hukum ohm
... 1. Construct a circuit containing dc low voltage supply, resistor, voltmeter and ammeter based on circuit diagram provided by your teacher. 2. Turn the power supply ON with the voltage control initially set to zero. Using the voltage adjustment control, increase the current through the resistor to 0 ...
... 1. Construct a circuit containing dc low voltage supply, resistor, voltmeter and ammeter based on circuit diagram provided by your teacher. 2. Turn the power supply ON with the voltage control initially set to zero. Using the voltage adjustment control, increase the current through the resistor to 0 ...
MEASURING VOLTS
... Since a parallel circuit has more than one path for current flow, adding additional paths (loads) will decrease the total resistance in the circuit. The formula to calculate the total resistance in a parallel circuit is: ...
... Since a parallel circuit has more than one path for current flow, adding additional paths (loads) will decrease the total resistance in the circuit. The formula to calculate the total resistance in a parallel circuit is: ...
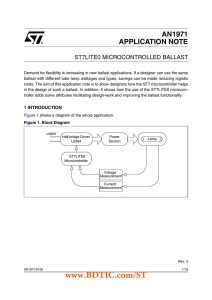
TL7660 CMOS VOLTAGE CONVERTER FEATURES APPLICATIONS
... eliminate output voltage ripple but also to employ a correspondingly large value for C1 in order to achieve maximum efficiency of operation. Do's and Don'ts • Do not exceed maximum supply voltages. • Do not connect LV terminal to GND for supply voltages greater than 3.5 V. • Do not short circuit the ...
... eliminate output voltage ripple but also to employ a correspondingly large value for C1 in order to achieve maximum efficiency of operation. Do's and Don'ts • Do not exceed maximum supply voltages. • Do not connect LV terminal to GND for supply voltages greater than 3.5 V. • Do not short circuit the ...
Switched-Capacitor Voltage Converters _______________General Description ____________________________Features
... positive terminal of C1 to ground and shifts the negative terminal to VOUT. This connects C1 in parallel with the reservoir capacitor C2. If the voltage across C2 is smaller than the voltage across C1, then charge flows from C1 to C2 until the voltages across them are equal. During successive cycles ...
... positive terminal of C1 to ground and shifts the negative terminal to VOUT. This connects C1 in parallel with the reservoir capacitor C2. If the voltage across C2 is smaller than the voltage across C1, then charge flows from C1 to C2 until the voltages across them are equal. During successive cycles ...
LTC6103 - Dual High Voltage, High Side Current Sense Amplifier
... independent except for sharing the same V– pin. So supply voltage and component values can be chosen independently for each amplifier. Selection of External Current Sense Resistor The external sense resistor, RSENSE, has a significant effect on the function of a current sensing system and must be chos ...
... independent except for sharing the same V– pin. So supply voltage and component values can be chosen independently for each amplifier. Selection of External Current Sense Resistor The external sense resistor, RSENSE, has a significant effect on the function of a current sensing system and must be chos ...
CSLA Series Linear Current Sensor
... defective materials and faulty workmanship. Honeywell’s standard product warranty applies unless agreed to otherwise ...
... defective materials and faulty workmanship. Honeywell’s standard product warranty applies unless agreed to otherwise ...
ISL6308 - Intersil
... These pins make up the 2-bit input that selects the fixed DAC reference voltage. These pins respond to TTL logic thresholds. The ISL6308 decodes these inputs to establish one of four fixed reference voltages; see Table 1 for correspondence between REF0 and REF1 inputs and reference voltage settings. ...
... These pins make up the 2-bit input that selects the fixed DAC reference voltage. These pins respond to TTL logic thresholds. The ISL6308 decodes these inputs to establish one of four fixed reference voltages; see Table 1 for correspondence between REF0 and REF1 inputs and reference voltage settings. ...
OP77
... Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise ...
... Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise ...
4. Electrical characteristics
... According to IEC 60871 standard requirements, capacitor units include internal discharge resistors so that the residual voltage is less than 75V within 10 minutes after disconnection. 4.7 Switch The capacitor bank is operated by a SF1 switch from Schneider-Electric range of switchgear. This switch u ...
... According to IEC 60871 standard requirements, capacitor units include internal discharge resistors so that the residual voltage is less than 75V within 10 minutes after disconnection. 4.7 Switch The capacitor bank is operated by a SF1 switch from Schneider-Electric range of switchgear. This switch u ...
Switched-Capacitor Voltage Converters _______________General Description ____________________________Features
... positive terminal of C1 to ground and shifts the negative terminal to VOUT. This connects C1 in parallel with the reservoir capacitor C2. If the voltage across C2 is smaller than the voltage across C1, then charge flows from C1 to C2 until the voltages across them are equal. During successive cycles ...
... positive terminal of C1 to ground and shifts the negative terminal to VOUT. This connects C1 in parallel with the reservoir capacitor C2. If the voltage across C2 is smaller than the voltage across C1, then charge flows from C1 to C2 until the voltages across them are equal. During successive cycles ...
Current
... build-up of an electric charge on the surface of an object. The charge builds up but does not flow. Static electricity is potential energy. It does not move. It is stored. ...
... build-up of an electric charge on the surface of an object. The charge builds up but does not flow. Static electricity is potential energy. It does not move. It is stored. ...
MAX16952 36V, 2.2MHz Step-Down Controller with Low Operating Current General Description
... The MAX16952 is a current-mode, synchronous PWM step-down controller designed to operate with input voltages from 3.5V to 36V while using only 50μA of quiescent current at no load. The switching frequency is adjustable from 1MHz to 2.2MHz by an external resistor and can be synchronized to an externa ...
... The MAX16952 is a current-mode, synchronous PWM step-down controller designed to operate with input voltages from 3.5V to 36V while using only 50μA of quiescent current at no load. The switching frequency is adjustable from 1MHz to 2.2MHz by an external resistor and can be synchronized to an externa ...
TRIAC
TRIAC, from triode for alternating current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor.TRIACs are a subset of thyristors and are closely related to silicon controlled rectifiers (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (that is, they can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so allow current in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIAC current can be enabled by either a positive or negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by positive current into the gate. To create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the MT1 terminal (otherwise known as A1).Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold called the holding current.The bidirectionality makes TRIACs very convenient switches for alternating-current (AC) circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows control of the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps, and in controlling AC heating resistors.