Keegan_6e_02_im - Glendale Community College
... Mistaken assumption #2: The poor are too concerned with fulfilling basic needs to “waste” money on non-essential goods. ...
... Mistaken assumption #2: The poor are too concerned with fulfilling basic needs to “waste” money on non-essential goods. ...
3. National Income: Where it Comes From and Where it Goes
... The above assumptions imply a fixed supply of goods and services. Output is determined by the fixed factor supplies and the fixed state of technology. ...
... The above assumptions imply a fixed supply of goods and services. Output is determined by the fixed factor supplies and the fixed state of technology. ...
Socialism after Hayek: A Post Keynesian Contribution to Burczak`s
... would not be exploited since they own the output they produce and are the last owners of their labor time. This definition, however, does not recognize that workers in general are exploited by (global) competitive market structures regardless of employers. It also implies that a self-employed individ ...
... would not be exploited since they own the output they produce and are the last owners of their labor time. This definition, however, does not recognize that workers in general are exploited by (global) competitive market structures regardless of employers. It also implies that a self-employed individ ...
Indiana Department of Education Academic Standards in Economics
... productive resources; how they engage in trade to satisfy their economic wants and needs; how they use a variety of sources to gather and apply information about economic changes in the community; and how they compare costs and benefits in economic decision making. ...
... productive resources; how they engage in trade to satisfy their economic wants and needs; how they use a variety of sources to gather and apply information about economic changes in the community; and how they compare costs and benefits in economic decision making. ...
The economic situation from the vantage point of the delegates for
... the reason cited was the under-utilisation of capacities in their company and their industry in general. On the one hand, the decline in demand can lead to an increase in average production costs owing to large blocks of fixed costs. On the other, the global economy’s excess capacity makes it diffic ...
... the reason cited was the under-utilisation of capacities in their company and their industry in general. On the one hand, the decline in demand can lead to an increase in average production costs owing to large blocks of fixed costs. On the other, the global economy’s excess capacity makes it diffic ...
EC 132 Discussion Note PS4 CHIU P.1 Disclaimer:
... capital) is closely related to the cost of capital. Why? At the same time, economists disagree about whether investment demand is closely related to the cost of capital. Explain why there is a difference between the demand for capital and the demand for investment in this regard. Net return of inves ...
... capital) is closely related to the cost of capital. Why? At the same time, economists disagree about whether investment demand is closely related to the cost of capital. Explain why there is a difference between the demand for capital and the demand for investment in this regard. Net return of inves ...
- Centre for Economic Policy Research
... against which we should defend ourselves, but for the most part an opportunity for the market economy. By reallocating resources to where productivity and demand are, the capitalist system can exploit volatility. The developments of the last two decades again highlight the importance of reallocation ...
... against which we should defend ourselves, but for the most part an opportunity for the market economy. By reallocating resources to where productivity and demand are, the capitalist system can exploit volatility. The developments of the last two decades again highlight the importance of reallocation ...
19 The Participatory Economy: The Case of Yugoslavia
... some of the detriments of capitalism. Indeed, some authors have argued that through the growing tendency to pay workers at least in part with shares or attractively priced options, participation has in fact come to capitalism. Vanek offered several advantages for labor management, which are discusse ...
... some of the detriments of capitalism. Indeed, some authors have argued that through the growing tendency to pay workers at least in part with shares or attractively priced options, participation has in fact come to capitalism. Vanek offered several advantages for labor management, which are discusse ...
Unit 6 - Wsfcs
... 1) The United States is in a period of economic contraction, or a recession. - Explain the type of monetary policy the Federal Reserve should use during this period, and what effect this would have on the money supply. - Explain a tool that the Federal Reserve has to impact the money supply and how ...
... 1) The United States is in a period of economic contraction, or a recession. - Explain the type of monetary policy the Federal Reserve should use during this period, and what effect this would have on the money supply. - Explain a tool that the Federal Reserve has to impact the money supply and how ...
PRESIDENT'S REPORT TO THE BOARD OF DIRECTORS,
... Data released since your last Directors' meeting show the economy is growing at a solid pace, but one that is not as fast as previously expected. While continued employment growth will be important in maintaining this level of growth, the economic effects of Hurricane Katrina may play a significant ...
... Data released since your last Directors' meeting show the economy is growing at a solid pace, but one that is not as fast as previously expected. While continued employment growth will be important in maintaining this level of growth, the economic effects of Hurricane Katrina may play a significant ...
Social Studies Standards
... SS.6.E.1.1 Identify the factors (new resources, increased productivity, education, technology, slave economy, territorial expansion) that increase economic growth. SS.6.E.1.2 Describe and identify traditional and command economies as they appear in different civilizations. SS.6.E.1.3 Describe the fo ...
... SS.6.E.1.1 Identify the factors (new resources, increased productivity, education, technology, slave economy, territorial expansion) that increase economic growth. SS.6.E.1.2 Describe and identify traditional and command economies as they appear in different civilizations. SS.6.E.1.3 Describe the fo ...
Economic_Roles - Solanco School District Moodle
... way you live as measured by the kinds and quality of goods and services you can afford. – The more money you earn the higher standard of living you can ...
... way you live as measured by the kinds and quality of goods and services you can afford. – The more money you earn the higher standard of living you can ...
Economic Development And Structural Change
... labor, and capital (both physical and human). These are simply factor endowments, which firms can use for production. Conceptually, it is useful to add infrastructure as one more component of an economy’s endowments.2 Infrastructure can be hard (tangible) or soft (intangible). Examples of hard infra ...
