LR8506 INTRODUCTION FEATURE
... main (P-channel MOSFET) and synchronous (N-channel MOSFET) switches are internal. During normal operation, the internal top power MOSFET is turned on each cycle when the oscillator sets the RS latch, and turned off when the current comparator, ICOMP, resets the RS latch. The peak inductor current at ...
... main (P-channel MOSFET) and synchronous (N-channel MOSFET) switches are internal. During normal operation, the internal top power MOSFET is turned on each cycle when the oscillator sets the RS latch, and turned off when the current comparator, ICOMP, resets the RS latch. The peak inductor current at ...
Power supply description
... Usually, DC voltages are required to operate various electronic equipment and these voltages are 5V, 9V or 12V. But these voltages cannot be obtained directly. Thus the a.c input available at the mains supply i.e., 230V is to be brought down to the required voltage level. This is done by a transform ...
... Usually, DC voltages are required to operate various electronic equipment and these voltages are 5V, 9V or 12V. But these voltages cannot be obtained directly. Thus the a.c input available at the mains supply i.e., 230V is to be brought down to the required voltage level. This is done by a transform ...
S1SD-1TI-1U Temperature Converter Connection
... devices: - resistance thermometers - thermocouples - PTC thermistors - potentiometers - voltage sources - field device with its own characteristic ...
... devices: - resistance thermometers - thermocouples - PTC thermistors - potentiometers - voltage sources - field device with its own characteristic ...
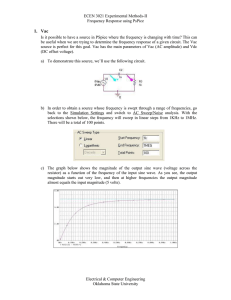
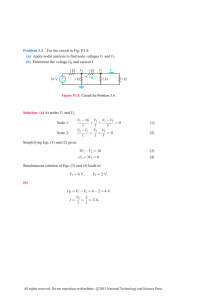
Tutorial 2 (AC Fundamentals)
... 5. Three circuit elements are connected in series and the voltages across the circuit elements are given by: v1 =50 sin (ωt), v2 =40 sin (ωt + 60) and v3 =60 sin (ωt-30) Calculate the total voltage appearing across the three components and its phase angle with reference to v1. Answer 1222.17 V 6 ...
... 5. Three circuit elements are connected in series and the voltages across the circuit elements are given by: v1 =50 sin (ωt), v2 =40 sin (ωt + 60) and v3 =60 sin (ωt-30) Calculate the total voltage appearing across the three components and its phase angle with reference to v1. Answer 1222.17 V 6 ...
Electric Circuits
... Although a little confusing (and more than a little irritating) we need to recall that electric potential is defined in terms of moving positive charge. And the direction of an electric field is defined as the direction that a positive charge will move in that field. ...
... Although a little confusing (and more than a little irritating) we need to recall that electric potential is defined in terms of moving positive charge. And the direction of an electric field is defined as the direction that a positive charge will move in that field. ...
Final Report
... LED in order to get to the red LED. As a result if the current in the red LED were to increase the current in the green LED would also increase causing both to light. In order to solve this dilemma, a medium resistance resistor can be placed in parallel with the green LED and series resistor. This w ...
... LED in order to get to the red LED. As a result if the current in the red LED were to increase the current in the green LED would also increase causing both to light. In order to solve this dilemma, a medium resistance resistor can be placed in parallel with the green LED and series resistor. This w ...
doc - Cornerstone Robotics
... Direct Current (dc): o Direct current moves in only one direction in a circuit. o Though dc must travel in only one direction, its value does not necessarily have to remain constant. See Figure 1. Constant dc typical of a battery or regulated dc power supply ...
... Direct Current (dc): o Direct current moves in only one direction in a circuit. o Though dc must travel in only one direction, its value does not necessarily have to remain constant. See Figure 1. Constant dc typical of a battery or regulated dc power supply ...
100 HVT Series AC Hipot Tester FEATURES
... The 100 HVT Series AC test sets are specifically designed to perform quick and accurate AC dielectric tests. The 100 HVT has a maximum output of 100 kV at 50 mA or 50 kV at 100 mA. This test set can be used for testing bucket trucks and aerial platforms, hot sticks, blankets, ropes or any other high ...
... The 100 HVT Series AC test sets are specifically designed to perform quick and accurate AC dielectric tests. The 100 HVT has a maximum output of 100 kV at 50 mA or 50 kV at 100 mA. This test set can be used for testing bucket trucks and aerial platforms, hot sticks, blankets, ropes or any other high ...
Ohm`s Law Lab
... For reference, see: http://njc.tl/181 Background: Ohm’s law states that if the temperature of a resistor remains constant, the electric current (I) flowing in a circuit is directly proportional to the applied voltage (V) and inversely proportional to the resistance (R) of the circuit. ...
... For reference, see: http://njc.tl/181 Background: Ohm’s law states that if the temperature of a resistor remains constant, the electric current (I) flowing in a circuit is directly proportional to the applied voltage (V) and inversely proportional to the resistance (R) of the circuit. ...
example abstract
... voltage is directly converted into a variable frequency and voltage without using any DClink. The most significant advantage of these types of converters is that they have bidirectional power flow, sinusoidal input and output voltage and high unity power factor. Such an arrangement is generally prod ...
... voltage is directly converted into a variable frequency and voltage without using any DClink. The most significant advantage of these types of converters is that they have bidirectional power flow, sinusoidal input and output voltage and high unity power factor. Such an arrangement is generally prod ...
Chapter 10.3
... 1. A battery can produce 1.5 V. When connected to a light bulb a current of 2 A (Ampere) runs through the bulb. What is the resistance of the bulb? 2. A bulb in a lamp that is connected to a household outlet has a resistance of 100 W. What current flows through it? ...
... 1. A battery can produce 1.5 V. When connected to a light bulb a current of 2 A (Ampere) runs through the bulb. What is the resistance of the bulb? 2. A bulb in a lamp that is connected to a household outlet has a resistance of 100 W. What current flows through it? ...
SEMI CONDUCTOR AND COMMUNICATION
... 18. (a) Why is a Photo Diode is operated in reverse bias mode? (b) For what purpose a photodiode is used? (c) Draw its I – V characteristics for different intensities of illumination. 19. A transistor has a current amplification factor of 50. In a Common Emitter amplifier circuit, the collector resi ...
... 18. (a) Why is a Photo Diode is operated in reverse bias mode? (b) For what purpose a photodiode is used? (c) Draw its I – V characteristics for different intensities of illumination. 19. A transistor has a current amplification factor of 50. In a Common Emitter amplifier circuit, the collector resi ...
Power MOSFET
A power MOSFET is a specific type of metal oxide semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) designed to handle significant power levels.Compared to the other power semiconductor devices, for example an insulated-gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) or a thyristor, its main advantages are high commutation speed and good efficiency at low voltages. It shares with the IGBT an isolated gate that makes it easy to drive. They can be subject to low gain, sometimes to degree that the gate voltage needs to be higher than the voltage under control.The design of power MOSFETs was made possible by the evolution of CMOS technology, developed for manufacturing integrated circuits in the late 1970s. The power MOSFET shares its operating principle with its low-power counterpart, the lateral MOSFET.The power MOSFET is the most widely used low-voltage (that is, less than 200 V) switch. It can be found in most power supplies, DC to DC converters, and low voltage motor controllers.