Molecular Genetics
... every cell in a person’s body has the same DNA. Most DNA is located in the cell nucleus, but a small amount of DNA can also be found in the mitochondria. Genes are sections of DNA molecules. DNA controls the cellular activities by controlling the production of enzymes. ...
... every cell in a person’s body has the same DNA. Most DNA is located in the cell nucleus, but a small amount of DNA can also be found in the mitochondria. Genes are sections of DNA molecules. DNA controls the cellular activities by controlling the production of enzymes. ...
What is a pedigree?
... the parents must have the disorder. – If the disorder is recessive, neither parent has to have the disorder because they can be heterozygous. ...
... the parents must have the disorder. – If the disorder is recessive, neither parent has to have the disorder because they can be heterozygous. ...
基因的性質和基因體 基因的性質和基因體
... • Eukaryotic genomes have repetitive sequences – Many copies of short DNA sequences • Moderately repetitive sequences – Few hundred to several thousand times – rRNA genes, multiple origins of replication, or role in gene transcription and translation • Highly repetitive sequences – Tens of thousand ...
... • Eukaryotic genomes have repetitive sequences – Many copies of short DNA sequences • Moderately repetitive sequences – Few hundred to several thousand times – rRNA genes, multiple origins of replication, or role in gene transcription and translation • Highly repetitive sequences – Tens of thousand ...
Replication, Translation and Transcription Notes
... phosphate group, and a nitrogen base. There are four possible nitrogen bases in DNA—adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). In DNA, the nucleotides pair using hydrogen bonds to form a double strand. Because these two strands are twisted, it is referred to as a double helix. When bas ...
... phosphate group, and a nitrogen base. There are four possible nitrogen bases in DNA—adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). In DNA, the nucleotides pair using hydrogen bonds to form a double strand. Because these two strands are twisted, it is referred to as a double helix. When bas ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿
... may revert by loss of the inserted material, but deletions cannot revert. Mutations may also be suppressed indirectly when a mutation in a different gene counters the original defect. ...
... may revert by loss of the inserted material, but deletions cannot revert. Mutations may also be suppressed indirectly when a mutation in a different gene counters the original defect. ...
DNA
... • Bases are A,G,T,C • Can be damaged by exposure to ultra violet rays. • Double-stranded molecule ...
... • Bases are A,G,T,C • Can be damaged by exposure to ultra violet rays. • Double-stranded molecule ...
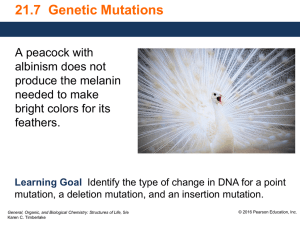
Genetic Mutation
... Mutations, Deletion and Insertion • In a deletion mutation, a base is deleted from the normal order of bases in the template strand of DNA. All the codons that follow are changed, producing a different sequence of amino acids from that point. • In an insertion mutation, a base is inserted into the ...
... Mutations, Deletion and Insertion • In a deletion mutation, a base is deleted from the normal order of bases in the template strand of DNA. All the codons that follow are changed, producing a different sequence of amino acids from that point. • In an insertion mutation, a base is inserted into the ...
plasmid to transform
... 3. Prepare bacterial cells for transformation of plasmid. a. Treat with calcium chloride, which allows plasmid to pass through bacterial cell walls. This is the most common ...
... 3. Prepare bacterial cells for transformation of plasmid. a. Treat with calcium chloride, which allows plasmid to pass through bacterial cell walls. This is the most common ...
Name_______________________________
... Name_____________________________________Date__________________Period________ Protein Synthesis Practice Molecules of DNA carry the genetic instructions for protein formation. Converting these DNA instructions into proteins requires a series of coordinated steps in transcription and translation. Co ...
... Name_____________________________________Date__________________Period________ Protein Synthesis Practice Molecules of DNA carry the genetic instructions for protein formation. Converting these DNA instructions into proteins requires a series of coordinated steps in transcription and translation. Co ...
