From Quantum Gates to Quantum Learning
... states, and are characterized by a wave function . As an example (), it is possible to have light polarizations other than purely horizontal or vertical, such as slant 45 corresponding to the linear superposition of . In ternary logic, the notation for the superposition is , where , , and are c ...
... states, and are characterized by a wave function . As an example (), it is possible to have light polarizations other than purely horizontal or vertical, such as slant 45 corresponding to the linear superposition of . In ternary logic, the notation for the superposition is , where , , and are c ...
Superconducting Circuits and Quantum Computation—T. P. Orlando
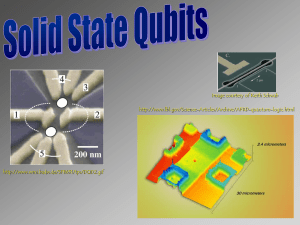
... Figure 1a shows a SEM image of the persistent current qubit (inner loop) and the measuring dc SQUID (outer) loop. A schematic of the qubit and the measuring circuit is shown in Figure 1b, where the Josephson junctions are denoted by x's. The sample is fabricated at MIT Lincoln Laboratory in niobium ...
... Figure 1a shows a SEM image of the persistent current qubit (inner loop) and the measuring dc SQUID (outer) loop. A schematic of the qubit and the measuring circuit is shown in Figure 1b, where the Josephson junctions are denoted by x's. The sample is fabricated at MIT Lincoln Laboratory in niobium ...
Quantum Energy Teleportation - UWSpace
... The relation between energy and information has intrigued physicists for quite some time now. Usually, we speak of such a relation in the context of thermodynamics or black hole physics. Recently, quite a bit of work has been interested in the thermodynamics of spacetime itself[37, 14], and on emerg ...
... The relation between energy and information has intrigued physicists for quite some time now. Usually, we speak of such a relation in the context of thermodynamics or black hole physics. Recently, quite a bit of work has been interested in the thermodynamics of spacetime itself[37, 14], and on emerg ...
Introduction to Quantum Computation THE JOY OF ENTANGLEMENT
... (Here, as in the previous section, | ↑i and | ↓i represent spin parallel and antiparallel, respectively, to the z-axis.) We assume (implicitly, since spatial wave functions don’t appear in Eq. 9) that each particle is in a localized state remote from the other particles. We prepare an ensemble of pa ...
... (Here, as in the previous section, | ↑i and | ↓i represent spin parallel and antiparallel, respectively, to the z-axis.) We assume (implicitly, since spatial wave functions don’t appear in Eq. 9) that each particle is in a localized state remote from the other particles. We prepare an ensemble of pa ...
superconducting qubits solid state qubits
... The qubits levels can be formed by either the energy levels of an electron in a potential well (such as a quantum dot or an impurity ion) or by the spin states of the electron (or the nucleus). The former are examples of charge qubits. The charge qubits have high energy splitting, and can be manipul ...
... The qubits levels can be formed by either the energy levels of an electron in a potential well (such as a quantum dot or an impurity ion) or by the spin states of the electron (or the nucleus). The former are examples of charge qubits. The charge qubits have high energy splitting, and can be manipul ...
Quantum Computing
... Quantum Cryptography) used 200 km of standard fibre optic cable to interconnect six locations across Vienna and the town of St Poelten located 69 km to the west. 5.SwissQuantum network, installed in the Geneva metropolitan area in March 2009, was to validate the reliability and robustness of QKD in ...
... Quantum Cryptography) used 200 km of standard fibre optic cable to interconnect six locations across Vienna and the town of St Poelten located 69 km to the west. 5.SwissQuantum network, installed in the Geneva metropolitan area in March 2009, was to validate the reliability and robustness of QKD in ...
arXiv:math/0606118v4 [math.PR] 5 Dec 2006
... believe that the methods in the field can be understood perfectly well without being obscured by analytic complications. What we are going to do in this paper is to give a complete development of the basic theory of quantum filtering and feedback control in a simple toy model, which requires essenti ...
... believe that the methods in the field can be understood perfectly well without being obscured by analytic complications. What we are going to do in this paper is to give a complete development of the basic theory of quantum filtering and feedback control in a simple toy model, which requires essenti ...
How to Construct Quantum Random Functions
... path from root to the leaf corresponding to the input. The security proof consists of two hybrid arguments: the first across levels of the tree, and the second across the nodes in a particular level. The first step has only polynomially many hybrids since the tree’s depth is a polynomial. For the se ...
... path from root to the leaf corresponding to the input. The security proof consists of two hybrid arguments: the first across levels of the tree, and the second across the nodes in a particular level. The first step has only polynomially many hybrids since the tree’s depth is a polynomial. For the se ...
Feynman-Kac formula for L´evy processes and semiclassical (Euclidean) momentum representation
... In addition we also study the limiting behaviors of the solutions given by FeynmanKac type formulas in terms of large deviations. In particular we show in detail that these limiting behaviors have exactly the same patterns as the semiclassical limits of (Euclidean) quantum mechanics in several speci ...
... In addition we also study the limiting behaviors of the solutions given by FeynmanKac type formulas in terms of large deviations. In particular we show in detail that these limiting behaviors have exactly the same patterns as the semiclassical limits of (Euclidean) quantum mechanics in several speci ...
Commun. Math. Phys. 110, 33-49
... Hamiltonians, which are defined precisely in Sect. 3, are time dependent Hamiltonians depending on one parameter, the flux Φ2 in Fig. 1.2. The time dependence comes from the flux Φί which increases with time to generate an emf. Although the two fluxes play distinct roles in the Hamiltonian, in the a ...
... Hamiltonians, which are defined precisely in Sect. 3, are time dependent Hamiltonians depending on one parameter, the flux Φ2 in Fig. 1.2. The time dependence comes from the flux Φί which increases with time to generate an emf. Although the two fluxes play distinct roles in the Hamiltonian, in the a ...
Microscopic quantum coherence in a photosynthetic-light
... (3.4) [52]. Following these lines of thought, the appearance of a classical world in quantum theory has been explored [51,52,55,56]. On the other hand, an example of fake decoherence is to interpret the result of an ensemble average over different noisy realizations of a system as the description of ...
... (3.4) [52]. Following these lines of thought, the appearance of a classical world in quantum theory has been explored [51,52,55,56]. On the other hand, an example of fake decoherence is to interpret the result of an ensemble average over different noisy realizations of a system as the description of ...
The Homological Nature of Entropy
... Abstract: We propose that entropy is a universal co-homological class in a theory associated to a family of observable quantities and a family of probability distributions. Three cases are presented: (1) classical probabilities and random variables; (2) quantum probabilities and observable operators ...
... Abstract: We propose that entropy is a universal co-homological class in a theory associated to a family of observable quantities and a family of probability distributions. Three cases are presented: (1) classical probabilities and random variables; (2) quantum probabilities and observable operators ...







![arXiv:math/0606118v4 [math.PR] 5 Dec 2006](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/013514025_1-1bac3cda767b4b11f4a6d27e549df5b9-300x300.png)