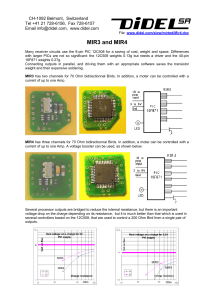
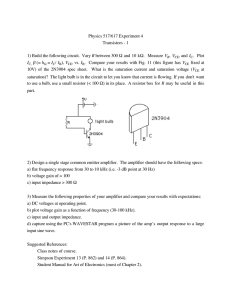
PDF Print Version - Glassman High Voltage
... pulse-width modulation provides high efficiency and a reduced parts count for improved reliability. Air Insulation. Both PG series feature “air” as the primary dielectric medium. No oil or encapsulation is used that could impede serviceability or increase weight. Constant Voltage/Constant Current Op ...
... pulse-width modulation provides high efficiency and a reduced parts count for improved reliability. Air Insulation. Both PG series feature “air” as the primary dielectric medium. No oil or encapsulation is used that could impede serviceability or increase weight. Constant Voltage/Constant Current Op ...
electricity - chapter 1 quiz
... 12. A thermocouple produces electrical energy from heat energy. 13. A photocell produces electrical energy from light energy. 14. In an electrochemical cell, the difference in charges between the positive and negative terminals is called the potential – difference. 15. A circuit is a complete path f ...
... 12. A thermocouple produces electrical energy from heat energy. 13. A photocell produces electrical energy from light energy. 14. In an electrochemical cell, the difference in charges between the positive and negative terminals is called the potential – difference. 15. A circuit is a complete path f ...
Slide
... • Voltage stability is important for reliability, performance • Low-power techniques have a negative side effect: current variation ...
... • Voltage stability is important for reliability, performance • Low-power techniques have a negative side effect: current variation ...
DT002_1_Industrial_Electronics_summer_2006_ans
... Identify the type of rectifier circuit represented in figure 1 and explain the operation of the circuit with reference to the function of each component within the circuit. This is a bridge rectifier circuit. The mains voltage is applied to the primary winding of the transformer T1. This typically p ...
... Identify the type of rectifier circuit represented in figure 1 and explain the operation of the circuit with reference to the function of each component within the circuit. This is a bridge rectifier circuit. The mains voltage is applied to the primary winding of the transformer T1. This typically p ...
Circuit Components
... - output voltage or current is dependent or controlled by some other voltage or current in the circuit - arise from complex physical interactions in electronic devices - e.g. base current controls collector current in a bipolar junction transistor Voltage Controlled Voltage Source (VCVS): - vi is in ...
... - output voltage or current is dependent or controlled by some other voltage or current in the circuit - arise from complex physical interactions in electronic devices - e.g. base current controls collector current in a bipolar junction transistor Voltage Controlled Voltage Source (VCVS): - vi is in ...
ppt
... Active device (Voltage or Current Source): Current exits + side, Current enters – side + side is at a higher voltage than – side (if current direction is correct) ...
... Active device (Voltage or Current Source): Current exits + side, Current enters – side + side is at a higher voltage than – side (if current direction is correct) ...
Solutions Manual
... 13. Output Voltage Explain why the output voltage of an electric generator increases ...
... 13. Output Voltage Explain why the output voltage of an electric generator increases ...
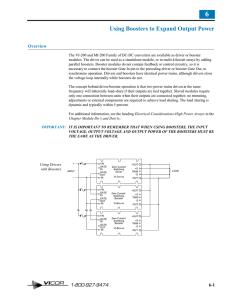
Using Boosters to Expand Output Power
... modules. The driver can be used as a standalone module, or in multi-kilowatt arrays by adding parallel boosters. Booster modules do not contain feedback or control circuitry, so it is necessary to connect the booster Gate In pin to the preceding driver or booster Gate Out, to synchronize operation. ...
... modules. The driver can be used as a standalone module, or in multi-kilowatt arrays by adding parallel boosters. Booster modules do not contain feedback or control circuitry, so it is necessary to connect the booster Gate In pin to the preceding driver or booster Gate Out, to synchronize operation. ...
8.1.2 Basic Time Consuming Processes
... in a Si integrated circuit. e.g., gives a τRC of roughly 10–9 s, and this value (per cm line length) is directly determined by the product of the specific resistivity ρ of the conducting material times the relative dielectric constant εrof the dielectric separating individual wires - it is thus a ra ...
... in a Si integrated circuit. e.g., gives a τRC of roughly 10–9 s, and this value (per cm line length) is directly determined by the product of the specific resistivity ρ of the conducting material times the relative dielectric constant εrof the dielectric separating individual wires - it is thus a ra ...
An Introduction to Electrical Power for the Non-Power
... Direct current means that current always flows in one direction and is the simplest type of circuit to grasp for reasons we’ll cover soon. Alternating current means the voltage and current are sine waves that change direction (flow) or oscillate continuously. In North America this typically happens ...
... Direct current means that current always flows in one direction and is the simplest type of circuit to grasp for reasons we’ll cover soon. Alternating current means the voltage and current are sine waves that change direction (flow) or oscillate continuously. In North America this typically happens ...
GS5802 - Globaltech Semiconductor
... ceramic capacitors with low ESR are recommended. X5R and X7R types are suitable because of their wider voltage and temperature ranges. Diode Selection Schottky diode is a good choice for GS5802 because of its low forward voltage drop and fast reverses recovery. Using Schottky diode can get better ef ...
... ceramic capacitors with low ESR are recommended. X5R and X7R types are suitable because of their wider voltage and temperature ranges. Diode Selection Schottky diode is a good choice for GS5802 because of its low forward voltage drop and fast reverses recovery. Using Schottky diode can get better ef ...
Power MOSFET
A power MOSFET is a specific type of metal oxide semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) designed to handle significant power levels.Compared to the other power semiconductor devices, for example an insulated-gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) or a thyristor, its main advantages are high commutation speed and good efficiency at low voltages. It shares with the IGBT an isolated gate that makes it easy to drive. They can be subject to low gain, sometimes to degree that the gate voltage needs to be higher than the voltage under control.The design of power MOSFETs was made possible by the evolution of CMOS technology, developed for manufacturing integrated circuits in the late 1970s. The power MOSFET shares its operating principle with its low-power counterpart, the lateral MOSFET.The power MOSFET is the most widely used low-voltage (that is, less than 200 V) switch. It can be found in most power supplies, DC to DC converters, and low voltage motor controllers.