Multiplex STR Analysis by Capillary Electrophoresis
... Most short tandem repeat loci used in identity testing have repeats that are four base pairs in length, with allele sizes between 100bp and 300bp. Table 1 lists some of the commonly used STRs. The relatively small size of STR alleles reduces the effects of preferential amplification. Thus, more high ...
... Most short tandem repeat loci used in identity testing have repeats that are four base pairs in length, with allele sizes between 100bp and 300bp. Table 1 lists some of the commonly used STRs. The relatively small size of STR alleles reduces the effects of preferential amplification. Thus, more high ...
DNA and the Language of Life
... phosphorus atom surrounded by four oxygen atoms) A nitrogenous base ("nitrogen-containing") : a single or double ring of carbon and nitrogen atoms with functional groups ...
... phosphorus atom surrounded by four oxygen atoms) A nitrogenous base ("nitrogen-containing") : a single or double ring of carbon and nitrogen atoms with functional groups ...
Transcription - Santa Susana High School
... – 5' receives a cap that consists of GTP and around 20-40 nucleotides – 3' end receives a cap of A (50-250 nucleotides) to extend the poly-A tail • both help protect the mRNA from degradation • are considered NTR - nontranslated regions ...
... – 5' receives a cap that consists of GTP and around 20-40 nucleotides – 3' end receives a cap of A (50-250 nucleotides) to extend the poly-A tail • both help protect the mRNA from degradation • are considered NTR - nontranslated regions ...
Teacher`s Notes - University of California, Irvine
... First a gel is prepared. Gels are made of agarose , a seaweed extract similar to gelatin. The finished gel has a consistency similar to very firm jello. This consistency offers resistance to the pieces of DNA as they try to move through the gel matrix. The gel is prepared with wells at one end so ...
... First a gel is prepared. Gels are made of agarose , a seaweed extract similar to gelatin. The finished gel has a consistency similar to very firm jello. This consistency offers resistance to the pieces of DNA as they try to move through the gel matrix. The gel is prepared with wells at one end so ...
Protein Synthesis Questions
... B shows the peptide synthesized after a mutation in this piece of DNA. A. proline - arginine - aspartic acid - lysine - glycine B. proline - glutamine - aspartic acid - lysine - glycine The type of change in the DNA most likely to be responsible for the difference between the peptides is a. a frame- ...
... B shows the peptide synthesized after a mutation in this piece of DNA. A. proline - arginine - aspartic acid - lysine - glycine B. proline - glutamine - aspartic acid - lysine - glycine The type of change in the DNA most likely to be responsible for the difference between the peptides is a. a frame- ...
Mech63-RvwGeneticDisordersPt1
... Gene responsible for the disease resides on the X chromosome X-linked traits can be dominant or recessive Lack of transmission from father to son because dad passes his Y to the son. Most X-linked traits are recessive so that heterozygous females do not exhibit the disease E. Fragile X Syndr ...
... Gene responsible for the disease resides on the X chromosome X-linked traits can be dominant or recessive Lack of transmission from father to son because dad passes his Y to the son. Most X-linked traits are recessive so that heterozygous females do not exhibit the disease E. Fragile X Syndr ...
DNA
... • 3.4 Angstrom between two nucleotides in a single strand and 34 Angstrom every complete turn of the helix • The two strands of the helix are 20 Angstrom apart • major groove and a minor groove alternate ...
... • 3.4 Angstrom between two nucleotides in a single strand and 34 Angstrom every complete turn of the helix • The two strands of the helix are 20 Angstrom apart • major groove and a minor groove alternate ...
DNA
... Replication will make 2 identical strands of DNA which can then be passed on to a new cell during mitosis or meiosis When all the DNA in all the cells has replicated, there are 2 copies of the organism’s genetic information. ...
