Eubacteria- Archaebacteria
... Vitamin B12 is synthesized exclusively by bacteria through a process called fermentation. ...
... Vitamin B12 is synthesized exclusively by bacteria through a process called fermentation. ...
antibacterials
... A microorganism may become resistant as a result of mutation. A mutated bacteria may produce an enzyme that makes antibiotics ineffective. Result of these mutations: Need for constant renewal of antibiotics. Hence, antibiotics should only be used when no other treatment is effective. ...
... A microorganism may become resistant as a result of mutation. A mutated bacteria may produce an enzyme that makes antibiotics ineffective. Result of these mutations: Need for constant renewal of antibiotics. Hence, antibiotics should only be used when no other treatment is effective. ...
Serial dilution and plate counts
... To calculate the bacterial density in the original suspension follow this calculation: In this example let’s assume that you had 32 colonies on a plate obtained by plating 100µl of a 1x10-6 dilution of the original suspension. First, determine the correction factor to adjust the volume plated on eac ...
... To calculate the bacterial density in the original suspension follow this calculation: In this example let’s assume that you had 32 colonies on a plate obtained by plating 100µl of a 1x10-6 dilution of the original suspension. First, determine the correction factor to adjust the volume plated on eac ...
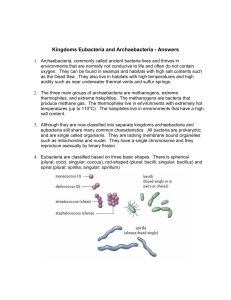
Kingdoms Eubacteria and Archaebacteria
... Source of antibiotics (streptomycin and erythromycin) ...
... Source of antibiotics (streptomycin and erythromycin) ...
The Microbial World
... – Photosynthetic bacteria which are found in environments high in dissolved oxygen, and produce free oxygen – Usually found in low depths of ocean – Contain chlorophyll a and b – First photosynthetic organisms on earth ...
... – Photosynthetic bacteria which are found in environments high in dissolved oxygen, and produce free oxygen – Usually found in low depths of ocean – Contain chlorophyll a and b – First photosynthetic organisms on earth ...
بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
... Prokaryotic structural components consist of macromolecules such as DNA, RNA, proteins, polysaccharides, phospholipids, or some combination .The macromolecules are made up of primary subunits such as nucleotides, amino acids and sugars (Table 1). It is the sequence in which the subunits are put toge ...
... Prokaryotic structural components consist of macromolecules such as DNA, RNA, proteins, polysaccharides, phospholipids, or some combination .The macromolecules are made up of primary subunits such as nucleotides, amino acids and sugars (Table 1). It is the sequence in which the subunits are put toge ...
BIO 220 General Microbiology
... Written examinations B. Written quizzes C. Laboratory work D. Comprehensive final E. Grades will be given based upon A = 90 – 100%, B = 80 – 89%, C = 70 – 79%, D = 60 – 69%, and F = below 60%. ...
... Written examinations B. Written quizzes C. Laboratory work D. Comprehensive final E. Grades will be given based upon A = 90 – 100%, B = 80 – 89%, C = 70 – 79%, D = 60 – 69%, and F = below 60%. ...
D. Growth and Reproduction
... Fun Facts about Bacteria 1. Bacteria help our bodies with digestion and produce needed vitamins. 2. Bacteria help us by destroying harmful organisms within our bodies. 3. There are more bacterial cells in your body than there are human cells. 4. Bacteria are used to make cheese, milk, sourdough bre ...
... Fun Facts about Bacteria 1. Bacteria help our bodies with digestion and produce needed vitamins. 2. Bacteria help us by destroying harmful organisms within our bodies. 3. There are more bacterial cells in your body than there are human cells. 4. Bacteria are used to make cheese, milk, sourdough bre ...
Useful Info
... of inhibition around the sample. Some antimicrobials, such as silver and quaternary ammonium silanes, have efficacy at the surface but do not diffuse at high enough rates to give a zone of inhibition. Fig. 2 on the next page shows the results of an AATCC TM147 test (the light colored streaks are the ...
... of inhibition around the sample. Some antimicrobials, such as silver and quaternary ammonium silanes, have efficacy at the surface but do not diffuse at high enough rates to give a zone of inhibition. Fig. 2 on the next page shows the results of an AATCC TM147 test (the light colored streaks are the ...
The Bacteria
... Gram-positive bacteria stain purple, whereas Gram-negative bacteria stain pink. This difference is dependent on the thick or thin (respectively) peptidoglycan cell wall. ...
... Gram-positive bacteria stain purple, whereas Gram-negative bacteria stain pink. This difference is dependent on the thick or thin (respectively) peptidoglycan cell wall. ...
Staphylococcus aureus
... Scanning electron micrograph of a cluster of Staphylococcus aureus. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3002151/ ...
... Scanning electron micrograph of a cluster of Staphylococcus aureus. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3002151/ ...
lecture 02d
... – Quick and convenient, shows relative change in the number of bacteria, useful for determining growth (increase in numbers). – Does NOT distinguish between live and dead cells. To create a calibration curve, best to plot OD vs. number of cells determined with microscope (not plate count). ...
... – Quick and convenient, shows relative change in the number of bacteria, useful for determining growth (increase in numbers). – Does NOT distinguish between live and dead cells. To create a calibration curve, best to plot OD vs. number of cells determined with microscope (not plate count). ...
