Comparative Genomic Hybridization for
... number with cell lines that contained previously reported amplification of oncogenes. CGH was performed with DNA from a colon cancer cell line, COLO 320HSR (Fig. 3A), known to contain more than a 50-fold amplification of a 300-kb region around the myc oncogene (1 1). The expected high green-to-red r ...
... number with cell lines that contained previously reported amplification of oncogenes. CGH was performed with DNA from a colon cancer cell line, COLO 320HSR (Fig. 3A), known to contain more than a 50-fold amplification of a 300-kb region around the myc oncogene (1 1). The expected high green-to-red r ...
Race for the Double Helix Name
... (1928- ), attending a conference in Italy, is jolted into active pursuit of the structure of DNA by an X-ray diffraction image of a DNA sample presented by the English biophysicist Maurice Wilkins. Since Wilkins’s image reveals the regularity of a crystal, Watson is convinced that DNA might be analy ...
... (1928- ), attending a conference in Italy, is jolted into active pursuit of the structure of DNA by an X-ray diffraction image of a DNA sample presented by the English biophysicist Maurice Wilkins. Since Wilkins’s image reveals the regularity of a crystal, Watson is convinced that DNA might be analy ...
DNA replication
... fingerprinting used in forensic and paternity testing (p. 70). Although often located near the telomeres, hypervariable minisatellite DNA also occurs at other locations in the chromosomes. ...
... fingerprinting used in forensic and paternity testing (p. 70). Although often located near the telomeres, hypervariable minisatellite DNA also occurs at other locations in the chromosomes. ...
mutation as a source of variation
... Genetic variation is essential for Darwin’s theory of natural selection and all genetic variation must come, ultimately, from mutations. A mutation is any hereditary change in the DNA sequence or in chromosome number, form or structure. Most mutations arise from errors during DNA replication that fa ...
... Genetic variation is essential for Darwin’s theory of natural selection and all genetic variation must come, ultimately, from mutations. A mutation is any hereditary change in the DNA sequence or in chromosome number, form or structure. Most mutations arise from errors during DNA replication that fa ...
Slides - Sapling Learning
... • Insertions and deletions cause frameshift mutations – Frameshift mutation – a mutation in which the codon reading frame is altered, potentially changing all codons following • Codons are read in groups of three nucleotides • Addition or removal of a nucleotide changes the reading frame • Different ...
... • Insertions and deletions cause frameshift mutations – Frameshift mutation – a mutation in which the codon reading frame is altered, potentially changing all codons following • Codons are read in groups of three nucleotides • Addition or removal of a nucleotide changes the reading frame • Different ...
DNA Typing/anthropology
... a. Nucleus of cells contain RNA/DNA b. DNA = deoxyribonucleic acid *** c. Nucleus has 23 pairs of chromosomes made up of DNA *** d. Within each pair, one chromosome from sperm and one from egg *** ...
... a. Nucleus of cells contain RNA/DNA b. DNA = deoxyribonucleic acid *** c. Nucleus has 23 pairs of chromosomes made up of DNA *** d. Within each pair, one chromosome from sperm and one from egg *** ...
Plasmid
... – Made of a segment of DNA wound around a protein core that is composed of 2 copies of each of 4 types of histones ...
... – Made of a segment of DNA wound around a protein core that is composed of 2 copies of each of 4 types of histones ...
Real-time monitoring of branched rolling
... forensics, and biodefense [1,2]. Recently emerged techniques that quantify the ampliWed DNA in real time have further advanced these Welds [3–5]. A key element in the real-time ampliWcation methods are Xuorogenic probes, with molecular beacons being among the most useful [4]. Despite an assortment o ...
... forensics, and biodefense [1,2]. Recently emerged techniques that quantify the ampliWed DNA in real time have further advanced these Welds [3–5]. A key element in the real-time ampliWcation methods are Xuorogenic probes, with molecular beacons being among the most useful [4]. Despite an assortment o ...
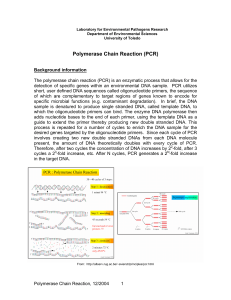
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) - Department of Environmental
... detection of specific genes within an environmental DNA sample. PCR utilizes short, user defined DNA sequences called oligonucleotide primers, the sequence of which are complementary to target regions of genes known to encode for specific microbial functions (e.g. contaminant degradation). In brief, ...