... Replication will make 2 identical strands of DNA which can then be passed on to a new cell during mitosis or meiosis When all the DNA in all the cells has replicated, there are 2 copies of the organism’s genetic information. ...
Genetic Mutations
... They may have little or no effect on the survival of an organism or on its ability to reproduce. They may result in the same kind of organism - ...
... They may have little or no effect on the survival of an organism or on its ability to reproduce. They may result in the same kind of organism - ...
HaeIII restriction endonuclease was used to digest the following
... 10. (up to 1.5 pts, 0.5 pts each) Assuming that this is a eukaryotic mRNA: A. What is one other non-translated RNa sequences that would be present in the primary mRNA as it is first transcribed from the template strand of the DNA? B. What are 2 other non-translated RNA sequences, added after transcr ...
... 10. (up to 1.5 pts, 0.5 pts each) Assuming that this is a eukaryotic mRNA: A. What is one other non-translated RNa sequences that would be present in the primary mRNA as it is first transcribed from the template strand of the DNA? B. What are 2 other non-translated RNA sequences, added after transcr ...
gene mutation 2
... Some genetic changes are very rare; others are common in the population. Genetic changes that occur in more than 1 percent of the population are called polymorphisms. They are common enough to be considered a normal variation in the DNA. Polymorphisms are responsible for many of the normal differenc ...
... Some genetic changes are very rare; others are common in the population. Genetic changes that occur in more than 1 percent of the population are called polymorphisms. They are common enough to be considered a normal variation in the DNA. Polymorphisms are responsible for many of the normal differenc ...
23 development of molecular markers to distinguish cytoplasm
... such as sudden increases in the virulence of pathogens or pests, or rapid changes in the environment. In the United States, the danger of genetic vulnerability of major modern crops was illustrated graphically by the epidemic of the Southern corn leaf blight, which caused a 15 % reduction in corn ou ...
... such as sudden increases in the virulence of pathogens or pests, or rapid changes in the environment. In the United States, the danger of genetic vulnerability of major modern crops was illustrated graphically by the epidemic of the Southern corn leaf blight, which caused a 15 % reduction in corn ou ...
Genome Organisation Definitions: Genome Investigations: what can
... In prokaryotes the bases are distributed evenly throughout the genome with a slightly lower (G + C) content in promoter and intergenic regions; these often have A + T rich segments which melt more readily than G+C rich regions. The relatively constant base distribution within a given bacterial genom ...
... In prokaryotes the bases are distributed evenly throughout the genome with a slightly lower (G + C) content in promoter and intergenic regions; these often have A + T rich segments which melt more readily than G+C rich regions. The relatively constant base distribution within a given bacterial genom ...
Genomics
... match between a query sequence and a subject sequence is the number of subject sequences in a completely random database that would have the same match score or better. The random database must be the same size as the one you are using. – Really bad matches have e-values of 1 or more: An e-value of ...
... match between a query sequence and a subject sequence is the number of subject sequences in a completely random database that would have the same match score or better. The random database must be the same size as the one you are using. – Really bad matches have e-values of 1 or more: An e-value of ...
Microsatellite

A microsatellite is a tract of repetitive DNA in which certain DNA motifs (ranging in length from 2–5 base pairs) are repeated, typically 5-50 times. Microsatellites occur at thousands of locations in the human genome and they are notable for their high mutation rate and high diversity in the population. Microsatellites and their longer cousins, the minisatellites, together are classified as VNTR (variable number of tandem repeats) DNA. The name ""satellite"" refers to the early observation that centrifugation of genomic DNA in a test tube separates a prominent layer of bulk DNA from accompanying ""satellite"" layers of repetitive DNA. Microsatellites are often referred to as short tandem repeats (STRs) by forensic geneticists, or as simple sequence repeats (SSRs) by plant geneticists.They are widely used for DNA profiling in kinship analysis and in forensic identification. They are also used in genetic linkage analysis/marker assisted selection to locate a gene or a mutation responsible for a given trait or disease.