AMPLIFIED PHOTODETECTOR USER`S GUIDE
... current is converted to an output voltage. Bandwidth: Unlike non-amplified photodetector bandwidth, which is defined as the range of frequencies from 0Hz (DC) to the frequency at which the amplitude decreases by 3dB, the amplified photodetectors have a low frequency cutoff of -3dB, which is greater ...
... current is converted to an output voltage. Bandwidth: Unlike non-amplified photodetector bandwidth, which is defined as the range of frequencies from 0Hz (DC) to the frequency at which the amplitude decreases by 3dB, the amplified photodetectors have a low frequency cutoff of -3dB, which is greater ...
soln_1-99
... Many of you developed a circuit in which the current from the AD590 was sensed by a series resistor, and the voltage across the resistor was used directly as the input to a comparator. While these circuits would work in principle, the change in voltage is so small that it makes the setting of the hy ...
... Many of you developed a circuit in which the current from the AD590 was sensed by a series resistor, and the voltage across the resistor was used directly as the input to a comparator. While these circuits would work in principle, the change in voltage is so small that it makes the setting of the hy ...
NC7WBD3125 2-Bit Low Power Bus Switch with Level Shifting NC7 WBD3
... guaranteed at the absolute maximum ratings. The “Recommended Operating Conditions” table will define the conditions for actual device operation. Note 2: The input and output negative voltage ratings may be exceeded if the input and output diode current ratings are observed. Note 3: Unused logic inpu ...
... guaranteed at the absolute maximum ratings. The “Recommended Operating Conditions” table will define the conditions for actual device operation. Note 2: The input and output negative voltage ratings may be exceeded if the input and output diode current ratings are observed. Note 3: Unused logic inpu ...
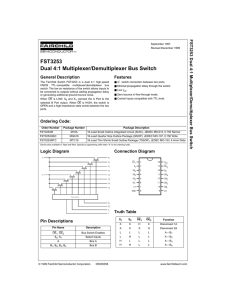
FST3253 Dual 4:1 Multiplexer/Demultiplexer Bus Switch FST3 253
... Note 4: Typical values are at VCC = 5.0V and T A = +25°C Note 5: Measured by the voltage drop between A and B pins at the indicated current through the switch. On resistance is determined by the lower of the voltages on the two (A or B) pins. ...
... Note 4: Typical values are at VCC = 5.0V and T A = +25°C Note 5: Measured by the voltage drop between A and B pins at the indicated current through the switch. On resistance is determined by the lower of the voltages on the two (A or B) pins. ...
Electromagnetism G. L. Pollack and D. R. Stump Four stepped exercises.
... General Strategy The surefire way to find the total resistance R between two terminals in any network is to let current I enter at one terminal and exit at the other. Use Kirchhoff’s laws (about which more below) together with any symmetries available to find the current through each of the conducto ...
... General Strategy The surefire way to find the total resistance R between two terminals in any network is to let current I enter at one terminal and exit at the other. Use Kirchhoff’s laws (about which more below) together with any symmetries available to find the current through each of the conducto ...
Pins were added to the layout of the cell so that an LVS test could be
... result, the expected sizes of between the NAND and NOR gates will be smaller than 4, although the NAND gate should still be smaller (or the same size) as the NOR gate. The layouts of all 3 gates can be seen in Figure 8. As can be seen, the inverter uses the smallest area (since it has the fewest tra ...
... result, the expected sizes of between the NAND and NOR gates will be smaller than 4, although the NAND gate should still be smaller (or the same size) as the NOR gate. The layouts of all 3 gates can be seen in Figure 8. As can be seen, the inverter uses the smallest area (since it has the fewest tra ...
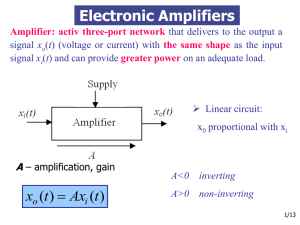
Amplificatoare electronice
... Electronic Amplifiers Amplifier: activ three-port network that delivers to the output a signal xo(t) (voltage or current) with the same shape as the input signal xi(t) and can provide greater power on an adequate load. ...
... Electronic Amplifiers Amplifier: activ three-port network that delivers to the output a signal xo(t) (voltage or current) with the same shape as the input signal xi(t) and can provide greater power on an adequate load. ...
Lecture Outlines Chapter 24 James S. Walker Physics, 3
... will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students except by instructors using the accompanying text in their classes. All recipients of this work are expected to abide by these restrictions and to honor the intended ...
... will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students except by instructors using the accompanying text in their classes. All recipients of this work are expected to abide by these restrictions and to honor the intended ...
brouchure
... Reduced coupling capacitance Lesser leakage current Suitable for higher harmonic loads Core will not saturate even if the applied voltage is high ...
... Reduced coupling capacitance Lesser leakage current Suitable for higher harmonic loads Core will not saturate even if the applied voltage is high ...
08c_Picture_This
... that the applied voltages are correct that the circuit is not powered that the circuit is grounded that the circuit is operating at the frequency ...
... that the applied voltages are correct that the circuit is not powered that the circuit is grounded that the circuit is operating at the frequency ...
TSL25x
... † Stresses beyond those listed under “absolute maximum ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under “recommended operating conditions” is not implied. Exposure to ...
... † Stresses beyond those listed under “absolute maximum ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under “recommended operating conditions” is not implied. Exposure to ...
Chapter07
... to the series resistance values. Each resistance provides an IR voltage drop equal to its proportional part of the applied voltage: VR = (R/RT) × VT This formula can be used for any number of series resistances because of the direct proportion between each voltage drop V and its resistance R. ...
... to the series resistance values. Each resistance provides an IR voltage drop equal to its proportional part of the applied voltage: VR = (R/RT) × VT This formula can be used for any number of series resistances because of the direct proportion between each voltage drop V and its resistance R. ...
Power MOSFET
A power MOSFET is a specific type of metal oxide semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) designed to handle significant power levels.Compared to the other power semiconductor devices, for example an insulated-gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) or a thyristor, its main advantages are high commutation speed and good efficiency at low voltages. It shares with the IGBT an isolated gate that makes it easy to drive. They can be subject to low gain, sometimes to degree that the gate voltage needs to be higher than the voltage under control.The design of power MOSFETs was made possible by the evolution of CMOS technology, developed for manufacturing integrated circuits in the late 1970s. The power MOSFET shares its operating principle with its low-power counterpart, the lateral MOSFET.The power MOSFET is the most widely used low-voltage (that is, less than 200 V) switch. It can be found in most power supplies, DC to DC converters, and low voltage motor controllers.