Prokaryote notes
... b. As aerobic saprotrophs, there is probably no natural organic molecule that cannot be broken down by some prokaryotic species. c. Detritivores (saprophytic bacteria) are critical in recycling materials in the ecosystem; they decompose dead organic matter and make it available to photosynthesizers. ...
... b. As aerobic saprotrophs, there is probably no natural organic molecule that cannot be broken down by some prokaryotic species. c. Detritivores (saprophytic bacteria) are critical in recycling materials in the ecosystem; they decompose dead organic matter and make it available to photosynthesizers. ...
1. dia
... • Chromosome – a single loop of DNA that is folded on itself - controls the cell’s function • Nucleoid – the region of the cytoplasm where the DNA is found • Plasmid – an accessory loop of DNA – small contains only a few genes - can be responsible for: conjugation, antibiotic resistance, unique meta ...
... • Chromosome – a single loop of DNA that is folded on itself - controls the cell’s function • Nucleoid – the region of the cytoplasm where the DNA is found • Plasmid – an accessory loop of DNA – small contains only a few genes - can be responsible for: conjugation, antibiotic resistance, unique meta ...
Lecture 4
... The growth of the cell is inhibited as the plasma • membrane pulls away from the cell wall. Thus, addition of salts or other solutes to solution can be used to preserve food. Loss of water from the cell results in Plasmolysis. • ...
... The growth of the cell is inhibited as the plasma • membrane pulls away from the cell wall. Thus, addition of salts or other solutes to solution can be used to preserve food. Loss of water from the cell results in Plasmolysis. • ...
(a) Gram-positive bacteria
... - gram-positive and gram negative bacteria, cyanobacteria (blue green bacteria) ...
... - gram-positive and gram negative bacteria, cyanobacteria (blue green bacteria) ...
knowledge quiz - Discovery Education
... C. Bacteria are the oldest and most diverse life forms. D. All three statements are true. 2. There are three common shapes of bacteria. They are A. rods, spheres, and spirals. B. rods, spirals, and tubes. C. spheres, hexagons, and spirals. D. none of the above. 3. Some bacteria are used to fight off ...
... C. Bacteria are the oldest and most diverse life forms. D. All three statements are true. 2. There are three common shapes of bacteria. They are A. rods, spheres, and spirals. B. rods, spirals, and tubes. C. spheres, hexagons, and spirals. D. none of the above. 3. Some bacteria are used to fight off ...
Bacteria
... from a mold or fungus 5. It is their specific waste product 6. There are different strains of E.coli and they all are different. In some strains, they are okay for the body…in some strains…they can harm the body. 7. It destroys microbes by heat…in things like milk, ...
... from a mold or fungus 5. It is their specific waste product 6. There are different strains of E.coli and they all are different. In some strains, they are okay for the body…in some strains…they can harm the body. 7. It destroys microbes by heat…in things like milk, ...
Ribosomes as Antibiotic Targets Ribosomes as
... Today: ~90,000 deaths/year from bacterial infections!!! • Challenge to design effective new generation antibiotics • Use of structure-based drug design to develop novel drugs based on high resolution structures of drug targets and their resistance mutants • The ribosome is the target of over 50% of ...
... Today: ~90,000 deaths/year from bacterial infections!!! • Challenge to design effective new generation antibiotics • Use of structure-based drug design to develop novel drugs based on high resolution structures of drug targets and their resistance mutants • The ribosome is the target of over 50% of ...
Uropathogenic Escherichia coli P and Type 1 Fimbriae Act in
... In this study, a GFP+ expressing variant of UPEC strain CFT073 and isogenic mutants were injected into rat glomerulus or proximal tubules. According to the live animal multiphoton microscopy (MPM), the bacteria colonized along the epithelium of the Bowman’s capsule within 2 h after infection, despit ...
... In this study, a GFP+ expressing variant of UPEC strain CFT073 and isogenic mutants were injected into rat glomerulus or proximal tubules. According to the live animal multiphoton microscopy (MPM), the bacteria colonized along the epithelium of the Bowman’s capsule within 2 h after infection, despit ...
Classification of Bacteria
... Classification of Bacteria Classification, nomenclature, and identification are the three separate but interrelated areas of taxonomy. Classification can be defined as the arrangement of organisms into taxonomic groups (taxa) on the basis of similarities or relationships. Classification of prokaryot ...
... Classification of Bacteria Classification, nomenclature, and identification are the three separate but interrelated areas of taxonomy. Classification can be defined as the arrangement of organisms into taxonomic groups (taxa) on the basis of similarities or relationships. Classification of prokaryot ...
Section 9.2 - CPO Science
... own food from sunlight and carbon dioxide, just like plants. • Bacteria that break down dead organisms get their food by absorbing it. ...
... own food from sunlight and carbon dioxide, just like plants. • Bacteria that break down dead organisms get their food by absorbing it. ...
Lipopolysaccharide
Lipopolysaccharides (LPS), also known as lipoglycans and endotoxin, are large molecules consisting of a lipid and a polysaccharide composed of O-antigen, outer core and inner core joined by a covalent bond; they are found in the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria, and elicit strong immune responses in animals.The term lipooligosaccharide (""LOS"") is used to refer to a low molecular weight form of bacterial lipopolysaccharides.