... detection of specific genes within an environmental DNA sample. PCR utilizes short, user defined DNA sequences called oligonucleotide primers, the sequence of which are complementary to target regions of genes known to encode for specific microbial functions (e.g. contaminant degradation). In brief, ...
CHAPTER 8 Applications of Recombinant DNA Technology
... b. Minisatellites, also called VNTRs (variable number of tandem repeats), have repeating units ranging in size from 5 to a few tens of base pairs. ...
... b. Minisatellites, also called VNTRs (variable number of tandem repeats), have repeating units ranging in size from 5 to a few tens of base pairs. ...
Mutations - GK-12 Program at the University of Houston
... changing the properties of nucleotides in the DNA. Overexposure to ultraviolet radiation is known to lead to skin cancer. X-rays and gamma radiation are also physical mutagens and forms of ionizing radiation; this means that these types of radiation possess enough energy to remove electrons from ato ...
... changing the properties of nucleotides in the DNA. Overexposure to ultraviolet radiation is known to lead to skin cancer. X-rays and gamma radiation are also physical mutagens and forms of ionizing radiation; this means that these types of radiation possess enough energy to remove electrons from ato ...
Quasi-Continuum Models of Low-Fkequency Oscillators in DNA
... spectra of some oligomers of DNA. The results are compared with experimental values. The basic idea involved in this work is to treat DNA in two regions. First, when the non-harmonic part of the potential is predominant, e.g., at high temperatures (this is the case studied in ref. [a]). In the secon ...
... spectra of some oligomers of DNA. The results are compared with experimental values. The basic idea involved in this work is to treat DNA in two regions. First, when the non-harmonic part of the potential is predominant, e.g., at high temperatures (this is the case studied in ref. [a]). In the secon ...
CRISPR-Cas9 in gene therapy: much control on breaking
... in Cell Stem Cell reports on certain small molecules that can tip the preference of DNA repair system towards a desired mode [1]. Although being in its early days, adaptation of such control over DNA repair system can make the CRISPR-Cas9 a more promising tool for human gene therapy. Since its devel ...
... in Cell Stem Cell reports on certain small molecules that can tip the preference of DNA repair system towards a desired mode [1]. Although being in its early days, adaptation of such control over DNA repair system can make the CRISPR-Cas9 a more promising tool for human gene therapy. Since its devel ...
Chapter 10 DNA RNA Protein Synthesis
... • Early scientists thought proteins were the heredity info….b/c more complex – 20 amino acids (building blocks of protein) – 4 nucleotides (building blocks of DNA: A, T, G, C) ...
... • Early scientists thought proteins were the heredity info….b/c more complex – 20 amino acids (building blocks of protein) – 4 nucleotides (building blocks of DNA: A, T, G, C) ...
GoTaq® DNA Polymerase
... blue and yellow dyes. In a 1% agarose gel, the blue dye migrates at the same rate as 3–5kb DNA fragments, and the yellow dye migrates at a rate faster than primers (<50bp). Green GoTaq® Reaction Buffer also increases the density of the sample, so it will sink into the well of the agarose gel, allowi ...
... blue and yellow dyes. In a 1% agarose gel, the blue dye migrates at the same rate as 3–5kb DNA fragments, and the yellow dye migrates at a rate faster than primers (<50bp). Green GoTaq® Reaction Buffer also increases the density of the sample, so it will sink into the well of the agarose gel, allowi ...
Mutations
... • You, as a microbiologist or a geneticist, have the ability to look at the sequence of an organism. You would do so to detect differences between “normal” DNA and mutations. • Your research objective today is to study the following mutant DNA sequences to detect the type of mutation and where it ta ...
... • You, as a microbiologist or a geneticist, have the ability to look at the sequence of an organism. You would do so to detect differences between “normal” DNA and mutations. • Your research objective today is to study the following mutant DNA sequences to detect the type of mutation and where it ta ...
This is a test - DNALC Lab Center
... of the host chromosome, allowing the DNA copy to integrate. This method of insertion also accounts for the identical sequences (direct repeats) found at the ends of all Alu elements. So it appears that LI can provide the necessary functions for Alu transposition. In this sense, Alu is a parasite of ...
... of the host chromosome, allowing the DNA copy to integrate. This method of insertion also accounts for the identical sequences (direct repeats) found at the ends of all Alu elements. So it appears that LI can provide the necessary functions for Alu transposition. In this sense, Alu is a parasite of ...
Timeline
... • a rare few have been found with thirty genes in them. • cells can have anywhere from a couple to fifty or more plasmids in them. • some pop into the bacterial chromosome = episomes. ...