... labor, and capital (both physical and human). These are simply factor endowments, which firms can use for production. Conceptually, it is useful to add infrastructure as one more component of an economy’s endowments.2 Infrastructure can be hard (tangible) or soft (intangible). Examples of hard infra ...
The International Monetary Fund and East Asian Financial Crisis
... collapsed. Historically, the bath was fixed to the U.S dollar and traded about 25 baht to the dollar. Subsequently, currency devaluation hit Korea, Malaysia, the Philippines, and Indonesia. The sentiment of investors changed almost overnight and billions of foreign portfolio capital left these count ...
... collapsed. Historically, the bath was fixed to the U.S dollar and traded about 25 baht to the dollar. Subsequently, currency devaluation hit Korea, Malaysia, the Philippines, and Indonesia. The sentiment of investors changed almost overnight and billions of foreign portfolio capital left these count ...
Econ 201 Fall 2003 Week 1
... – Public goods, the exclusion principle, the freerider problem and non-rival consumption – External costs and benefits – Examples: vaccines, education, pollution ...
... – Public goods, the exclusion principle, the freerider problem and non-rival consumption – External costs and benefits – Examples: vaccines, education, pollution ...
& LAOS OPPORTUNITIES INVESTMENT POLICY
... least 8% annual GDP growth, 60% will be from private investments – “NSEDP: The quality of growth, sustainable land and resource use, environmental management, and increasing resource use efficiency ...
... least 8% annual GDP growth, 60% will be from private investments – “NSEDP: The quality of growth, sustainable land and resource use, environmental management, and increasing resource use efficiency ...
Unit 1 Introduction to Economics Objectives Define economics
... Stream A: Households sell factors of production to firms and the government. Stream B: Households receive money (income) from firms and the government. Stream C: Goods and services are sold on the product market. Stream D: Households use their income to pay for goods and services. Stream E: This str ...
... Stream A: Households sell factors of production to firms and the government. Stream B: Households receive money (income) from firms and the government. Stream C: Goods and services are sold on the product market. Stream D: Households use their income to pay for goods and services. Stream E: This str ...
Chapter 5 Introduction to Macroeconomics
... A) for the government to directly control prices and wages. B) to increase the supply of money in the economy. C) to increase government production so that public-sector employment increases. D) to stimulate the supply of labor and capital and increase investment. True/False 1) Macroeconomic behavio ...
... A) for the government to directly control prices and wages. B) to increase the supply of money in the economy. C) to increase government production so that public-sector employment increases. D) to stimulate the supply of labor and capital and increase investment. True/False 1) Macroeconomic behavio ...
An Introduction to the Wealth of Nations
... modern growth theory i.e. a standard modern growth model would include for countries the legal framework, well defined property rights, existence of corruption, efficient police force, how democratic, etc. • As noted, the division of labour cannot function without a market for its specialities and S ...
... modern growth theory i.e. a standard modern growth model would include for countries the legal framework, well defined property rights, existence of corruption, efficient police force, how democratic, etc. • As noted, the division of labour cannot function without a market for its specialities and S ...
View/Open
... The economic measures which are to get primary role are those that affect how much the population spends, because spending is the most important component of aggregate demand and revenues. In the developed countries, spending makes between one half and two thirds of the overall aggregate demand. The ...
... The economic measures which are to get primary role are those that affect how much the population spends, because spending is the most important component of aggregate demand and revenues. In the developed countries, spending makes between one half and two thirds of the overall aggregate demand. The ...
Introduction to Macroeconomics
... is offset period of economic decline is known as long run growth.” ...
... is offset period of economic decline is known as long run growth.” ...
After the economic crisis!
... Healthcare accounts for 8.5 % of EU GDP, and about 10% of employment When other aspects of social care, and the "secondary market" for healthcare related products and services are considered the total impact on our economy may be twice this level – about 20% Moreover the economic impact of health ...
... Healthcare accounts for 8.5 % of EU GDP, and about 10% of employment When other aspects of social care, and the "secondary market" for healthcare related products and services are considered the total impact on our economy may be twice this level – about 20% Moreover the economic impact of health ...
Exercise 6 (+additional question) in Mankiw:
... A. Calculate GDP and GNP. 1point. B. Calculate public saving, private and national saving. 3points. C. Calculate private consumption(C). 1point. 1point 2. In a closed economy, what do we mean by “crowding-out”? Why might “crowding-out” be a problem? 1point 3. If inflation is 10 percent and the real ...
... A. Calculate GDP and GNP. 1point. B. Calculate public saving, private and national saving. 3points. C. Calculate private consumption(C). 1point. 1point 2. In a closed economy, what do we mean by “crowding-out”? Why might “crowding-out” be a problem? 1point 3. If inflation is 10 percent and the real ...
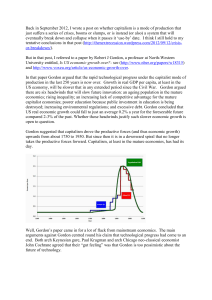
Gordon 050314 - Michael Roberts Blog
... However, his successor at Goldman Sachs, Jan Hatzius is less pessimistic. Hatzius points out that the trend in college attendance continues to expand strongly, so he does not see why the contribution of education to productivity growth should decline. Hatzius also reckons that the rise in the profi ...
... However, his successor at Goldman Sachs, Jan Hatzius is less pessimistic. Hatzius points out that the trend in college attendance continues to expand strongly, so he does not see why the contribution of education to productivity growth should decline. Hatzius also reckons that the rise in the profi ...