Document
... worked out by Dale Jorgenson and others: “User cost” formula – depreciation, net return, and revaluation. Used to decompose productivity growth into capital, labor, and residual (multifactor productivity) contributions. ...
... worked out by Dale Jorgenson and others: “User cost” formula – depreciation, net return, and revaluation. Used to decompose productivity growth into capital, labor, and residual (multifactor productivity) contributions. ...
CH03
... 實際上的選擇結果如何?視實質工資增加的持續時間而 定。加薪的持續時間越長,所得效果越大。 a long-term increase in the real wage a. The reward to working is greater: a substitution effect toward more work b. But with a higher wage, a person doesn’t need to work as much: an income effect toward less work c. The longer the high wage is expected t ...
... 實際上的選擇結果如何?視實質工資增加的持續時間而 定。加薪的持續時間越長,所得效果越大。 a long-term increase in the real wage a. The reward to working is greater: a substitution effect toward more work b. But with a higher wage, a person doesn’t need to work as much: an income effect toward less work c. The longer the high wage is expected t ...
Utility and Preference
... • The what, How and for Whom questions in a free market economy are determined primarily by a system of prices (or markets, of profits and losses). ...
... • The what, How and for Whom questions in a free market economy are determined primarily by a system of prices (or markets, of profits and losses). ...
PDF Download
... to sizable immigration towards Germany and the Euro Area as a whole. For each economy, we also distinguish between a sector producing goods which are tradable across borders and are thus subject to international competition and a sector producing non-tradable products sold only domestically (e.g. th ...
... to sizable immigration towards Germany and the Euro Area as a whole. For each economy, we also distinguish between a sector producing goods which are tradable across borders and are thus subject to international competition and a sector producing non-tradable products sold only domestically (e.g. th ...
Schumpeter Meeting Keynes: A Policy-Friendly Model of
... thus the dynamics in the “technological fundamentals” of the economy is endogenous. At the same time, “non-fundamental” (e.g. demand-related) fluctuations do not appear in this family of models. Refinements, such as Aghion and Howitt (1998)3 , do entail equilibrium fluctuations wherein Keynesian fea ...
... thus the dynamics in the “technological fundamentals” of the economy is endogenous. At the same time, “non-fundamental” (e.g. demand-related) fluctuations do not appear in this family of models. Refinements, such as Aghion and Howitt (1998)3 , do entail equilibrium fluctuations wherein Keynesian fea ...
Theme 1 revision points from Edexcel1.41 MB
... organising the economy. Students are required to consider the distinction between a free market economy, a mixed economy and a command economy. Students should have an awareness of the perspectives of Adam Smith, Friedrich Hayek and Karl Marx; however, there is no requirement for detailed considerat ...
... organising the economy. Students are required to consider the distinction between a free market economy, a mixed economy and a command economy. Students should have an awareness of the perspectives of Adam Smith, Friedrich Hayek and Karl Marx; however, there is no requirement for detailed considerat ...
Barriers to Accumulation and Productivity Differences in a
... change and productivity growth in an economy where factors are not allocated efficiently. Following the approach of Parente and Prescott (2000), Restuccia and Urrutia (2001), and Gollin, Parente and Rogerson (2004), we consider the impact of barriers to capital accumulation. Within this setting, how ...
... change and productivity growth in an economy where factors are not allocated efficiently. Following the approach of Parente and Prescott (2000), Restuccia and Urrutia (2001), and Gollin, Parente and Rogerson (2004), we consider the impact of barriers to capital accumulation. Within this setting, how ...
Chapter 6 - The University of Utah
... On the other hand, the liberal intellectuals have lost most of their political influence that they had before 1989. Their exiling party abroad has bankrupted and they do not have any organized political force in China. Without any significant social base, the very existence (or extinguishment) of t ...
... On the other hand, the liberal intellectuals have lost most of their political influence that they had before 1989. Their exiling party abroad has bankrupted and they do not have any organized political force in China. Without any significant social base, the very existence (or extinguishment) of t ...
privitazation and nationalization - Dictionnaire encyclopédique de l
... Privatization and nationalization are two sides of the same coin. The state is responsible for the social and economic stability of its citizens. This stability often depends on the implementation of large-scale economic or social activities. In this context, it is conceivable for the state to assum ...
