that the difference in current could be the current flowing through a person’s body, and a circuit interrupter rapidly trips. They have the following limitations [3,5]: ...
... conductors (usually phase and neutral) serving a load is monitored. If the difference exceeds a predetermined level, it is assumed that the difference in current could be the current flowing through a person’s body, and a circuit interrupter rapidly trips. They have the following limitations [3,5]: ...
IEEEPD-shock - Stanford University
... The difference in the current flowing between the power conductors (usually phase and neutral) serving a load is monitored. If the difference exceeds a predetermined level, it is assumed that the difference in current could be the current flowing through a person’s body, and a circuit interrupter ra ...
... The difference in the current flowing between the power conductors (usually phase and neutral) serving a load is monitored. If the difference exceeds a predetermined level, it is assumed that the difference in current could be the current flowing through a person’s body, and a circuit interrupter ra ...
TPS64200 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... When delivering low or medium output current, the TPS6420x operate in discontinuous mode. With every switching cycle, the current in the inductor starts at zero, rises to a maximum value and ramps down to zero again. As soon as the current in the inductor drops to zero, ringing occurs at the resonan ...
... When delivering low or medium output current, the TPS6420x operate in discontinuous mode. With every switching cycle, the current in the inductor starts at zero, rises to a maximum value and ramps down to zero again. As soon as the current in the inductor drops to zero, ringing occurs at the resonan ...
Equivalent_Impedance
... I = V/Zeq = (12 -60o V)/ (10.1 5.7o W) V = 12 -60o V = 12V e-j60 (exponential form) Zeq = 10.1 5.7o W = 10.1 W ej5.7 (exponential form) I = V/Zeq = 12V e-j60/(10.1 ej5.7) = 1.19A e-j65.7 I = 1.19A -65.7o ...
... I = V/Zeq = (12 -60o V)/ (10.1 5.7o W) V = 12 -60o V = 12V e-j60 (exponential form) Zeq = 10.1 5.7o W = 10.1 W ej5.7 (exponential form) I = V/Zeq = 12V e-j60/(10.1 ej5.7) = 1.19A e-j65.7 I = 1.19A -65.7o ...
Tunnel Diodes (Esaki Diode)
... In this case the, electrons in the valence band of the p side tunnel directly towards the empty states present in the conduction band of the n side creating large tunneling current which increases with the application of reverse voltage. The TD reverse I-V is similar to the Zener diode with nearly z ...
... In this case the, electrons in the valence band of the p side tunnel directly towards the empty states present in the conduction band of the n side creating large tunneling current which increases with the application of reverse voltage. The TD reverse I-V is similar to the Zener diode with nearly z ...
ece2201_lab4
... IMPROVING ON RESISTANCE rDS BY INCREASING GATE DRIVE vGS L5. Modify the circuit of Fig. 3-1 as shown in Fig. 3-2, to use the DVM in ohmmeter mode to measure the on resistance rDS directly. As you vary vGS, you will see variation in the on resistance. NOTE: Unfortunately, this part requires lots of ...
... IMPROVING ON RESISTANCE rDS BY INCREASING GATE DRIVE vGS L5. Modify the circuit of Fig. 3-1 as shown in Fig. 3-2, to use the DVM in ohmmeter mode to measure the on resistance rDS directly. As you vary vGS, you will see variation in the on resistance. NOTE: Unfortunately, this part requires lots of ...
MAX366/MAX367 Signal-Line Circuit Protectors _______________General Description ____________________________Features
... A fault condition exists when the voltage on either signal pin is within about 1.5V of either supply rail or exceeds either supply rail. This definition is valid when power is applied and when it is off, as well as during all the states as power ramps up or down. During a fault, the protector acts a ...
... A fault condition exists when the voltage on either signal pin is within about 1.5V of either supply rail or exceeds either supply rail. This definition is valid when power is applied and when it is off, as well as during all the states as power ramps up or down. During a fault, the protector acts a ...
UC3849 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... threshold. After exceeding this threshold, the RS flip-flop is set driving CLKSYN high and RDEAD low which discharges CT. This discharge time with the RC time delay of 2 • CT • RDEAD is the minimum output low time. OSC continues to discharge until it reaches a 1.2 -V threshold and resets the RS flip ...
... threshold. After exceeding this threshold, the RS flip-flop is set driving CLKSYN high and RDEAD low which discharges CT. This discharge time with the RC time delay of 2 • CT • RDEAD is the minimum output low time. OSC continues to discharge until it reaches a 1.2 -V threshold and resets the RS flip ...
Aalborg Universitet Drive Applications
... will not cause a well-known variable switching frequency issue. To synchronize the current controller with the grid a second-order generalized integrator (SOGI) based phase locked loop (PLL) system is adopted [18]. As Fig. 4 depicted, for the simplicity, the line-to-line voltage is fed to the PLL th ...
... will not cause a well-known variable switching frequency issue. To synchronize the current controller with the grid a second-order generalized integrator (SOGI) based phase locked loop (PLL) system is adopted [18]. As Fig. 4 depicted, for the simplicity, the line-to-line voltage is fed to the PLL th ...
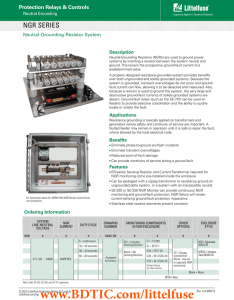
Download PGN-1000 Datasheet
... A properly designed resistance-grounded system provides benefits over both ungrounded and solidly grounded systems. Because the system is grounded, transient overvoltages do not occur and groundfault current can flow, allowing it to be detected and measured. Also, because a resistor is used to groun ...
... A properly designed resistance-grounded system provides benefits over both ungrounded and solidly grounded systems. Because the system is grounded, transient overvoltages do not occur and groundfault current can flow, allowing it to be detected and measured. Also, because a resistor is used to groun ...
ADP1876 英文数据手册DataSheet 下载
... capacitor (MLCC) between BST1 and SW1. There is an internal boost diode or rectifier connected between VDL and BST1. Current-Limit Sense Comparator Inverting Input for Channel 1. Connect a resistor between ILIM1 and SW1 to set the current-limit offset. For accurate current-limit sensing, connect ILI ...
... capacitor (MLCC) between BST1 and SW1. There is an internal boost diode or rectifier connected between VDL and BST1. Current-Limit Sense Comparator Inverting Input for Channel 1. Connect a resistor between ILIM1 and SW1 to set the current-limit offset. For accurate current-limit sensing, connect ILI ...
Celestron TLP/VF-TLP Test System
... © 2015 Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. All rights reserved. Windows is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries. All other trademarks are the property of Thermo Fisher Scientific and its subsidiaries. Results may vary under different operating condition ...
... © 2015 Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. All rights reserved. Windows is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries. All other trademarks are the property of Thermo Fisher Scientific and its subsidiaries. Results may vary under different operating condition ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.