Network_Analysis_Part_I
... Ideal Voltage Sources in parallel are permissible only when each has the same terminal voltage at every ...
... Ideal Voltage Sources in parallel are permissible only when each has the same terminal voltage at every ...
lec14
... opened and a person discharges the capacitor. Then, that same person places a second capacitor in parallel with the first one, while leaving the original circuit intact. The person closes the switch and again measures the time it takes for the voltage across the original capacitor to reach 99% of th ...
... opened and a person discharges the capacitor. Then, that same person places a second capacitor in parallel with the first one, while leaving the original circuit intact. The person closes the switch and again measures the time it takes for the voltage across the original capacitor to reach 99% of th ...
Managing Inrush Current
... the PCB traces and selecting connectors, not taking the inrush current peak into account can damage the power path and lead to system failure; however, appropriately designing for a large inrush current peak will lead to thicker PCB traces and more durable connectors which can increase the size and ...
... the PCB traces and selecting connectors, not taking the inrush current peak into account can damage the power path and lead to system failure; however, appropriately designing for a large inrush current peak will lead to thicker PCB traces and more durable connectors which can increase the size and ...
Zo: Transmission Lines, Reflections, and Termination
... halfway between the driver and U2. As shown in the figure, U1 sees an input of only 2.5 V for an interval T. A receiving gate positioned closer to the driver would see this input voltage even longer. This is a problem, because 2.5 V is right at the switching threshold for 5-V CMOS inputs. If this in ...
... halfway between the driver and U2. As shown in the figure, U1 sees an input of only 2.5 V for an interval T. A receiving gate positioned closer to the driver would see this input voltage even longer. This is a problem, because 2.5 V is right at the switching threshold for 5-V CMOS inputs. If this in ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Int2 Physics Unit2
... Remember to use a ruler and pencil, draw components carefully, draw wires as straight lines (with corners as right angles!), and make sure all components are correctly draw and joined in the circuit. ...
... Remember to use a ruler and pencil, draw components carefully, draw wires as straight lines (with corners as right angles!), and make sure all components are correctly draw and joined in the circuit. ...
TPS2376-H 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... Inrush current limiting prevents current drawn by the bulk capacitor from causing the line voltage to sag below the lower UVLO threshold. Adjustable inrush current limiting allows the use of arbitrarily large capacitors and also accommodates legacy systems that require low inrush currents. The ILIM ...
... Inrush current limiting prevents current drawn by the bulk capacitor from causing the line voltage to sag below the lower UVLO threshold. Adjustable inrush current limiting allows the use of arbitrarily large capacitors and also accommodates legacy systems that require low inrush currents. The ILIM ...
Electricity - Buckeye Valley
... Remember to use a ruler and pencil, draw components carefully, draw wires as straight lines (with corners as right angles!), and make sure all components are correctly draw and joined in the circuit. ...
... Remember to use a ruler and pencil, draw components carefully, draw wires as straight lines (with corners as right angles!), and make sure all components are correctly draw and joined in the circuit. ...
ICL8038
... applied directly to pin 8, merely providing DC decoupling with a capacitor as shown in Figure 5A. An external resistor between pins 7 and 8 is not necessary, but it can be used to increase input impedance from about 8kΩ (pins 7 and 8 connected together), to about (R + 8kΩ). For larger FM deviations ...
... applied directly to pin 8, merely providing DC decoupling with a capacitor as shown in Figure 5A. An external resistor between pins 7 and 8 is not necessary, but it can be used to increase input impedance from about 8kΩ (pins 7 and 8 connected together), to about (R + 8kΩ). For larger FM deviations ...
operation modes of full-bridge voltage
... On the contrary, the switch turn-on takes place at very disadvantageous conditions – at full current and voltage equal to supply voltage. Additionally, high reverse-recovery diode current spikes flows also through the switches that have been turned-on (this is not seen in Fig. 6, because the element ...
... On the contrary, the switch turn-on takes place at very disadvantageous conditions – at full current and voltage equal to supply voltage. Additionally, high reverse-recovery diode current spikes flows also through the switches that have been turned-on (this is not seen in Fig. 6, because the element ...
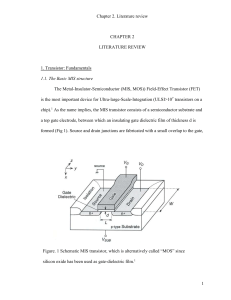
Literature review 7
... away from the surface, leaving behind a depletion region consisting of uncompensated acceptor ions. When larger positive voltage is applied, this surface depletion is widened. Correspondingly, the total electrostatic potential variation, as represented by the bending of the bands, increases so that ...
... away from the surface, leaving behind a depletion region consisting of uncompensated acceptor ions. When larger positive voltage is applied, this surface depletion is widened. Correspondingly, the total electrostatic potential variation, as represented by the bending of the bands, increases so that ...
MAX1760/MAX1760H 0.8A, Low-Noise, 1MHz, Step-Up DC-DC Converter General Description
... required for output voltages greater than 4V. The MAX1760 guarantees startup with an input voltage as low as 1.1V and remains operational down to an input of just 0.7V. It is optimized for use in cellular phones and other applications requiring low noise and low quiescent current for maximum battery ...
... required for output voltages greater than 4V. The MAX1760 guarantees startup with an input voltage as low as 1.1V and remains operational down to an input of just 0.7V. It is optimized for use in cellular phones and other applications requiring low noise and low quiescent current for maximum battery ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.