... Privatization and nationalization are two sides of the same coin. The state is responsible for the social and economic stability of its citizens. This stability often depends on the implementation of large-scale economic or social activities. In this context, it is conceivable for the state to assum ...
Build Economic Corridor alongside of Yellow River – On Tendency... Rising in Central Plain Region
... Civilization. The Yellow River within Henan enjoys rich cultural resources for tourism, such as Longshan Culture, Yangshao Culture, Peiligang Culture, the Hometown of Emperor Huang, Yin Ruins at Anyang, etc.. In modern times, the west part of the Yellow River bank was the traditional industrial base ...
... Civilization. The Yellow River within Henan enjoys rich cultural resources for tourism, such as Longshan Culture, Yangshao Culture, Peiligang Culture, the Hometown of Emperor Huang, Yin Ruins at Anyang, etc.. In modern times, the west part of the Yellow River bank was the traditional industrial base ...
The Free Trade Debate: A Left Keynesian Gaze Thomas I. Palley
... An immediate difficulty in assessing the welfare effects of free trade reforms concerns the questions of (i) whose welfare, and (ii) trade reform with whom. Real world economies are constituted by heterogeneous agents, and economies also differ in their typologies. Together, these features compel a ...
... An immediate difficulty in assessing the welfare effects of free trade reforms concerns the questions of (i) whose welfare, and (ii) trade reform with whom. Real world economies are constituted by heterogeneous agents, and economies also differ in their typologies. Together, these features compel a ...
DEMOCRACY and GROWTH RECONSIDERED: WHY ECONOMIC
... starts with weak institutions - weak democracy and little rule of law - an increase in democracy is less important than an expansion of the rule of law as a stimulus for economic growth and investment. In addition, democracy does not seem to have a strong direct role in fostering the rule of law. Th ...
... starts with weak institutions - weak democracy and little rule of law - an increase in democracy is less important than an expansion of the rule of law as a stimulus for economic growth and investment. In addition, democracy does not seem to have a strong direct role in fostering the rule of law. Th ...
Schumpeter Meeting Keynes: A Policy
... thus the dynamics in the “technological fundamentals” of the economy is endogenous. At the same time, “non-fundamental” (e.g. demand-related) fluctuations do not appear in this family of models. Refinements, such as Aghion and Howitt (1998)3 , do entail equilibrium fluctuations wherein Keynesian fea ...
... thus the dynamics in the “technological fundamentals” of the economy is endogenous. At the same time, “non-fundamental” (e.g. demand-related) fluctuations do not appear in this family of models. Refinements, such as Aghion and Howitt (1998)3 , do entail equilibrium fluctuations wherein Keynesian fea ...
Advances in Environmental Biology
... The resistive economy means that we move towards domestic production to grow 8% prosperity and not let work force to be unemployed, in the community. On the resistive economy rather than a slogan, it is planned that import does not be done frequently but it is added to domestic production. Resistive ...
... The resistive economy means that we move towards domestic production to grow 8% prosperity and not let work force to be unemployed, in the community. On the resistive economy rather than a slogan, it is planned that import does not be done frequently but it is added to domestic production. Resistive ...
National Income and Related Aggregates
... National Income -Excluded Items NI excludes sale & purchase of second hand goods. It excludes income from illegal activities – smuggling, ...
... National Income -Excluded Items NI excludes sale & purchase of second hand goods. It excludes income from illegal activities – smuggling, ...
Contents - Scuola Superiore Sant`Anna
... concerned with long-run equilibrium. Keynes’s analysis, which culminated with the publication of the General Theory (Keynes, 1936), shifted the emphasis to the short-run, and to out-of-equilibrium states of the economy. In his work Keynes aimed to explain the causes of economic instability since he ...
... concerned with long-run equilibrium. Keynes’s analysis, which culminated with the publication of the General Theory (Keynes, 1936), shifted the emphasis to the short-run, and to out-of-equilibrium states of the economy. In his work Keynes aimed to explain the causes of economic instability since he ...
PDF
... gains by capitalists would imply either (a) returns from their existing holdings of land or capital assets have gone up for some reason, or (b) they have somehow come into possession of more land or capital stock, or both. Reasons typically cited for possibility (a) include population growth, biase ...
... gains by capitalists would imply either (a) returns from their existing holdings of land or capital assets have gone up for some reason, or (b) they have somehow come into possession of more land or capital stock, or both. Reasons typically cited for possibility (a) include population growth, biase ...