... • a rare few have been found with thirty genes in them. • cells can have anywhere from a couple to fifty or more plasmids in them. • some pop into the bacterial chromosome = episomes. ...
Chapter 12: DNA & RNA
... • Mutations – heritable changes in genetic information (changes to the DNA sequence) • Two types - gene and chromosomal mutations • Mutations can be caused by chemical or physical agents (mutagens) – Chemical – pesticides, tobacco smoke, environmental pollutants – Physical – X-rays and ultraviolet l ...
... • Mutations – heritable changes in genetic information (changes to the DNA sequence) • Two types - gene and chromosomal mutations • Mutations can be caused by chemical or physical agents (mutagens) – Chemical – pesticides, tobacco smoke, environmental pollutants – Physical – X-rays and ultraviolet l ...
DNA structure and replication power point
... • He found that R strain could become virulent when it took in DNA from heat-killed S strain • Study suggested that DNA was probably the genetic material ...
... • He found that R strain could become virulent when it took in DNA from heat-killed S strain • Study suggested that DNA was probably the genetic material ...
Lab 4 Questions (Answers)
... not, these are either hydrogen bonds or dipole-ion interactions. Q9) (15 points) Into what type of groove are the two arginines and the glutamate projecting into? How do these three amino acid side chains specifically recognize the DNA sequence 5’TCxC-3’ on one strand (or 5’-GxGA-3’ on the complemen ...
... not, these are either hydrogen bonds or dipole-ion interactions. Q9) (15 points) Into what type of groove are the two arginines and the glutamate projecting into? How do these three amino acid side chains specifically recognize the DNA sequence 5’TCxC-3’ on one strand (or 5’-GxGA-3’ on the complemen ...
CHEM642-14 Powerpoint
... convective mixing caused by small differences in temperature or solute concentration, the tube contains a continuous shallow gradient of sucrose that increases in concentration toward the bottom of the tube (typically from 5% to 20% sucrose). Following centrifugation, the different components can be ...
... convective mixing caused by small differences in temperature or solute concentration, the tube contains a continuous shallow gradient of sucrose that increases in concentration toward the bottom of the tube (typically from 5% to 20% sucrose). Following centrifugation, the different components can be ...
Rethinking “time” in 3.1 Programming Languages
... “Generative music is about sowing seeds, comparable with genetic modification; altering DNA, putting the DNA in eggs, and watching it grow to see/hear the effects. In contrast, live coding is more about piecing animals together from scratch in the womb, splicing different live animals together, modi ...
... “Generative music is about sowing seeds, comparable with genetic modification; altering DNA, putting the DNA in eggs, and watching it grow to see/hear the effects. In contrast, live coding is more about piecing animals together from scratch in the womb, splicing different live animals together, modi ...
14–16 Video transcript: Chickens and Campylobacter
... on the DNA sequencer. So when I've set up the sequencing reactions and they've all been cleaned up, then we take them to our sequencing lab upstairs, and they're run through an automated DNA analyser. We get the data back as electropherograms. We then assemble a forward and reverse strand, so that's ...
... on the DNA sequencer. So when I've set up the sequencing reactions and they've all been cleaned up, then we take them to our sequencing lab upstairs, and they're run through an automated DNA analyser. We get the data back as electropherograms. We then assemble a forward and reverse strand, so that's ...
Unit 2.1.2a - DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid)
... Above is an example of a nucleotide. In DNA, the sugar is deoxyribose and the organic base is either: A T ...
... Above is an example of a nucleotide. In DNA, the sugar is deoxyribose and the organic base is either: A T ...
Microsatellite

A microsatellite is a tract of repetitive DNA in which certain DNA motifs (ranging in length from 2–5 base pairs) are repeated, typically 5-50 times. Microsatellites occur at thousands of locations in the human genome and they are notable for their high mutation rate and high diversity in the population. Microsatellites and their longer cousins, the minisatellites, together are classified as VNTR (variable number of tandem repeats) DNA. The name ""satellite"" refers to the early observation that centrifugation of genomic DNA in a test tube separates a prominent layer of bulk DNA from accompanying ""satellite"" layers of repetitive DNA. Microsatellites are often referred to as short tandem repeats (STRs) by forensic geneticists, or as simple sequence repeats (SSRs) by plant geneticists.They are widely used for DNA profiling in kinship analysis and in forensic identification. They are also used in genetic linkage analysis/marker assisted selection to locate a gene or a mutation responsible for a given trait or disease.