Macroeconomic theories of investment and development of a New
... for outputs in the future. This assumption allowed Jorgenson to see firms as renting capital to themselves during each period and the rental price was referred to as the user cost of capital. Jorgenson also assumed that adjustment from current to desired levels of capital stock were instantaneous an ...
... for outputs in the future. This assumption allowed Jorgenson to see firms as renting capital to themselves during each period and the rental price was referred to as the user cost of capital. Jorgenson also assumed that adjustment from current to desired levels of capital stock were instantaneous an ...
- City Research Online
... Nearly a century ago, one of the leading forefathers of the school of evolutionary economics, John R. Commons, coined the term ‘futurity’ to describe an epochal change in late 19th advanced economies. Common’s notion of futurity is somewhat ambiguous. For it combines a philosophical statement about ...
... Nearly a century ago, one of the leading forefathers of the school of evolutionary economics, John R. Commons, coined the term ‘futurity’ to describe an epochal change in late 19th advanced economies. Common’s notion of futurity is somewhat ambiguous. For it combines a philosophical statement about ...
The Emperor Has New Clothes Mainstream Theories of Economic Growth .
... consumption rate of interest, r. Weitzman states that this total stock of capital includes produced capital (“..equipment, structures and inventories”..), but also human capital, technology and natural resources. He assumes that all sources of growth can be attributed to one of these capital stocks. ...
... consumption rate of interest, r. Weitzman states that this total stock of capital includes produced capital (“..equipment, structures and inventories”..), but also human capital, technology and natural resources. He assumes that all sources of growth can be attributed to one of these capital stocks. ...
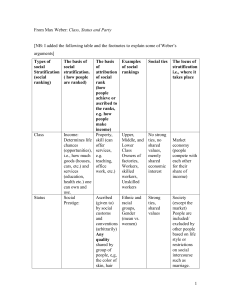
Class, Status, Party
... 'mere economic' power, and especially 'naked' money power, is by no means a recognized basis of social honor. Nor is power the only basis of social honor. Indeed, social honor; or prestige, may even be the basis of political or economic power, and very frequently has been. Power, as well as honor, m ...
... 'mere economic' power, and especially 'naked' money power, is by no means a recognized basis of social honor. Nor is power the only basis of social honor. Indeed, social honor; or prestige, may even be the basis of political or economic power, and very frequently has been. Power, as well as honor, m ...
Lec1-GDP - Columbia College
... – Used goods and second-hand sales do NOT count. (e.g. selling a used car ) - inventory should be included. inventories: goods that are produced but unsold count as firms’ own investment ...
... – Used goods and second-hand sales do NOT count. (e.g. selling a used car ) - inventory should be included. inventories: goods that are produced but unsold count as firms’ own investment ...
Impact of Trade Freedom, Property Rights, Fiscal Freedom, and
... people could take (or endeavor to do so) whatever good or service they chose without paying for same. Indeed, people and firms would have to devote both resources and time to the protection not only of their goods and possessions (assets) but also their earnings, savings, and accumulated wealth in o ...
... people could take (or endeavor to do so) whatever good or service they chose without paying for same. Indeed, people and firms would have to devote both resources and time to the protection not only of their goods and possessions (assets) but also their earnings, savings, and accumulated wealth in o ...
SCARCITY, CHOICE AND THE PRODUCTION POSSIBILITIES
... output per worker. As we move up along this axis our level of investment increases. In order fund this higher level of investment, there needs to be a decrease in current consumption. Note the label of the x-axis. This axis is labeled as current consumption and as we move outward from the origin, th ...
... output per worker. As we move up along this axis our level of investment increases. In order fund this higher level of investment, there needs to be a decrease in current consumption. Note the label of the x-axis. This axis is labeled as current consumption and as we move outward from the origin, th ...
Unclassified DAF/COMP/GF/WD(2013)
... It is widely documented that the world’s poorest nations also have the most uneven distribution of resources. This observation is clearly evident in Zambia. It is not uncommon to see highly affluent communities living side-by-side with extremely poor communities who spend literally everything they e ...
... It is widely documented that the world’s poorest nations also have the most uneven distribution of resources. This observation is clearly evident in Zambia. It is not uncommon to see highly affluent communities living side-by-side with extremely poor communities who spend literally everything they e ...